Page 11932
Oct 31, 2015
What if some celestial bodies were closer to us
Posted by Sean Brazell in category: space
Oct 30, 2015
Mind Control Device Alters Emotions on Demand
Posted by Sean Brazell in categories: electronics, finance, mobile phones, neuroscience
Think of all the possibilities!
Mind control has been a topic of many great suspense and science fiction movies until recent. Now, an emotion altering device that will work in conjunction with a smart phone app is now being developed by Thync, and is slated for release to the public in 2015.
Thync announced on Oct. 8 that it’s raised $13 million from financial contributors to develop technology combining neuroscience and consumer electronics.
Continue reading “Mind Control Device Alters Emotions on Demand” »
Oct 30, 2015
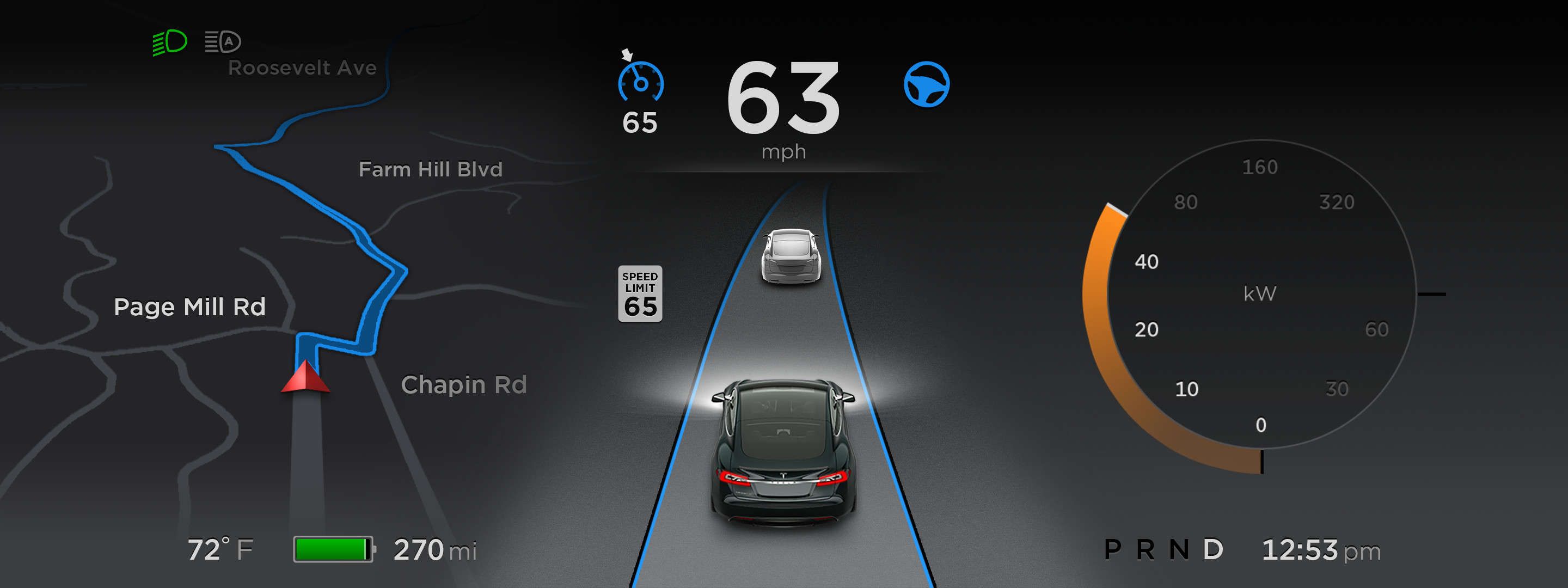
The Autopilot is learning fast: Model S owners are already reporting that Tesla’s Autopilot is self-improving
Posted by Julius Garcia in categories: Elon Musk, neuroscience, robotics/AI, sustainability, transportation
During the press conference for the release of the Autopilot, Tesla CEO Elon Musk referred to each Model S owners as “expert trainers” – meaning that each driver will train the autonomous features of the system to feed the collective network intelligence of the fleet by simply driving the electric vehicle on Autopilot.
