Page 801
Jan 13, 2024
Unlocking Hypnosis: Stanford Enhances Brain Power With Neurostimulation
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: biotech/medical, neuroscience
Stanford Medicine scientists used transcranial magnetic stimulation to temporarily enhance hypnotizability in patients with chronic pain, making them better candidates for hypnotherapy.
How deeply someone can be hypnotized — known as hypnotizability — appears to be a stable trait that changes little throughout adulthood, much like personality and IQ. But now, for the first time, Stanford Medicine researchers have demonstrated a way to temporarily heighten hypnotizablity — potentially allowing more people to access the benefits of hypnosis-based therapy.
In the new study, published on January 4 in Nature Mental Health, the researchers found that less than two minutes of electrical stimulation targeting a precise area of the brain could boost participants’ hypnotizability for about one hour.
Jan 13, 2024
Light-Matter Magic Explained: Broken Symmetry Drives Polaritons
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: nanotechnology, particle physics
Scientists uncover new insights on polaritons, showing potential for breakthroughs in light manipulation and nanotechnology applications.
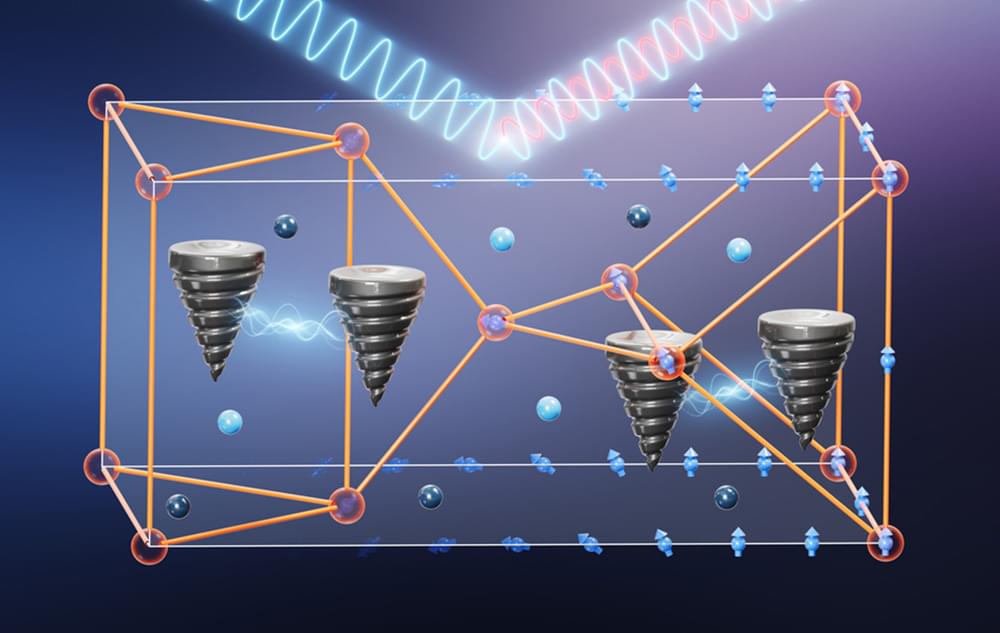
An international team of scientists provides an overview of the latest research on light-matter interactions. A team of scientists from the Fritz Haber Institute, the City University of New York, and the Universidad de Oviedo has published a comprehensive review article in the scientific journal Nature Reviews Materials. In this article, they provide an overview of the latest research on polaritons, tiny particles that arise when light and material interact in a special way.
Understanding Polaritons
Jan 13, 2024
Elon Musk’s Starlink satellites are “leaking” signals
Posted by Kelvin Dafiaghor in categories: Elon Musk, internet, physics, satellites

Thousands of satellites have been launched into Earth orbit over the past decade or so, with tens of thousands more planned in coming years. Many of these will be in “mega-constellations” such as Starlink, which aim to cover the entire globe.
These bright, shiny satellites are putting at risk our connection to the cosmos, which has been important to humans for countless millennia and has already been greatly diminished by the growth of cities and artificial lighting. They are also posing a problem for astronomers – and hence for our understanding of the universe.
