Apr 8, 2016
Limb regeneration activation genes found in mammals and regenration of heart tissue and paws activitated in mice
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in category: biotech/medical
If you trace our evolutionary tree way back to its roots — long before the shedding of gills or the development of opposable thumbs — you will likely find a common ancestor with the amazing ability to regenerate lost body parts.
Researchers have built a running list of the genes that enable regenerating animals to grow back a severed tail or repair damaged tissues. Surprisingly, they have found that genes important for regeneration in these creatures also have counterparts in humans. The key difference might not lie in the genes themselves but in the sequences that regulate how those genes are activated during injury.
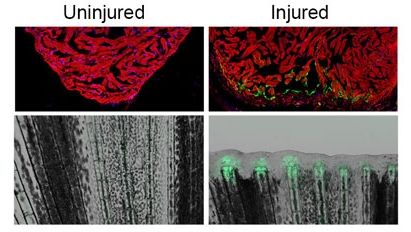
A Duke study appearing April 6 in the journal Nature has discovered the presence of these regulatory sequences in zebrafish, a favored model of regeneration research. Called “tissue regeneration enhancer elements” or TREEs, these sequences can turn on genes in injury sites and even be engineered to change the ability of animals to regenerate.