He said that the system should improve everyday, but that improvements might only become noticeable every week or so by adding up. Just a few weeks after the release, Model S owners are already taking to the Tesla Motors Club forum to describe how the Autopilot is improving…
Oct 30, 2015
Scientist Claims He Has Found Evidence Of Other Universes
Posted by Andreas Matt in category: cosmology
A new study submitted to the Astrophysical Journal has claimed to have found evidence of interactions between our universe and other universes by looking at the cosmic microwave background (CMB). The scientist discovered an anomaly associated with some regions of the CMB, and he believes it is evidence for alternate universes.
Dr Ranga Chary, the author of the study, wrote that his observations could “possibly be due to the collision of our universe with an alternate universe whose baryon to photon ratio is a factor of about 65 larger than ours.” A pre-print of the study, which is yet to be peer reviewed, is available on ArXiv.
The CMB is the first light that shone in the universe. It was emitted 370,000 years after the Big Bang when the universe was cool enough for hydrogen to form and the original photons were free to move without getting absorbed by the primordial matter.
Oct 30, 2015
Awe, curiosity over sudden, huge ‘gash’ in Wyoming’s Bighorn Mountains
Posted by Sean Brazell in category: futurism
A sudden, deep “crack” or “gash” in the Earth around Wyoming’s Bighorn Mountains has left many in awe and curious about the explanation.
Oct 30, 2015
Study finds new way of computing with interaction-dependent state change of nanomagnets
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: computing, engineering, nanotechnology
Researchers from the University of South Florida College of Engineering have proposed a new form of computing that uses circular nanomagnets to solve quadratic optimization problems orders of magnitude faster than that of a conventional computer.
A wide range of application domains can be potentially accelerated through this research such as finding patterns in social media, error-correcting codes to Big Data and biosciences.
In an article published in the current issue of Nature Nanotechnology, “Non Boolean computing with nanomagnets for computer vision applications,” authors Sanjukta Bhanja, D.K. Karunaratne, Ravi Panchumarthy, Srinath Rajaram, and Sudeep Sarkar discuss how their work harnessed the energy-minimization nature of nanomagnetic systems to solve the quadratic optimization problems that arise in computer vision applications, which are computationally expensive.
Oct 30, 2015
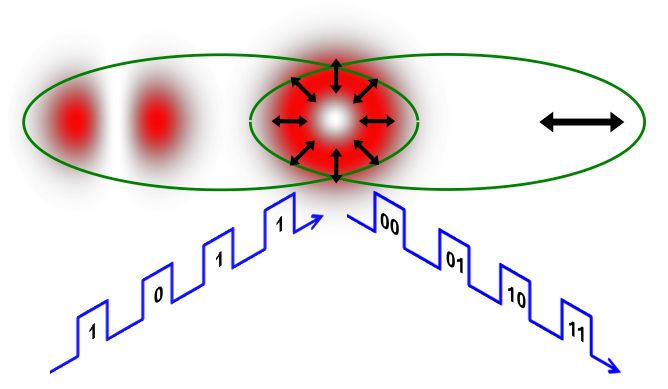
Physicists mimic quantum entanglement with laser pointer to double data speeds
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: information science, quantum physics
In a classic eureka moment, a team of physicists led by The City College of New York and including Herriot-Watt University and Corning Incorporated is showing how beams from ordinary laser pointers mimic quantum entanglement with the potential of doubling the data speed of laser communication.
Quantum entanglement is a phrase more likely to be heard on popular sci-fi television shows such as “Fringe” and “Doctor Who.” Described by Albert Einstein as “spooky action at a distance,” when two quantum things are entangled, if one is ‘touched’ the other will ‘feel it,’ even if separated by a great distance.
“At the heart of quantum entanglement is ‘nonseparability’ — two entangled things are described by an unfactorizable equation,” said City College PhD student Giovanni Milione. “Interestingly, a conventional laser beam (a laser pointer)’s shape and polarization can also be nonseparable.”
