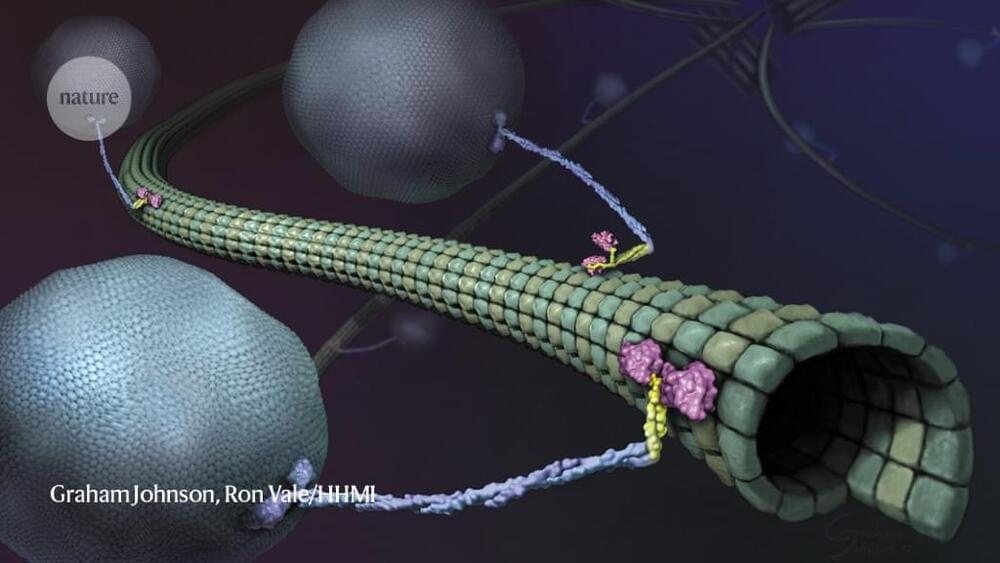
Almost as soon as there were super-resolution microscopes, scientists pointed them towards molecular motors called kinesins. These proteins, powered by the molecular fuel ATP, drive crucial processes including cell division, cell signalling and intracellular transport by shuttling cargo along protein highways called microtubules. Researchers have long wanted to understand how these motors work, but to visualize them, scientists have had to slow them down or isolate them in simplified, in vitro systems.
Now, in papers published concurrently in Science, two teams working independently have used a super-resolution tool called MINFLUX to study the motor in near-real time at physiologically relevant concentrations of ATP. The first paper, led by MINFLUX’s inventor, Stefan Hell, who has a joint appointment at the Max Planck Institute (MPI) for Multidisciplinary Sciences in Göttingen and the MPI for Medical Research in Heidelberg, both in Germany, used a new instrument design to track the protein in 3D, revealing details about its motion1. The second, led by biophysicist Jonas Ries at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory in Heidelberg, showed for the first time that MINFLUX is capable of tracking kinesin even amid the bustle of living cells2.
“This technology requires a lot of different things to work, and it’s fun to see all of these things coming together,” says Michelle Digman, a biomedical engineer at the University of California, Irvine, who develops imaging strategies but was not involved in either study. “It seemed like a proof of concept to show that they’re able to track kinesin very precisely. And when you have the live cell system, that’s even more spectacular.”


















