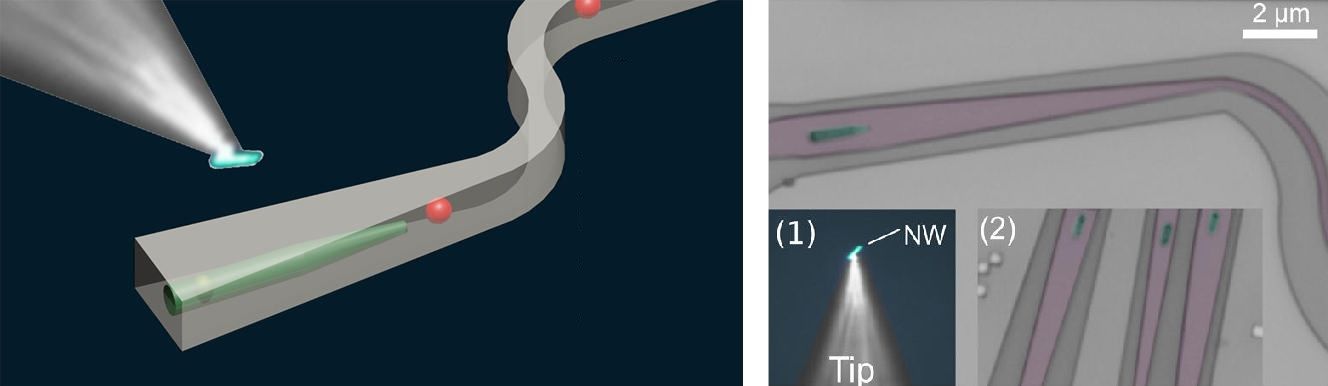
(Phys.org)—One promising approach for scalable quantum computing is to use an all-optical architecture, in which the qubits are represented by photons and manipulated by mirrors and beam splitters. So far, researchers have demonstrated this method, called Linear Optical Quantum Computing, on a very small scale by performing operations using just a few photons. In an attempt to scale up this method to larger numbers of photons, researchers in a new study have developed a way to fully integrate single-photon sources inside optical circuits, creating integrated quantum circuits that may allow for scalable optical quantum computation.
The researchers, Iman Esmaeil Zadeh, Ali W. Elshaari, and coauthors, have published a paper on the integrated quantum circuits in a recent issue of Nano Letters.
As the researchers explain, one of the biggest challenges facing the realization of an efficient Linear Optical Quantum Computing system is integrating several components that are usually incompatible with each other onto a single platform. These components include a single-photon source such as quantum dots; routing devices such as waveguides; devices for manipulating photons such as cavities, filters, and quantum gates; and single-photon detectors.
Read more