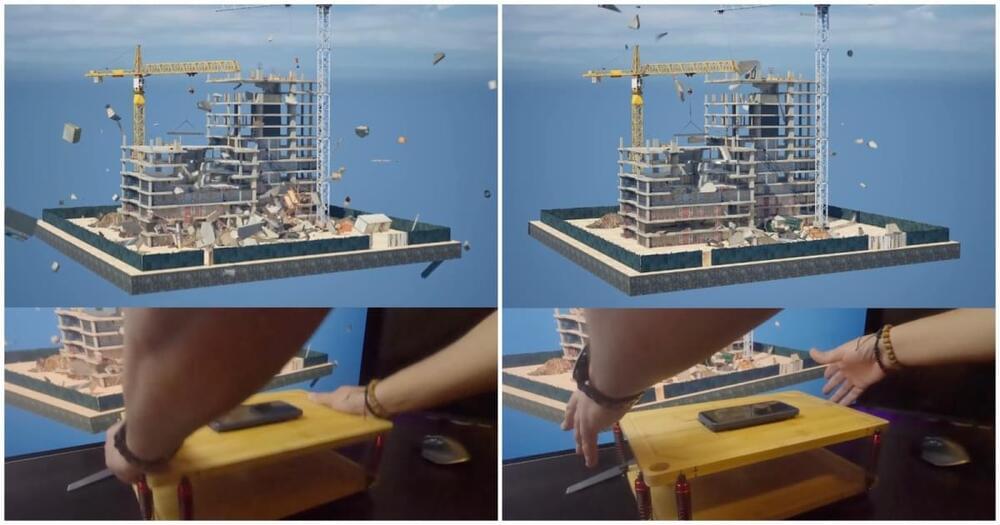
While a lot of theories have been centred around attraction, the team found that the insects do not steer directly towards the light, but instead turn their dorsum towards the light. In natural light, this tilting helps insects to maintain the proper flight attitude and control. However, the models developed by the researchers showed that dorsal tilting creates the erratic flight paths around artificial light, causing the insects to continuously steer around the light and become trapped in a constant motion.
“It is the idea that short-range light entrapment is not a navigational disruption, but instead subversion of a basic flight stability reflex, predicting that requirements for stable flight can explain this phenomenon,” says Sondhi.
“The most standout result is that artificial lights confuse insects as to which way is up,” Fabian tells Physics World. “On the ground, we find this obvious. In the air, this is a lot more challenging. In-flight accelerations are indistinguishable from acceleration due to gravity. Simply taking the direction of light as being the sky works, even at night. The night has a lot less light, obviously, but the contrast between sky and ground is just as strong. This is a beautiful, robust way to work out which way is up – until we started lighting up the night.”