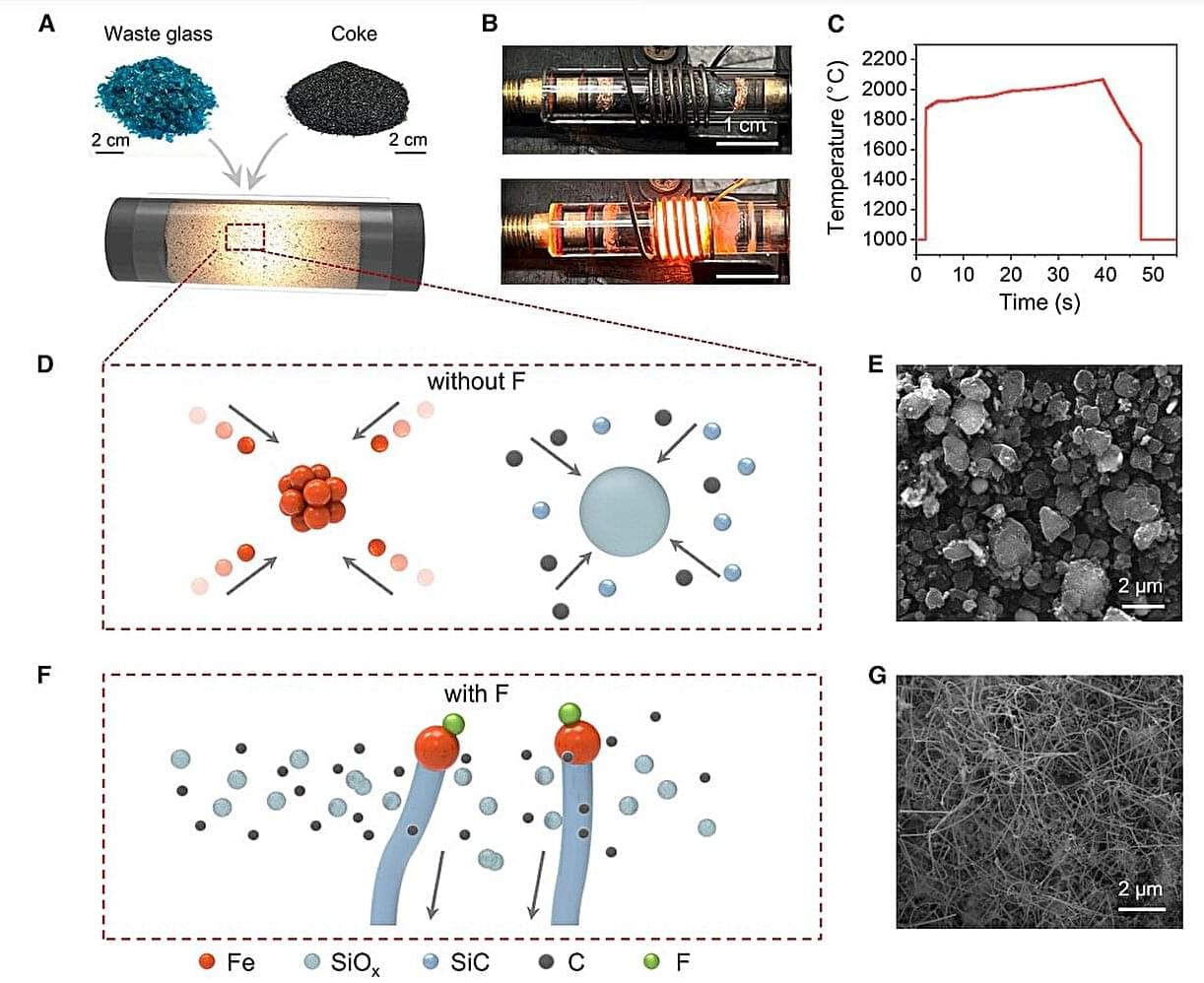
Engineering silicon carbide (SiC) with tailored morphologies for electronics and structural reinforcement materials has always been a costly and time-consuming affair, but scientists can now do it in a flash. A new study shows how discarded glass and silicon-rich coal waste can be turned into valuable SiC nanowires in seconds using a process known as Fluorine-Assisted Flash (FAF) Joule heating, where a quick pulse of electricity instantly heats up the reaction mixture to extremely high temperatures.
In FAF, the fluorine additives trigger the catalytic materials, such as the iron oxides found naturally in waste glass, to act as seeds that drive selective growth of one-dimensional nanowires in under a minute and with an impressive yield of 96%. When used as a reinforcement material in composites, SiC nanowires emerged as clear winners over SiC powders in providing hardness and wear resistance. The findings are published in Matter.