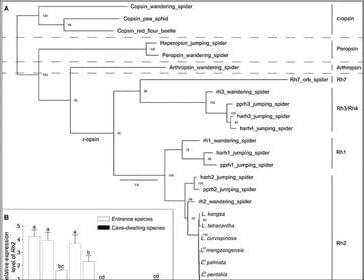
First, we halved the deep methane abundance (model A), since we know the polar regions are methane-depleted, but found that although such a change produces changes in (I/F)0 and k that reasonably approximate the shape of observed differences between the polar and equatorial regions in Fig. 12, the amplitude is not sufficiently large and is close to zero at blue wavelengths. Secondly, we tried halving the methane abundance and increasing the opacity of the Aerosol-2 layer, τ2, by 1.0 (model B), from 4.6 to 5.6. Note that all opacities quoted here are at a reference wavelength of 800 nm. Here, we see an increase in the (I/F)0 and k difference at green wavelengths, but a decrease at blue wavelengths. The reason for this is that the Aerosol-2 particles are retrieved to have increased imaginary refractive index at blue wavelengths (Irwin et al. 2022), which lowers the single-scattering albedo here. Hence, increasing the Aerosol-2 opacity reduces the reflectivity at blue wavelengths, rather than increasing it. How then can we match the observed differences between the polar and equatorial spectra of the 2002 HST/STIS data? In the study of James et al. (2023), noted earlier, it was found that the optimal solution was to not only increase the opacity of the particles in the Aerosol-2 layer, but also make them more reflective at wavelengths longer than 500 nm. We could have similarly adjusted the imaginary refractive index spectra, nimag, of the Aerosol-2 particles (lower nimag values increase the single-scattering albedo), but in a parallel analysis of VLT/MUSE observations of Neptune, Irwin et al. (2023b) found that the observed spectra of deep bright spots could be well approximated by adding a component of bright particles to the existing Aerosol-1 layer at ∼5 bar. We wondered whether a similar approach might be applicable here. Changes in the Aerosol-1 layer cannot account for the observed HST/STIS pole–equator differences, since this layer is only detectable in narrow wavelength bands of very low methane absorption, but in Fig. 12 it can be seen that if we add a unit opacity of conservatively scattering particles to the Aerosol-2 layer at 1–2 bar (with the same Gamma size distribution as the Aerosol-2 particles, with mean radius 0.6 μm and variance σ = 0.3) the (I/F)0 and k difference increases at all wavelengths longer than ∼ 480 nm (model X), although not as much as the difference between polar and equatorial latitudes. However, if we add this additional opacity and simultaneously halve the methane abundance (Model C1) we find that the differences in the (I/F)0 and k spectra agree moderately well with the observed pole–equator difference spectra at most wavelengths. What might be responsible for this extra component of bright particles in the Aerosol-2 layer will be discussed further, but it could indicate that more methane ice particles are present in the haze/methane-ice layer, or that more methane ice is condensed onto the haze Cloud Condensation Nuclei (CCN). Whatever the cause, it is clear that the spectral difference between the polar and equatorial regions seen by HST/STIS in 2002 is consistent with a reduction in methane abundance coupled with an increase in the reflectivity of the particles in the Aerosol-2 layer that could be caused by the addition of a conservatively scattering component.
Having surveyed the possible interpretations of the HST/STIS polar and equatorial spectra, we then tested these models against the seasonal photometric magnitude data. While the Lowell Observatory magnitude data accurately preserve the quantities that were measured, they are a less intuitive measure for interpreting the changes in Uranus’s reflectivity spectrum with atmospheric models. Hence, we converted the magnitudes to the mean disc-averaged reflectivities of Uranus, which also corrects out the solid-angle variations of Uranus’s disc size, noted earlier. This conversion was done using the procedures outlined in Appendix B. The resulting seasonal variations in disc-averaged reflectivity at the blue and green wavelengths of the Strömgren b and y filters are shown in Fig. 13. Here, it can be seen that the disc-averaged green reflectivity of Uranus changes from ∼0.47 to ∼0.
 עברית (Hebrew)
עברית (Hebrew)