Continue reading “Elon Musk’s Starlink satellites are ‘leaking’ signals” »
Jan 13, 2024
Making More Magnetism Possible with Topology
Posted by Dan Breeden in categories: engineering, quantum physics
Researchers who have been working for years to understand electron arrangement, or topology, and magnetism in certain semimetals have been frustrated by the fact that the materials only display magnetic properties if they are cooled to just a few degrees above absolute zero.
A new MIT study led by Mingda Li, associate professor of nuclear science and engineering, and co-authored by Nathan Drucker, a graduate research assistant in MIT’s Quantum Measurement Group and PhD student in applied physics at Harvard University, along with Thanh Nguyen and Phum Siriviboon, MIT graduate students working in the Quantum Measurement Group, is challenging that conventional wisdom.
The open-access research, published in Nature Communications, for the first time shows evidence that topology can stabilize magnetic ordering, even well above the magnetic transition temperature — the point at which magnetism normally breaks down.
Jan 13, 2024
The Attention Schema Theory: A Foundation for Engineering Artificial Consciousness
Posted by Dan Breeden in categories: biological, neuroscience, robotics/AI
The purpose of the attention schema theory is to explain how an information-processing device, the brain, arrives at the claim that it possesses a non-physical, subjective awareness and assigns a high degree of certainty to that extraordinary claim. The theory does not address how the brain might actually possess a non-physical essence. It is not a theory that deals in the non-physical. It is about the computations that cause a machine to make a claim and to assign a high degree of certainty to the claim. The theory is offered as a possible starting point for building artificial consciousness. Given current technology, it should be possible to build a machine that contains a rich internal model of what consciousness is, attributes that property of consciousness to itself and to the people it interacts with, and uses that attribution to make predictions about human behavior. Such a machine would “believe” it is conscious and act like it is conscious, in the same sense that the human machine believes and acts.
This article is part of a special issue on consciousness in humanoid robots. The purpose of this article is to summarize the attention schema theory (AST) of consciousness for those in the engineering or artificial intelligence community who may not have encountered previous papers on the topic, which tended to be in psychology and neuroscience journals. The central claim of this article is that AST is mechanistic, demystifies consciousness and can potentially provide a foundation on which artificial consciousness could be engineered. The theory has been summarized in detail in other articles (e.g., Graziano and Kastner, 2011; Webb and Graziano, 2015) and has been described in depth in a book (Graziano, 2013). The goal here is to briefly introduce the theory to a potentially new audience and to emphasize its possible use for engineering artificial consciousness.
The AST was developed beginning in 2010, drawing on basic research in neuroscience, psychology, and especially on how the brain constructs models of the self (Graziano, 2010, 2013; Graziano and Kastner, 2011; Webb and Graziano, 2015). The main goal of this theory is to explain how the brain, a biological information processor, arrives at the claim that it possesses a non-physical, subjective awareness and assigns a high degree of certainty to that extraordinary claim. The theory does not address how the brain might actually possess a non-physical essence. It is not a theory that deals in the non-physical. It is about the computations that cause a machine to make a claim and to assign a high degree of certainty to the claim. The theory is in the realm of science and engineering.
