Dec 12, 2023
Cyborg computer with living brain organoid aces machine learning tests
Posted by Paul Battista in categories: biotech/medical, cyborgs, mathematics, robotics/AI
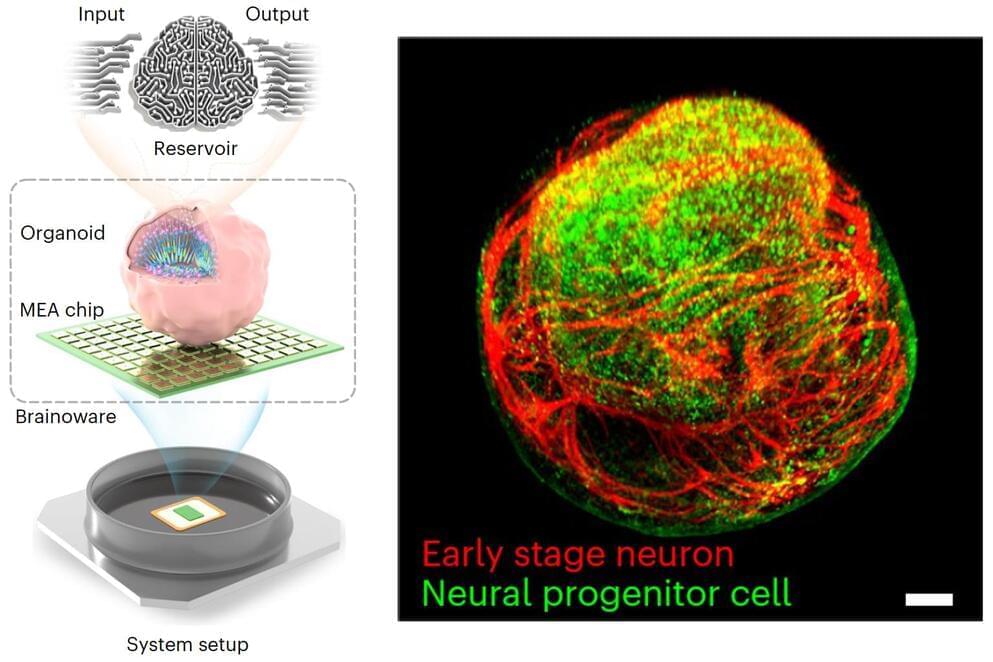
Scientists have grown a tiny brain-like organoid out of human stem cells, hooked it up to a computer, and demonstrated its potential as a kind of organic machine learning chip, showing it can quickly pick up speech recognition and math predictions.
As incredible as recent advances have been in machine learning, artificial intelligence still lags way behind the human brain in some important ways. For example, the brain happily learns and adapts all day long on an energy budget of about 20 watts, where a comparably powerful artificial neural network needs about 8 million watts to achieve anything remotely comparable.
What’s more, the human brain’s neural plasticity, its ability to grow new nervous tissue and expand existing connective channels, has granted it an ability to learn from noisy, low-quality data streams, with minimal training and energy expenditure. What AI systems accomplish with brute force and massive energy, the brain achieves with an effortless elegance. It’s a credit to the billions of years of high-stakes trial and error that delivered the human brain to the state it’s in today, in which it’s chiefly used to watch vast numbers of other people dancing while we’re on the toilet.