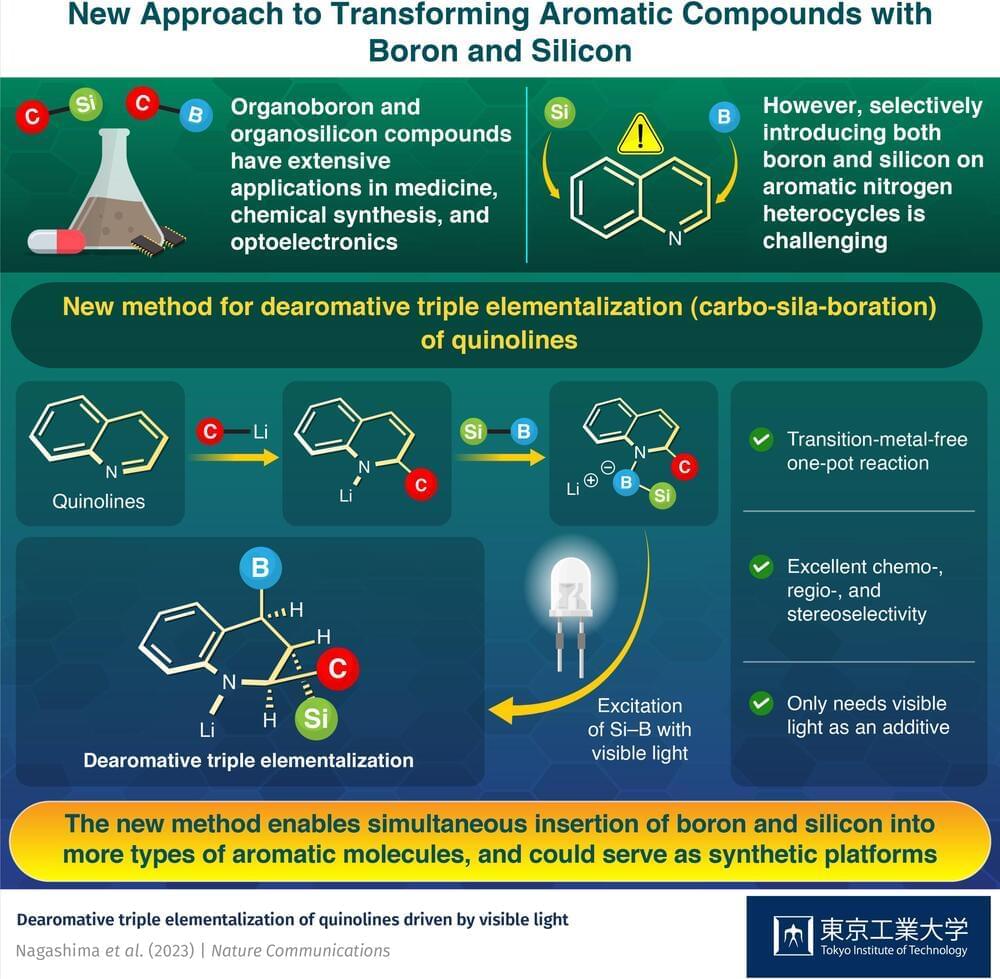
In recent years, organic chemicals containing boron (B) and silicon (Si) have found applications in various fields, including optoelectronics and pharmaceuticals. Moreover, they can also serve as building blocks for complex organic chemicals. As a result, scientists are actively looking for new ways to leverage these versatile chemical tools as well as produce more kinds of organosilicon and organoboron compounds.
One limitation of the synthesis methods currently available for these chemicals is that we cannot introduce multiple B-and Si-containing groups in aromatic nitrogen heterocycles, i.e., carbon rings in which one of the carbon atoms is replaced by a nitrogen atom. If we could produce and freely transform such molecules, it would unlock the synthesis of several compounds relevant in medicinal chemistry.
Fortunately, a research team including Assistant Professor Yuki Nagashima from Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech), Japan has found a straightforward way around this limitation. As explained in their most recent study published in Nature Communications, the team has developed a method that allows them to modify quinolines, small organic molecules with an aromatic nitrogen heterocycle, with B-, Si-, and carbon-containing groups simultaneously.