Jan 13, 2024
Towards a mathematical model of the brain — Lai-Sang Young
Posted by Dan Breeden in categories: mathematics, neuroscience
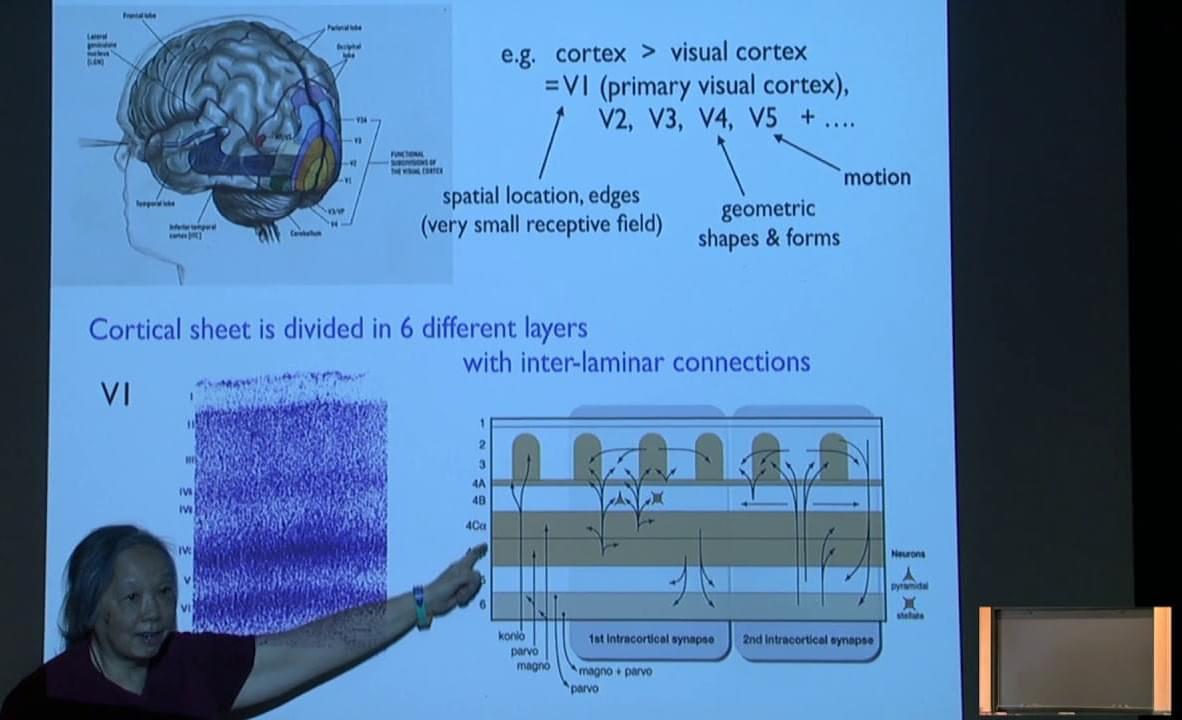
Members’ SeminarTopic: Towards a mathematical model of the brainSpeaker: Lai-Sang YoungAffiliation: New York University; Distinguished Visiting Professor, Sc…
Jan 13, 2024
Solar-powered airship will circle the world non-stop without fuel
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: finance, solar power, sustainability, transportation

Zero-emissions long-distance aviation is absolutely possible… Provided you’re not in a hurry. Solar Airship One will take 20 days to fly all the way around the equator, some 40,000 km (~25,000 miles), in a single zero-emissions hop.
The 151-m (495-ft)-long airship will have its entire upper surface covered in solar film – some 4,800 square meters (51,700 sq ft) of it, or about nine-tenths of an NFL football field for those of you who prefer the standard units.
Continue reading “Solar-powered airship will circle the world non-stop without fuel” »
Jan 13, 2024
Why does depression cause difficulties with learning?
