Feb 7, 2024
Cardiac Arrests Linked to Drug ODs Are Killing the Healthy Young
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in category: biotech/medical
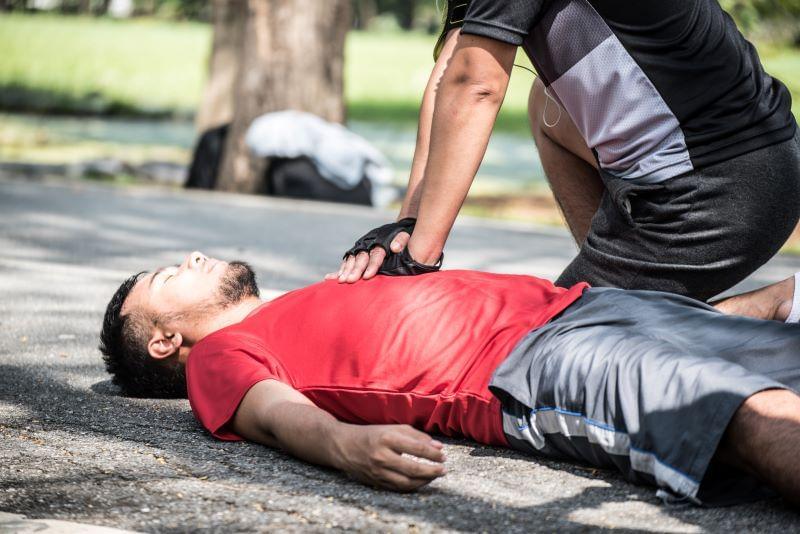
THURSDAY, Feb. 1, 2024 (HealthDay News) — Drug overdoses resulting in cardiac arrest occur most often among young adults, a new study finds.
People tend to have OD-related cardiac arrests at an average age of 39, compared to an average age of 64 for those suffering cardiac arrests not related to opioids, results show.
“Many communities face ongoing challenges with increases in drug overdoses, which tend to affect a younger, healthier population,” said lead researcher Aditya Shekhar, a medical student at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City.