In a dramatic departure, Google is open sourcing software that sits at the heart of its online empire.
Page 11993
Nov 9, 2015
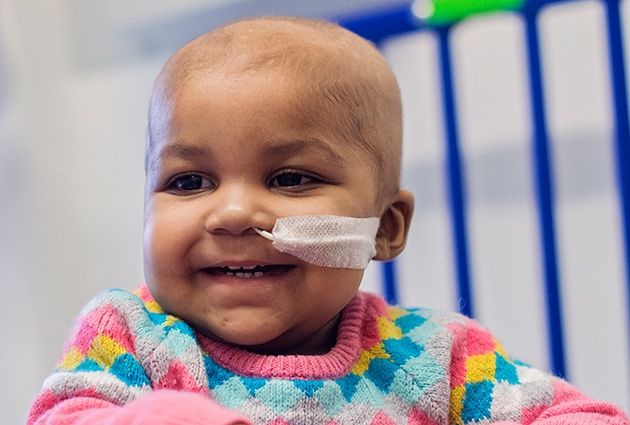
A Bright Future: Breakthrough Gene Editing Trial Reverses Leukaemia
Posted by Roy in categories: biotech/medical, innovation
A pioneering gene editing therapy has shown remarkable success in a unique trial at Great Ormond Street, paving the way for a wave of gene editing trials.
A world first
Not long ago, 1 year old Layla Richards had an incurable form of leukaemia and the prognosis wasn’t looking good. After a determined search for a cure, Layla underwent an experimental therapy in which ‘designer’ immune cells were implanted that would destroy and replace her own ailing immune system.
Nov 9, 2015
The Imminent, the Possible, and the Irreversible: The Disruptive Potential of Artificial Intelligence
Posted by Amnon H. Eden in categories: computing, military, robotics/AI
Major technological changes have a transformative effect on every aspect of human life. Increasingly intelligent programs are responsible to paradigm shifts at a steadily accelerating rate, a trend which acceleration theories suggest is all but guaranteed to continue.
We explore some of the most disruptive applications of artificial intelligence, examining in particular the impact of computer trading programs (algotraders) on stock markets. We explore some such imminent technologies (such as autonomous military robots) and their consequences (eg on job markets). We conclude with a discussion in the potentially irreversible consequences of this trend, including that of superintelligence.
Nov 9, 2015
Inside the 50-year-quest to build a mechanical heart
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: biotech/medical, neuroscience
Steve Williams couldn’t breathe. The former athlete had cardiomyopathy, which occasionally choked his lungs with fluid, making him gasp for air. But this felt different; Williams felt like he was dying. He was raced to an Orange County hospital, and shortly after checking in, his heart stopped. For 30 minutes, ER workers compressed his chest in an attempt to revive him. At one point, his wife Mary remembers being called into his room to say goodbye to her husband of 24 years. It seemed Williams was a dead man.
Incredibly, doctors rebooted Williams’ heart — but for three days, he was in an induced coma, his body packed in ice to minimize brain damage. When he woke up, his mental facilities were intact, but his body was ravaged. His liver was congested, fluid reappeared in his lungs, and his heart’s right and left ventricles were practically destroyed, making it hard for blood to circulate throughout his body. Without a heart transplant, he would soon die.
Nov 8, 2015
Genes Responsible for Limb Regeneration in Crickets Identified
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: biotech/medical, genetics
Researchers just identified part of the epigenetic pathways responsible for limb regeneration in the two-spotted cricket Gryllus bimaculatus.
Cut off the leg of an insect, and not only will the insect survive, but the leg will also grow back after some time. Cut off the leg of a human, and they’ll bleed out without proper medical attention (alas for us). Ultimately, insects are able to accomplish this amazing feat because they retain the biological pathways required for cells to differentiate and reorganize at a wound site, which is required in order to regenerate entire limbs.
The processes involve the dedifferentiation and redifferentiation of cells; however, the exact nature of the process is largely a mystery. Fortunately, some light has recently been shed on the matter, as researchers at Okayama University identified key genes involved in the regenerative process of the two-spotted cricket, Gryllus bimaculatus.
Nov 8, 2015
New discovery changes everything we know about how blood is made
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in category: biotech/medical
Stem-cell scientists have upended current thinking on the way human blood is produced inside the body, opening the way for new studies and new treatments. The findings of principal investigator John Dick and his team from the University of Toronto in Canada challenge ideas that have been in place since the 1960s.
Essentially, the new research suggests that blood is formed in fewer steps than previously believed: earlier evidence indicated stem cells went through several intermediate steps before becoming white or red adult cells, like branches coming out from a tree trunk. Dick and his team think the process is much quicker and simpler, though their findings have yet to be confirmed by independent researchers.
“The whole classic ‘textbook’ view we thought we knew doesn’t actually even exist,” said Dick. “Instead, through a series of experiments we have been able to finally resolve how different kinds of blood cells form quickly from the stem cell – the most potent blood cell in the system – and not further downstream as has been traditionally thought.”
Nov 8, 2015
Stem-cell scientists redefine how blood is made
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in category: biotech/medical

Stem-cell scientists led by Dr. John Dick have discovered a completely new view of how human blood is made, upending conventional dogma from the1960s.
Nov 8, 2015
Rats Engineered to See Infrared Light, Use It to Seek Out Water
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: computing, neuroscience

The brain is a great information processor, but one that doesn’t care about where information comes from.
Sight, scent, taste, sound, touch — all of our precious senses, once communicated to the brain, are transformed into simple electrical pulses. Although we consciously perceive the world through light rays and sound waves, the computing that supports those experiences is all one tone — electrical.
