Hydrogen, the most abundant element in the universe, is found everywhere from the dust filling most of outer space to the cores of stars to many substances here on Earth. This would be reason enough to study hydrogen, but its individual atoms are also the simplest of any element with just one proton and one electron. For David Ceperley, a professor of physics at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, this makes hydrogen the natural starting point for formulating and testing theories of matter.
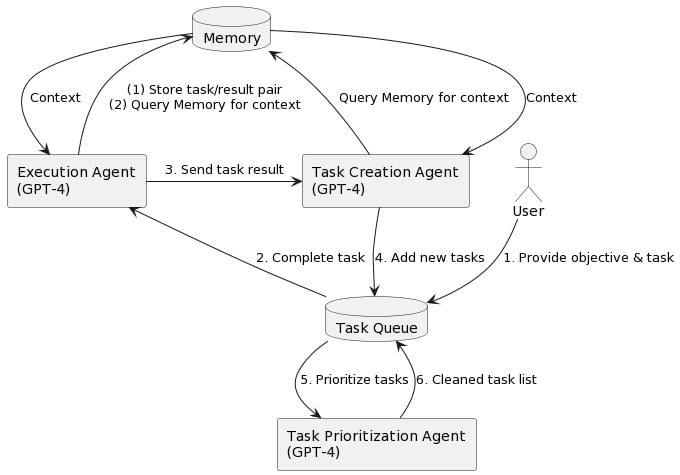
Ceperley, also a member of the Illinois Quantum Information Science and Technology Center, uses computer simulations to study how hydrogen atoms interact and combine to form different phases of matter like solids, liquids, and gases. However, a true understanding of these phenomena requires quantum mechanics, and quantum mechanical simulations are costly. To simplify the task, Ceperley and his collaborators developed a machine learning technique that allows quantum mechanical simulations to be performed with an unprecedented number of atoms. They reported in Physical Review Letters that their method found a new kind of high-pressure solid hydrogen that past theory and experiments missed.
“Machine learning turned out to teach us a great deal,” Ceperley said. “We had been seeing signs of new behavior in our previous simulations, but we didn’t trust them because we could only accommodate small numbers of atoms. With our machine learning model, we could take full advantage of the most accurate methods and see what’s really going on.”