Aug 18, 2023
UCLA Researchers Introduce GedankenNet: A Self-Supervised AI Model That Learns From Physics Laws and Thought Experiments Advancing Computational Imaging
Posted by Dan Breeden in categories: biotech/medical, holograms, information science, robotics/AI
Recent advancements in deep learning have significantly impacted computational imaging, microscopy, and holography-related fields. These technologies have applications in diverse areas, such as biomedical imaging, sensing, diagnostics, and 3D displays. Deep learning models have demonstrated remarkable flexibility and effectiveness in tasks like image translation, enhancement, super-resolution, denoising, and virtual staining. They have been successfully applied across various imaging modalities, including bright-field and fluorescence microscopy; deep learning’s integration is reshaping our understanding and capabilities in visualizing the intricate world at microscopic scales.
In computational imaging, prevailing techniques predominantly employ supervised learning models, necessitating substantial datasets with annotations or ground-truth experimental images. These models often rely on labeled training data acquired through various methods, such as classical algorithms or registered image pairs from different imaging modalities. However, these approaches have limitations, including the laborious acquisition, alignment, and preprocessing of training images and the potential introduction of inference bias. Despite efforts to address these challenges through unsupervised and self-supervised learning, the dependence on experimental measurements or sample labels persists. While some attempts have used labeled simulated data for training, accurately representing experimental sample distributions remains complex and requires prior knowledge of sample features and imaging setups.
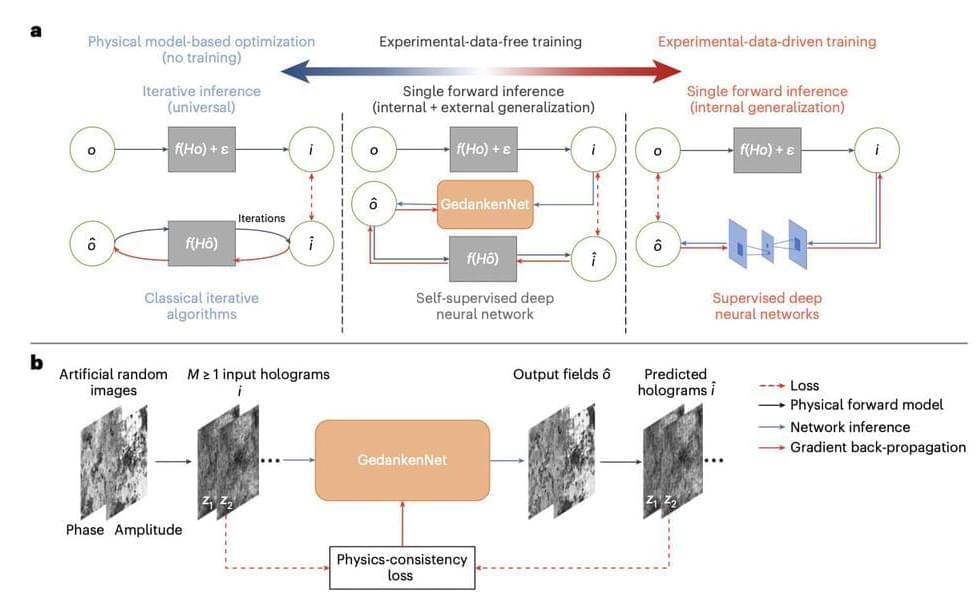
To address these inherent issues, researchers from the UCLA Samueli School of Engineering introduced an innovative approach named GedankenNet, which, on the other hand, presents a revolutionary self-supervised learning framework. This approach eliminates the need for labeled or experimental training data and any resemblance to real-world samples. By training based on physics consistency and artificial random images, GedankenNet overcomes the challenges posed by existing methods. It establishes a new paradigm in hologram reconstruction, offering a promising solution to the limitations of supervised learning approaches commonly utilized in various microscopy, holography, and computational imaging tasks.