May 1, 2014
Flowing salt water over graphene generates electricity
Posted by Seb in categories: energy, nanotechnology
ArsTechnica
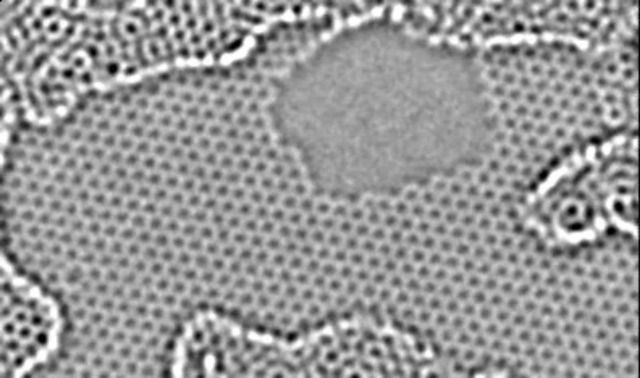
Hydroelectricity is one of the oldest techniques for generating electrical power, with over 150 countries using it as a source for renewable energy. Hydroelectric generators only work efficiently at large scales, though—scales large enough to interrupt river flow and possibly harm local ecosystems. And getting this sort of generation down to where it can power small devices isn’t realistic.
In recent years, scientists have investigated generating electrical power using nano-structures. In particular, they have looked at generating electricity when ionic fluids—a liquid with charged ions in it—are pushed through a system with a pressure gradient. However, the ability to harvest the generated electricity has been limited because it requires a pressure gradient to drive ionic fluid through a small tube. But scientists have now found that dragging small droplets of salt water on strips of graphene generates electricity without the need for pressure gradients.

 Jason Dorrier — Singularity Hub
Jason Dorrier — Singularity Hub

 In 1969, the United States put two men on the moon. The mission required more than 3,500 IBM employees and the most sophisticated programs ever written. Today, though, a single Apple iPhone holds more computing power than any of the technology used on Apollo 11. That rapid advance can be explained by a pattern called Moore’s Law: every 18 months, the amount of transistors that it’s possible to fit on to a one–
In 1969, the United States put two men on the moon. The mission required more than 3,500 IBM employees and the most sophisticated programs ever written. Today, though, a single Apple iPhone holds more computing power than any of the technology used on Apollo 11. That rapid advance can be explained by a pattern called Moore’s Law: every 18 months, the amount of transistors that it’s possible to fit on to a one–








