Oct 25, 2023
Astrophysicists scan the galaxy for signs of life
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: alien life, physics
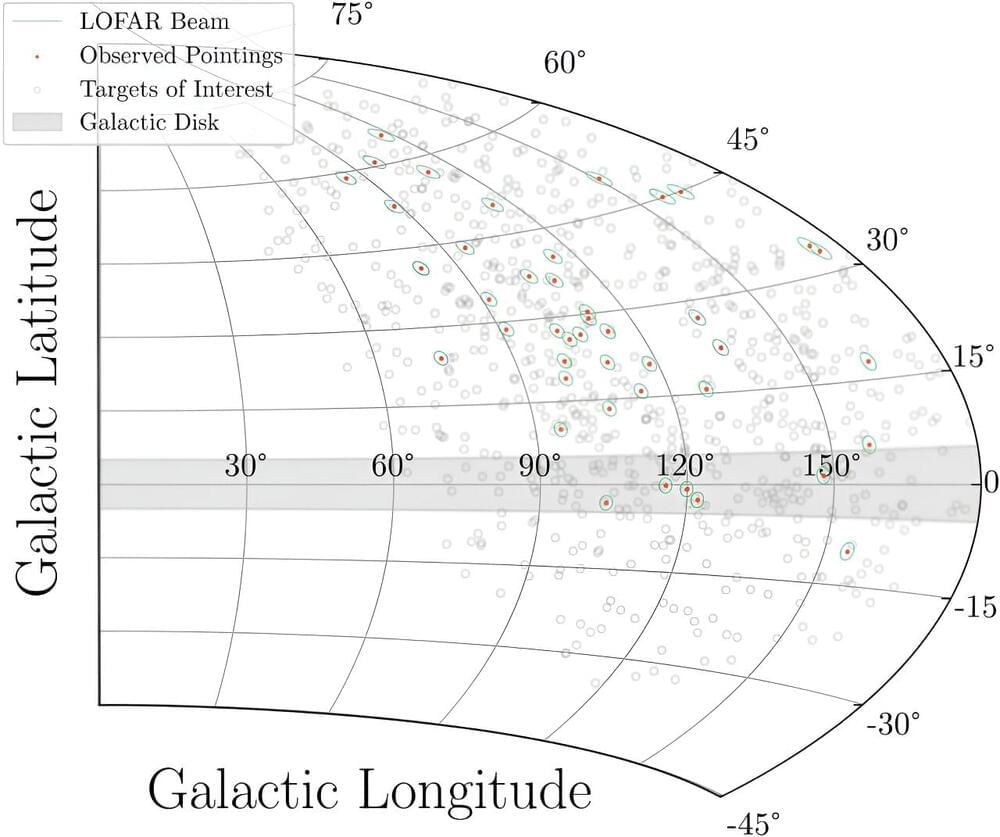
The astrophysicists, from Trinity and the Breakthrough Listen team and Onsala Space Observatory in Sweden, are scanning the universe for “technosignatures” emanating from distant planets that would provide support for the existence of intelligent, alien life.
Using the Irish LOFAR telescope and its counterpart in Onsala, Sweden, the team—led by Professor Evan Keane, Associate Professor of Radio Astronomy in Trinity’s School of Physics, and Head of the Irish LOFAR Telescope—plans to monitor millions of star systems.
Scientists have been searching for extraterrestrial radio signals for well over 60 years. Many of these have been carried out using single observatories which limits the ability to identify signals from the haze of terrestrial interference on Earth. Much of the effort has focused on frequencies above 1 GHz because the single-dish telescopes employed operate at these frequencies.