Continue reading “Rats Engineered to See Infrared Light, Use It to Seek Out Water” »
Nov 8, 2015
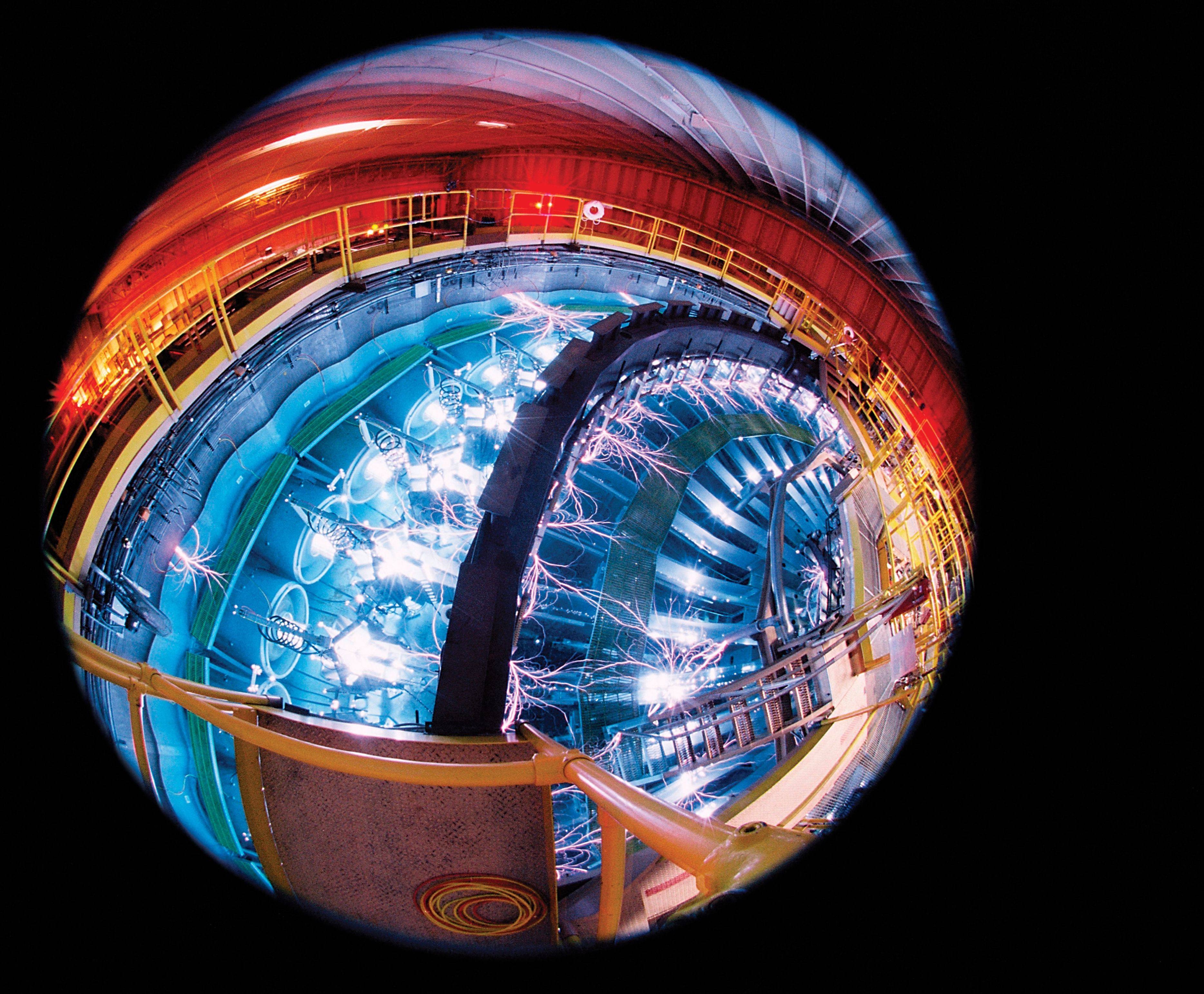
Inside The Z Machine, Where Scientists Turned Hydrogen Into Metal
Posted by Dan Kummer in category: physics
Nov 8, 2015
Theory of a Mach Effect Thruster II
Posted by Andreas Matt in categories: energy, information science, quantum physics, space travel
ABSTRACT
According to Einstein, General Relativity contains the essence of Mach’s ideas. Mach’s principle can be summarized by stating that the inertia of a body is determined by the rest of the mass-energy content of the universe. Inertia here arises from mass-energy there. The latter, was a statement made by John Wheeler in his 1995 book, Gravitation and Inertia, coauthored by Ciufolini. Einstein believed that to be fully Machian, gravity would need a radiative component, an action-at-a-dis- tance character, so that gravitational influences on a body from far away could be felt immediately. In 1960’s, Hoyle and Narlikar (HN) developed such a theory which was a gravitational version of the Absorber theory derived by Wheeler-Feynman for classical electrodynamics and later expanded upon by Davies and Narlikar for quantum electrodynamics. The HN-field equation has the same type of mass fluctuation terms as in the Woodward Mach effect thruster theory. The force equation, used to predict the thrust in our device, can be derived from the mass fluctuation. We outline a new method for deriving the force equation. We present new experimental tests of the thruster to show that the thrust seen in our device is not due to either heating or Dean Drive effects. Successful replications have been performed by groups in Austria and Canada, but their work is still pending in the peer review literature.
Keywords:
Mach Effect Drive, Transient Mass Fluctuations, Mach’s Principle, Action at a Distance, Advanced Waves, Event Horizon.