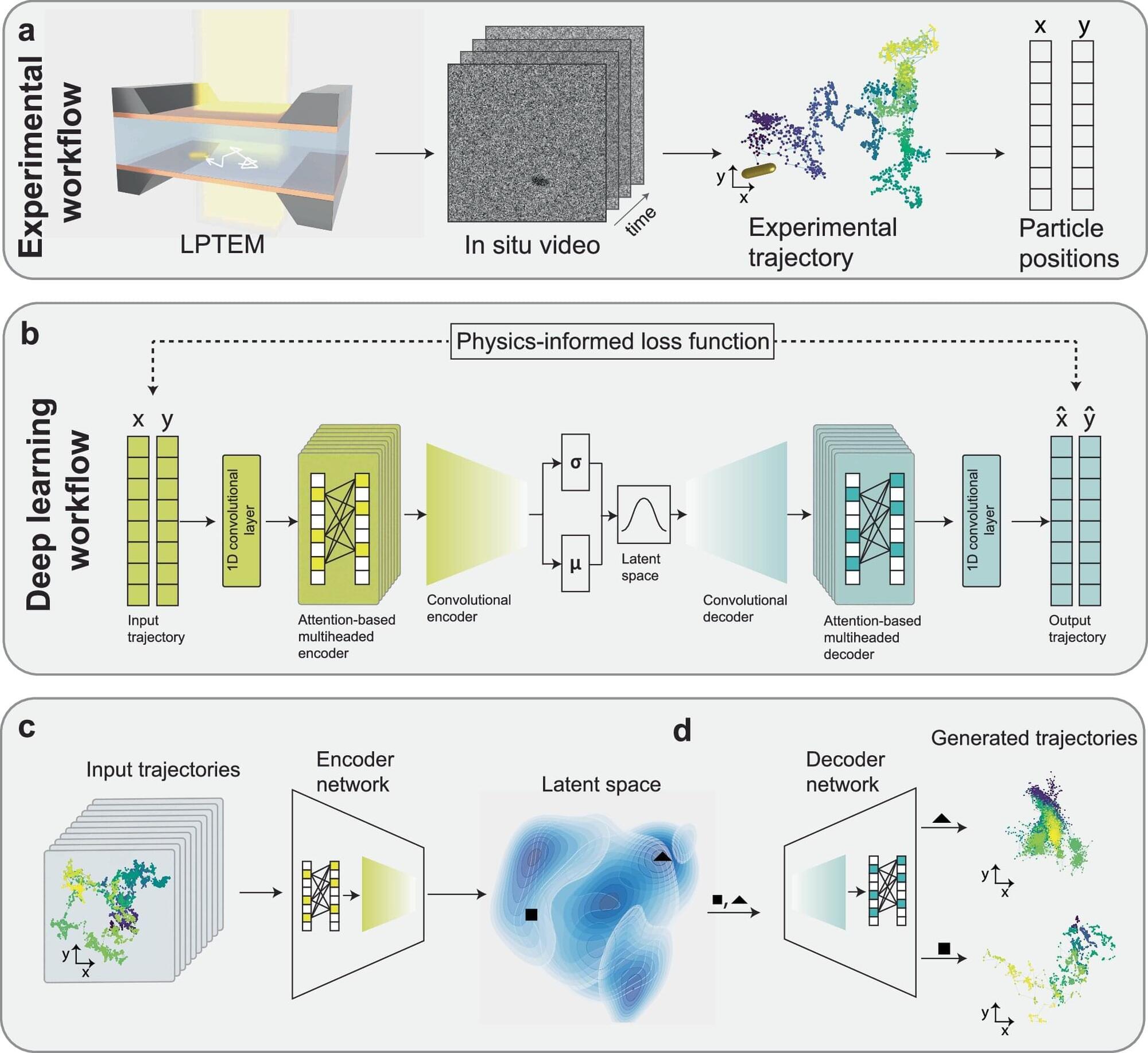
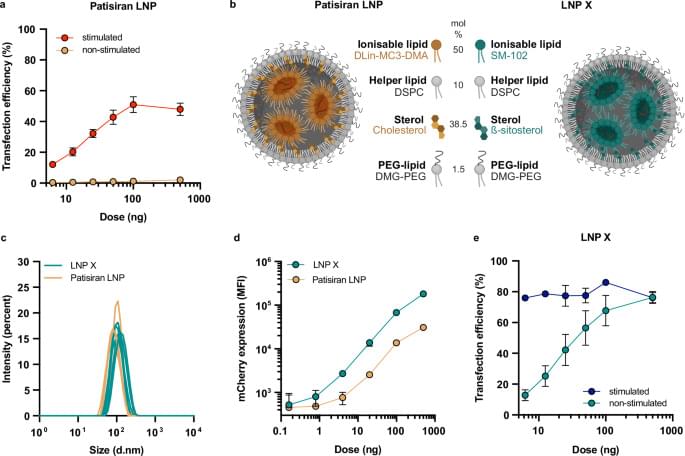
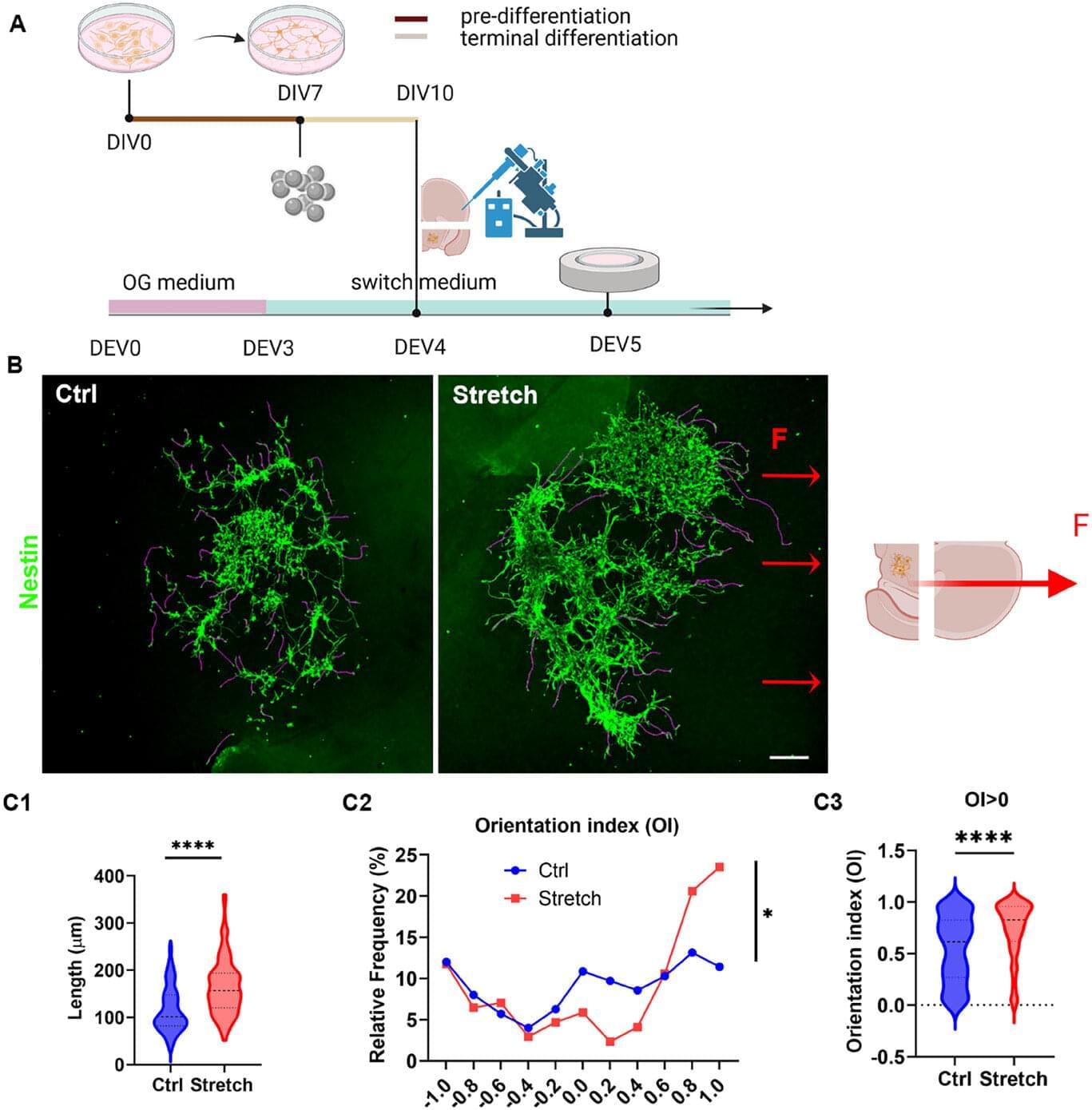
Nanoparticles—the tiniest building blocks of our world—are constantly in motion, bouncing, shifting, and drifting in unpredictable paths shaped by invisible forces and random environmental fluctuations.
Better understanding their movements is key to developing better medicines, materials, and sensors. But observing and interpreting their motion at the atomic scale has presented scientists with major challenges.
Researchers in Georgia Tech’s School of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering (ChBE) have developed an artificial intelligence (AI) model that learns the underlying physics governing those movements.