Jun 1, 2023
NLRP12 as a new drug target for infection, inflammation and hemolytic diseases
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in category: biotech/medical
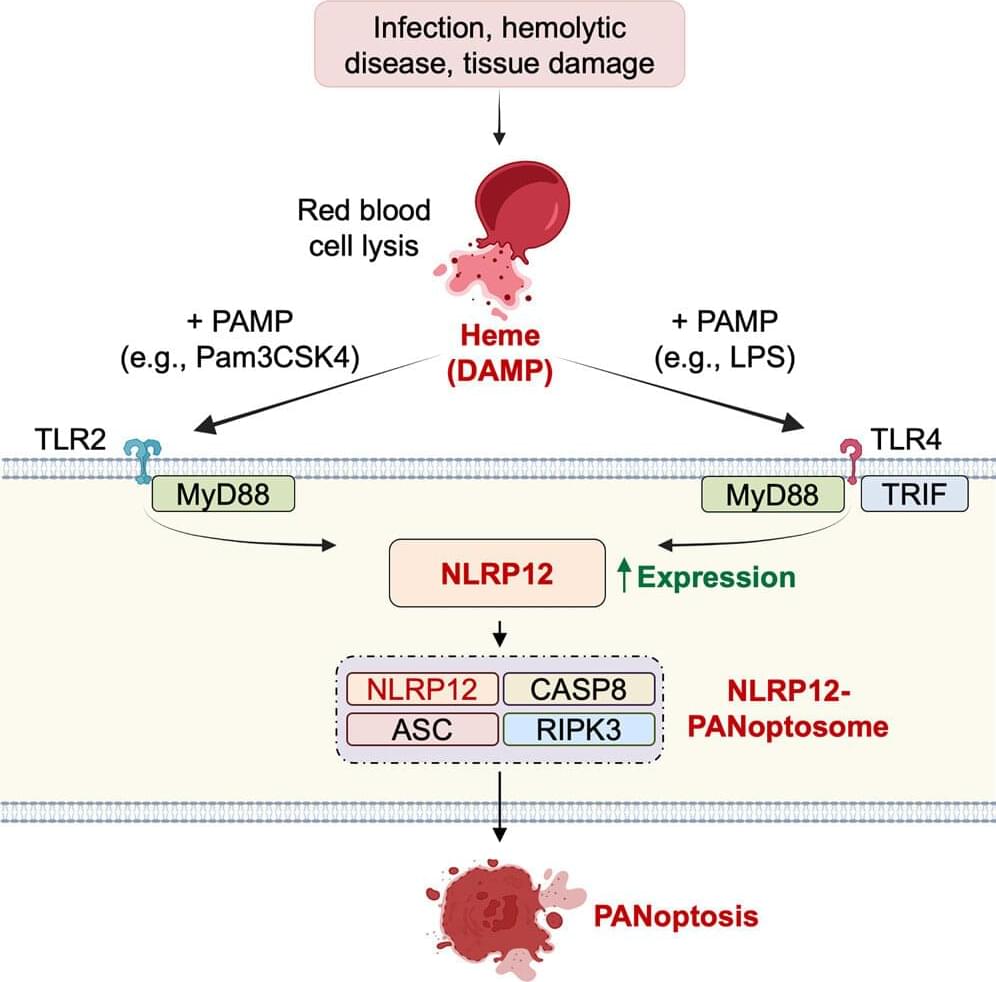
Infections and other diseases can cause red blood cells to rupture, releasing the oxygen-binding molecule hemoglobin, which breaks down into heme. Free heme can cause significant inflammation and organ damage, leading to morbidity and mortality.
Researchers from St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital discovered NLRP12, an innate immune pattern recognition receptor, to be the key molecule responsible for inducing inflammatory cell death and pathology in response to heme combined with other cellular damage or infection. The finding provides a new potential drug target to prevent morbidity in certain illnesses. The research was published today in Cell.
Many infectious and inflammatory diseases, including malaria or SARS-CoV-2 virus infections and sickle cell disease, cause red blood cells to break apart and spill their contents. The process, hemolysis, releases the hemoglobin. In the bloodstream, hemoglobin then breaks down into a substance called heme.