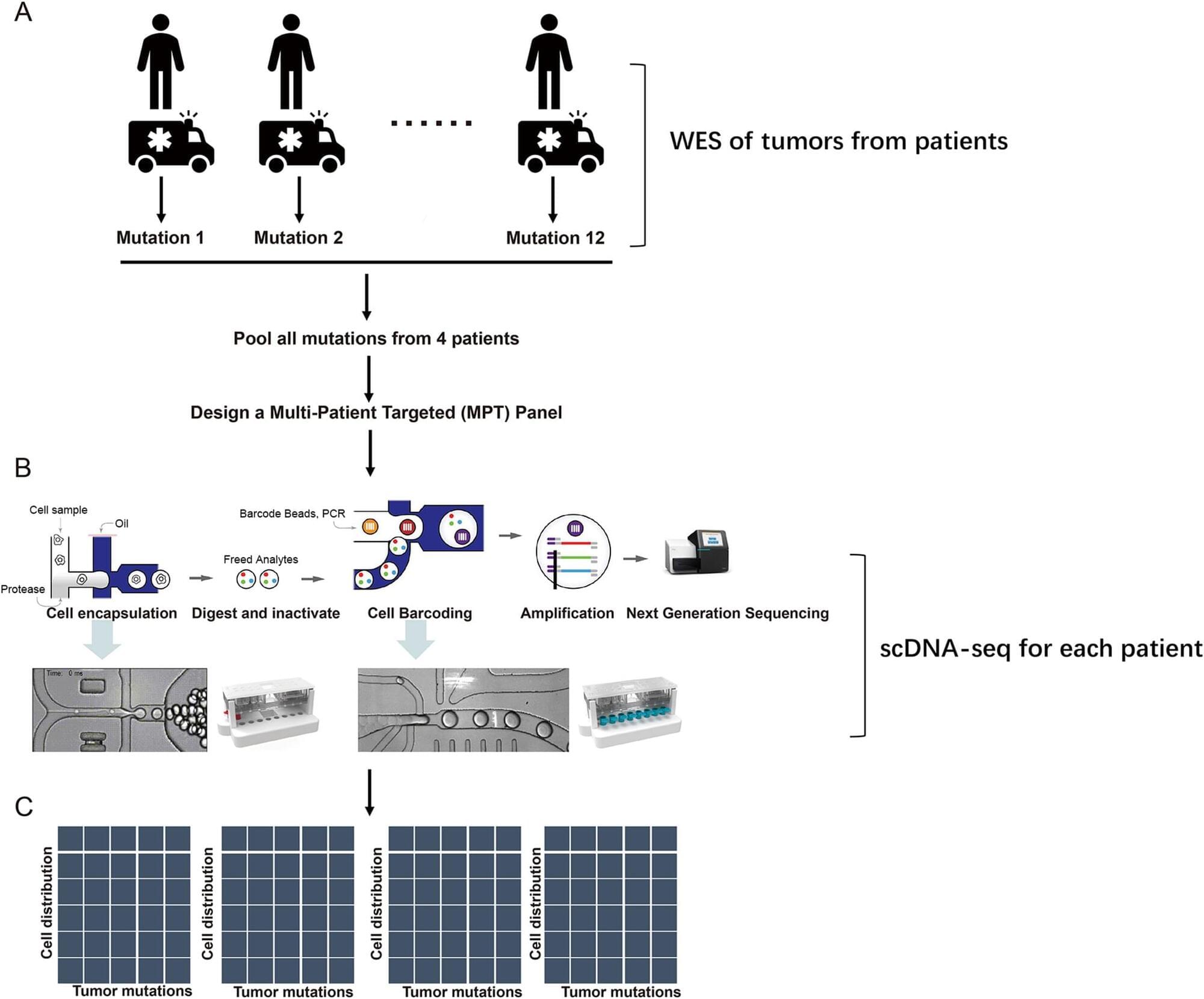
Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (CSCC) is a prevalent skin cancer with aggressive progression that poses significant challenges, especially in metastatic cases. Single-cell DNA sequencing (scDNA-seq) has become an advanced technology for elucidating tumor heterogeneity and clonal evolution. However, comprehensive scDNA-seq studies and tailored mutation panels for CSCC are lacking.
We analyzed the genomic landscape of Chinese CSCC patients via a Multi-Patient-Targeted (MPT) scDNA-seq approach. This method combined bulk exome sequencing with Tapestri scDNA-seq. Mutations identified through bulk sequencing were used to design a targeted panel for scDNA-seq. Comparative analysis was conducted to explore the associations between specific gene mutations and clinical characteristics such as tumor stage and patient sex. Clonal evolution analysis was performed to understand the evolutionary trajectories of the tumors.
Bulk sequencing revealed a diverse spectrum of somatic mutations in CSCC tumors, with missense mutations being predominant. The top tumor mutations, such as those in NOTCH1, TP53, NOTCH2, TTN, MUC16, RYR2, PRUNE2, DMD, HRAS, and CDKN2A, presented similar frequencies to those reported in studies in Korean and Caucasian populations. However, the mutation frequencies of HRAS, TTN, MUC16 and MUC4 were significantly different from the Korean and Caucasian populations. Comparative analysis revealed associations between specific gene mutations and clinical characteristics such as tumor stage and patient sex. Clonal evolution analysis via scDNA-seq revealed distinct evolutionary trajectories and their potential correlation with tumor development and patient prognosis. Furthermore, scDNA-seq identified two low-frequency mutation clones, NLRP5 and HMMR, which play important roles in the clonal evolution of CSCC.