Oct 4, 2024
A new era of solar observation: International team produces global maps of coronal magnetic field
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: mapping, space
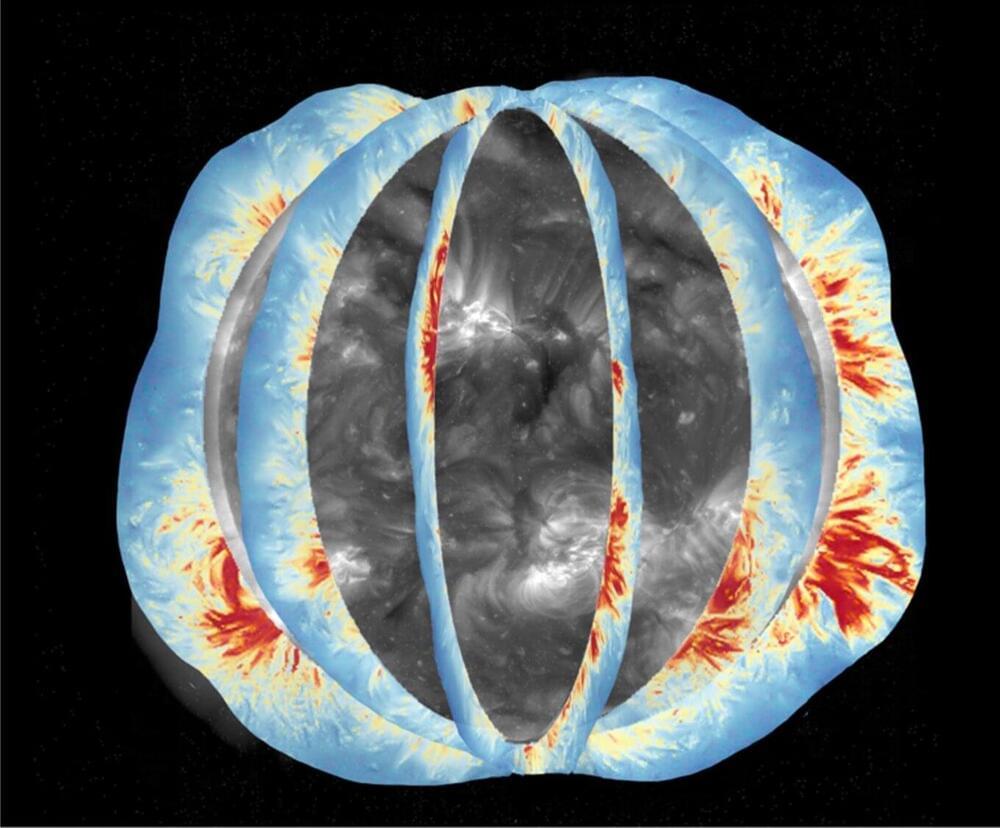
For the first time, scientists have taken near-daily measurements of the sun’s global coronal magnetic field, a region of the sun that has only been observed irregularly in the past. The resulting observations are providing valuable insights into the processes that drive the intense solar storms that impact fundamental technologies, and thus lives and livelihoods, here on Earth.