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in categories: biotech/medical, computing, mathematics, neuroscience
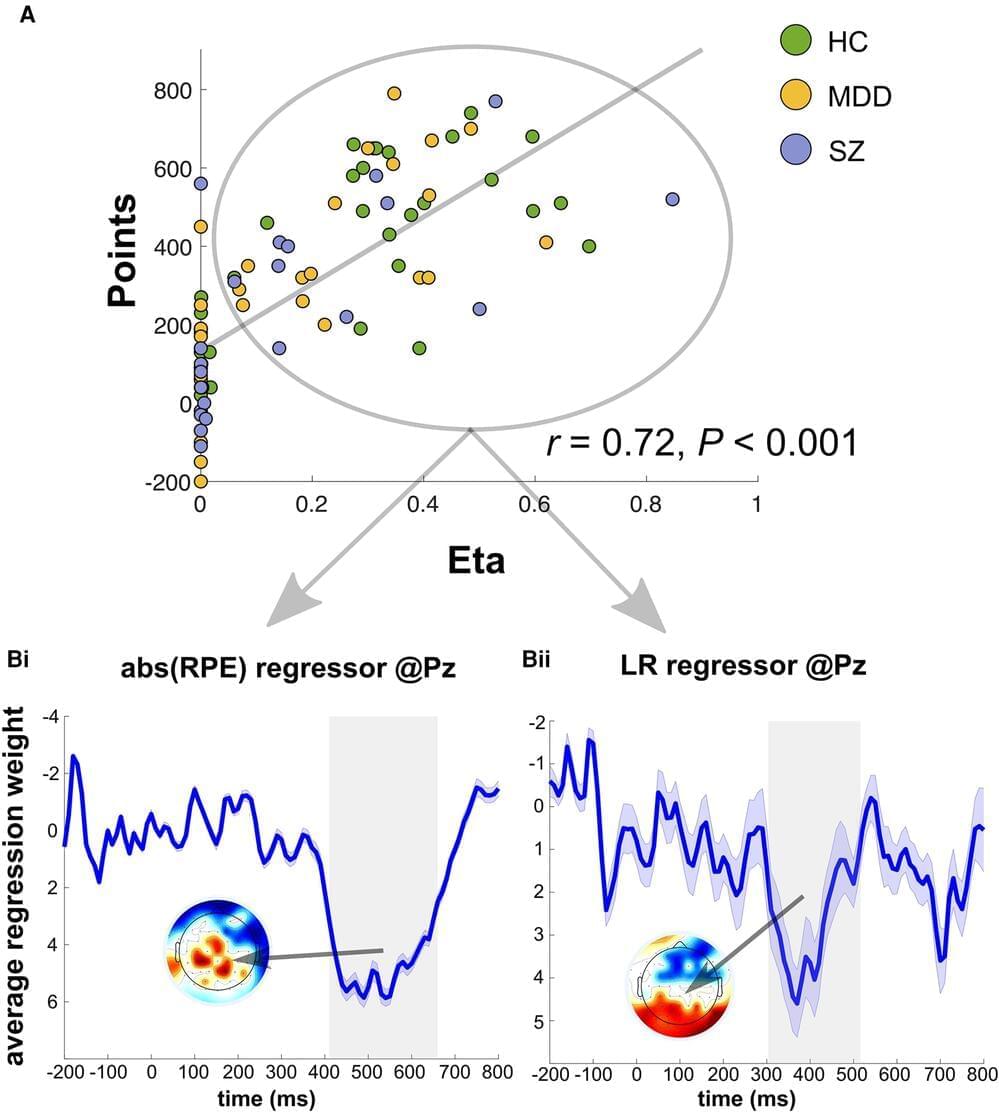
When learning, patients with schizophrenia or depression have difficulty making optimal use of information that is new to them. In the learning process, both groups of patients give greater weight to less important information and, as a result, make less than ideal decisions.
This was the finding of a several-months-long study conducted by a team led by neuroscientist Professor Dr. med. Markus Ullsperger from the Institute of Psychology at Otto von Guericke University Magdeburg in collaboration with colleagues from the University Clinic for Psychiatry & Psychotherapy and the German Center for Mental Health.
By using electroencephalography (EEG) and complex mathematical computer modeling, the team of researchers discovered that learning deficits in depressive and schizophrenic patients are caused by diminished/reduced flexibility in the use of new information.
Jan 13, 2024
To avoid the worst effects of aging, we might need to exercise harder than we thought
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in category: life extension
Those hoping to avoid one of the worst side effects of aging—bone, joint and muscle pain that doesn’t go away—might need to exercise a lot harder and more often than previously believed.
According to a new study, only high levels of activity at least once a week—playing tennis, running, swimming, digging with a spade, or doing hard physical labor as part of your job—appears to help ward off chronic musculoskeletal pain in the long-term.
The study, led by Dr. Nils Niederstrasser at the University of Portsmouth, examined the data of 5,802 people aged 50 or more over ten years.