May 29, 2024
New molecule found to suppress bacterial antibiotic resistance evolution
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: biotech/medical, chemistry, evolution
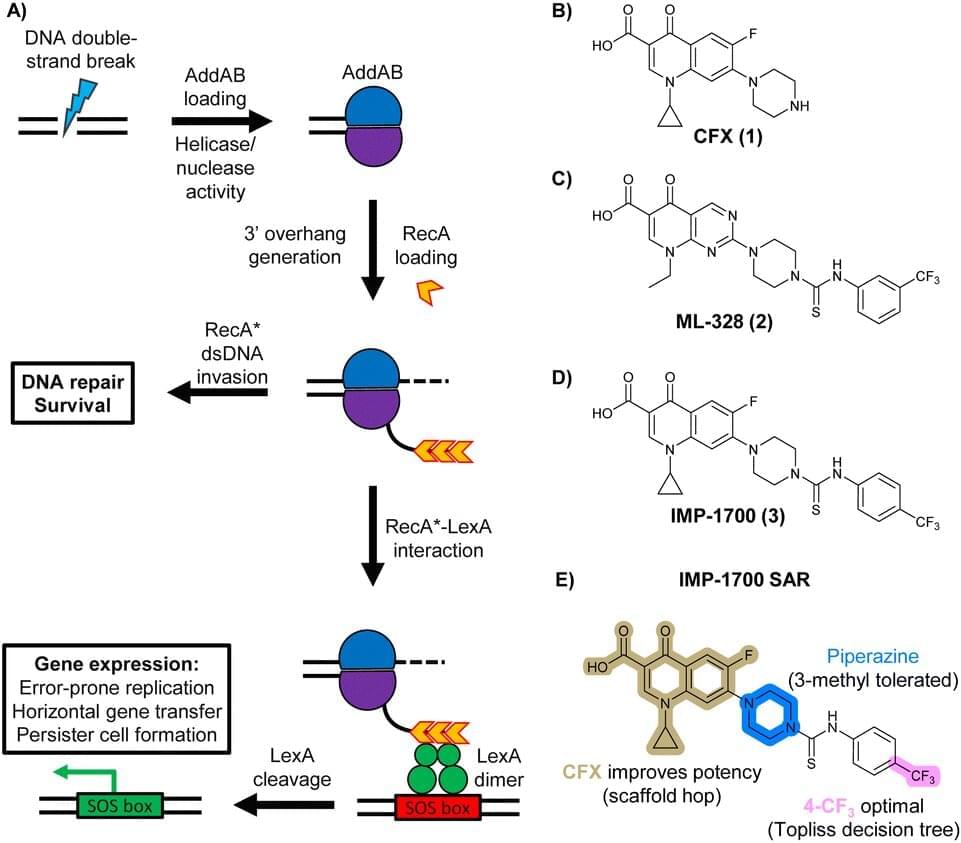
Researchers from the University of Oxford have developed a new small molecule that can suppress the evolution of antibiotic resistance in bacteria and make resistant bacteria more susceptible to antibiotics. The paper, “Development of an inhibitor of the mutagenic SOS response that suppresses the evolution of quinolone antibiotic resistance,” has been published in the journal Chemical Science.