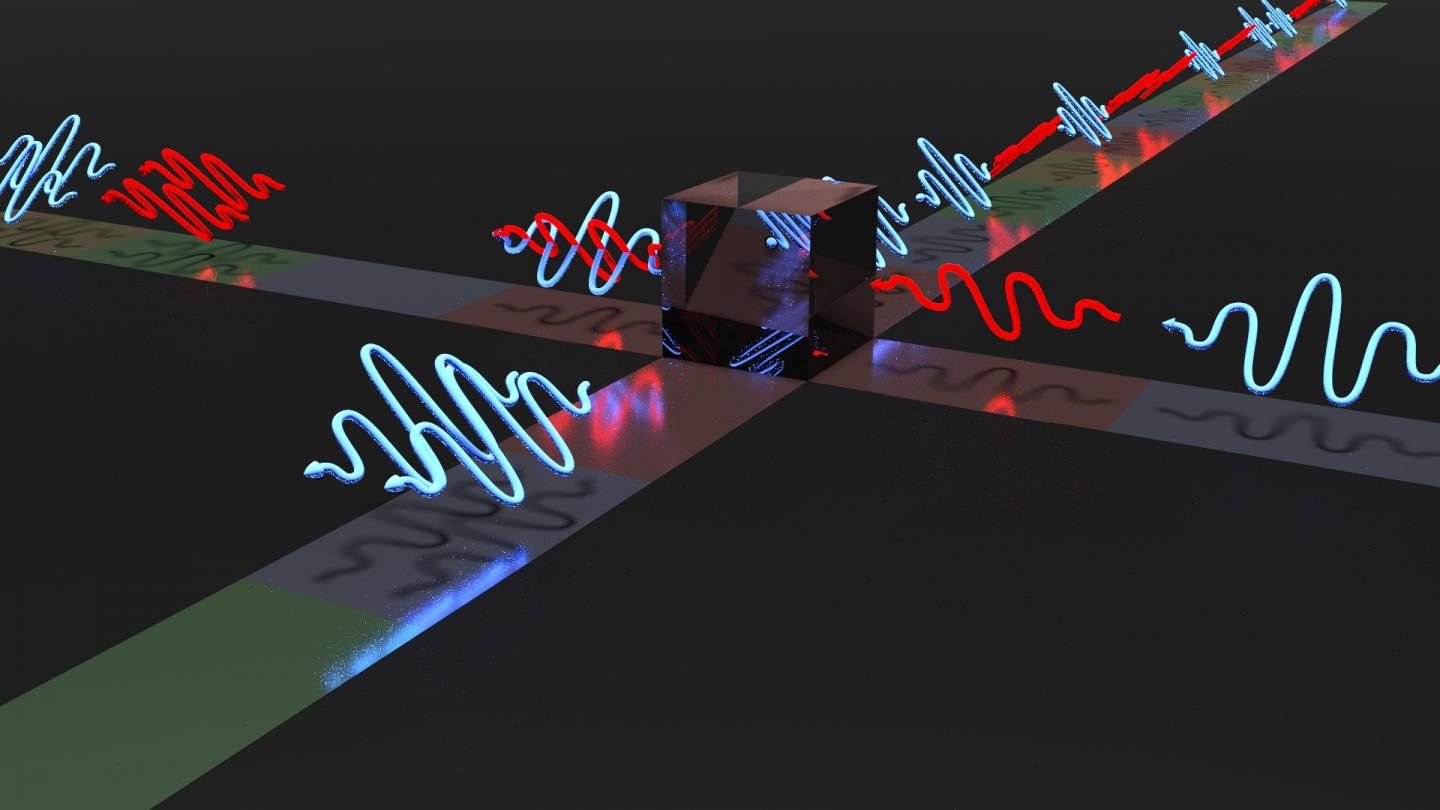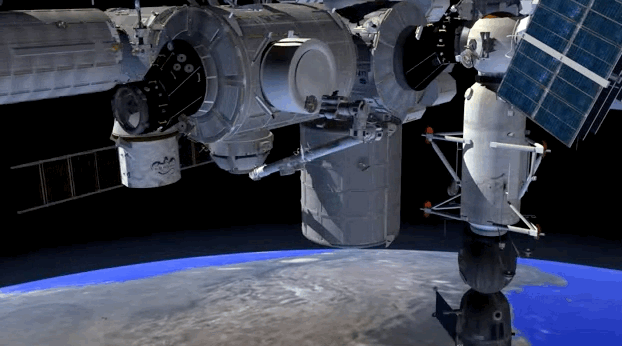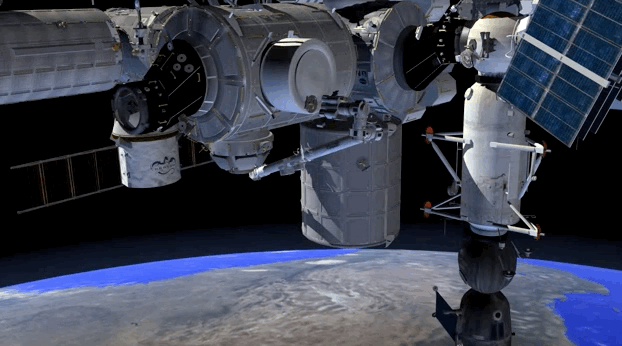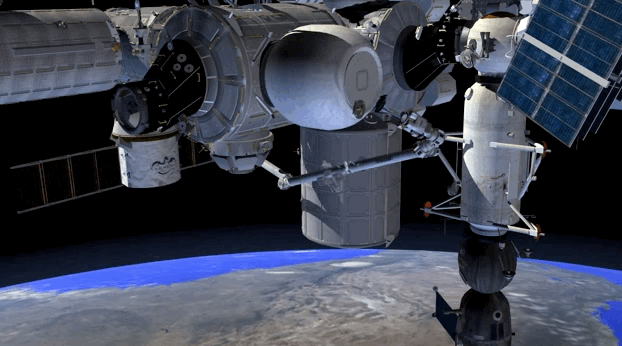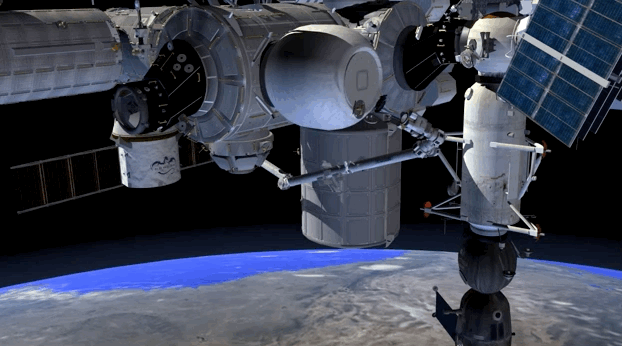
Next week, astronauts on the International Space Station are getting a brand new room. Called the BEAM, short for Bigelow Expandable Activity Module, the room is launching on top of one of SpaceX’s rockets on Friday; it will then be attached to the ISS sometime within the next four months. The BEAM, which is created by private company Bigelow Aerospace, will remain deflated during launch, but once in orbit, it will inflate up to four times its size, providing more overall volume for the interior of the ISS.
The BEAM isn’t a permanent addition to the space station, though. It will only stay attached to the ISS for two years, and the astronauts will go inside the habitat very rarely. That’s because the main goal of the BEAM is to test out if this expandable habitat technology actually works. A successful mission could be the first step to something bigger: an era when expandable space habitats orbit the Earth, allowing for scientists and tourists to visit these “space hotels.”
The concept of expandable spacecraft isn’t new. In the 1960s, NASA launched a series of expandable communication probes called the Echo satellites, which looked like big metallic balloons. The satellites inflated in space and turned into mirror-like reflectors that bounced signals from one spot on Earth to another. Since then, NASA and other private companies have toyed with the idea of scaling up expandable spacecraft so that they could house humans in space.
Continue reading “How expandable astronaut habitats could pave the way for private space hotels” »