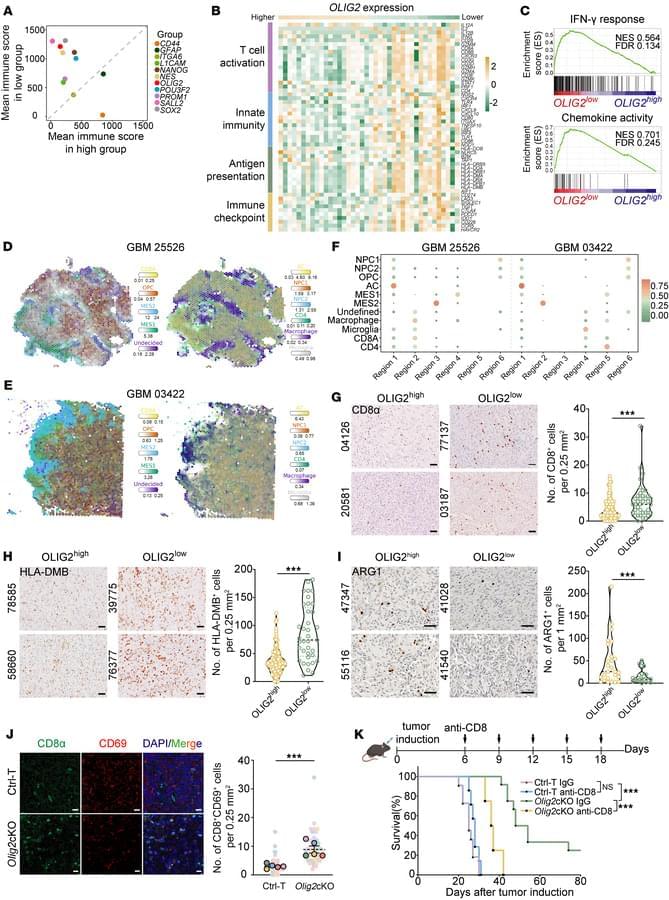
For sexual reproduction to yield healthy offspring, newly generated oocytes—immature egg cells—must receive the correct amount of DNA after cell division. This process of segregating chromosomes becomes more prone to failure as we age. Now, RIKEN researchers have identified a strategy that could help to prevent such errors and restore healthy production of oocytes.
Oocytes are produced by a cell-division process known as meiosis, during which every chromosome is duplicated. These replicates form X-shaped structures in which the chromosomes are joined via structures called centromeres, where a protein called cohesin locks chromosome copies together.
As division proceeds, protein fibers called microtubules spread from opposite poles of the dividing cell, attaching to each chromosome. These microtubules eventually pull the two apart, so that each newly formed cell receives one copy of each chromosome.