Oct 30, 2015
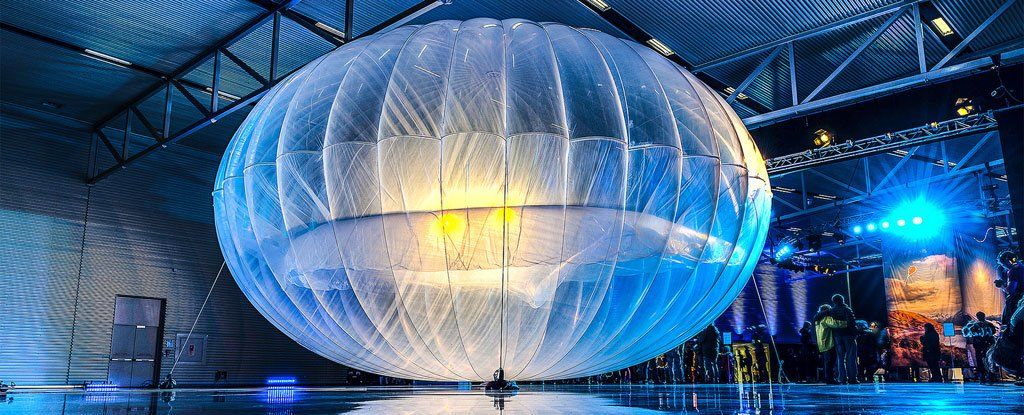
Project Loon is set to circle the planet with Internet balloons in 2016
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in category: internet
Google’s Project Loon is a massively ambitious plan to provide Internet connectivity to areas of the planet that don’t already enjoy good access to the web. How? Via a huge fleet of helium balloons that hang in the stratosphere 20 kilometres above the surface, assembling to form a high-tech communication network that beams the web to the surface.
And the undertaking is only getting more ambitious, with the company announcing this week that it plans to circle the planet with a ring of Project Loon balloons that will provide a perpetual data service for those living underneath its path.
It sounds like science fiction, but this isn’t some faraway ethereal concept we’re talking about. Google says it will do this next year, provided current tests work out as planned.
Oct 30, 2015
Bitcoin is 100 times More Powerful than Google
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: bitcoin, computing
Allow me to introduce you to someone who has the potential to be very important in the future of Bitcoin. His name is Balaji Srinivasan, and he is the chairman and co-founder of 21 Inc. What is 21 Inc? 21 Inc. is the Bitcoin startup that secured the most venture capital of any Bitcoin company in history, at $116 million. What do they need $116 million in venture capital for? They are investing in “future proprietary products designed to drive mainstream adoption of Bitcoin.” With that in mind, the research of 21 Inc. has highlighted some interesting Bitcoin factoids. One Srinivasan released at the second annual Bitcoin Job Fair held last weekend in Sunnyvale, California regarding how big Bitcoin has become in the computing world.
Honestly, I looked online to find out what a petahash rate and a gigahash rate was, and that is one long rabbit hole, so I’ll leave the technical ramble to techies like Mr. Srinivasan. He makes the comparison to Google based on the fair assumption that they are using 1e7 servers, for 1e7 H/s per Xeon, and ~10 Xeons/server = 1 PH/s. One petahash equals 1,000,000 gigahash or 1000 terahashes. Bitcoin reached 1 PH/s of computing power/speed on September 15th, 2013. It is now normally working at over 350 PH/s, or over 350,000,000 GH/s.
” All of Google today would represent less than 1% of all of mining (Bitcoin operations worldwide). The sheer degree of what is happening in (Bitcoin) mining is not being appreciated by the press,” said Balaji Srinivasan at the Bitcoin Job Fair. “If we assume there are 10 million Google servers, and each of these servers is running, you can multiply that through and get one petahash. If they turned off all of their data centers and pointed them at Bitcoin (mining network), they would be less than 1% of the network.”