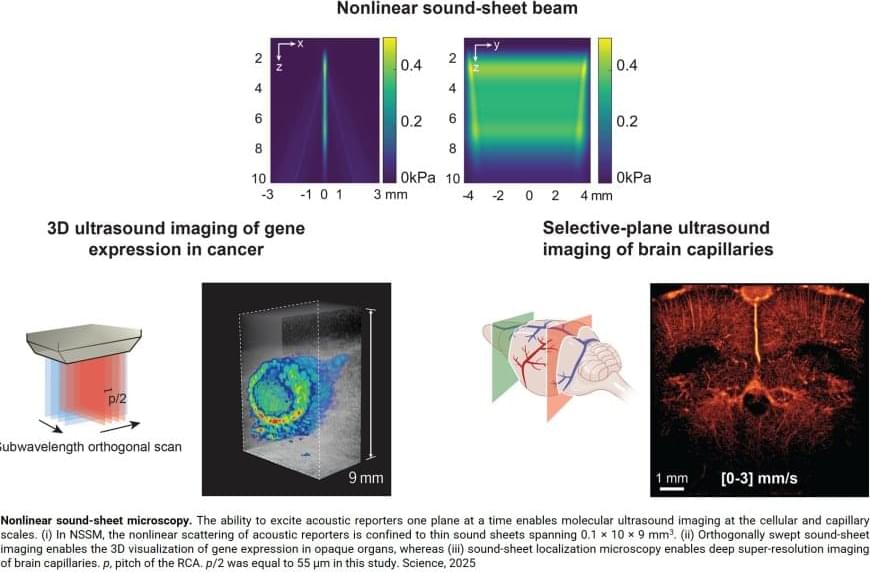
Key to this innovation in ultrasound imaging—a method called Nonlinear sound sheet microscopy —was the discovery of a sound-reflecting probe. The author said: “This probe is a nanoscale gas-filled vesicle that lights up in ultrasound images, making cells visible. These vesicles have a protein shell and we can engineer them to tune their brightness in images. We used these gas vesicles to track cancer cells.”
In addition to revealing cells, the team used ultrasound and microbubbles as probes circulating in the blood stream to detect brain capillaries. The author said: “To our knowledge, nonlinear sound sheet microscopy is the first technique capable of observing capillaries in living brains. This breakthrough has tremendous potential to diagnose small vessel diseases in patients.” Since microbubble probes are already approved for human use, this technique could be deployed in hospitals in a few years.
Ultrasound is one of the most widely used imaging techniques in medicine, but up until recently it hardly played a role in imaging the tiniest structures of our bodies such as cells. “Clinical ultrasound, like the kind used for pregnancy scans, creates real-time images of body parts”, the first author explains. “It allows diagnosis of various diseases, or to monitor a developing baby. However, what is going on at a microscopic level remains hidden.”
Now, a team of scientists managed to image specifically labelled cells in 3D with ultrasound. For the first time, they imaged living cells inside whole organs across volumes the size of a sugar cube. In comparison, current light-based microscopes often require imaging of non-living samples, the author says. “The sample or organ of interest has to be removed and processed, and you lose the ability to track activity of cells over time”