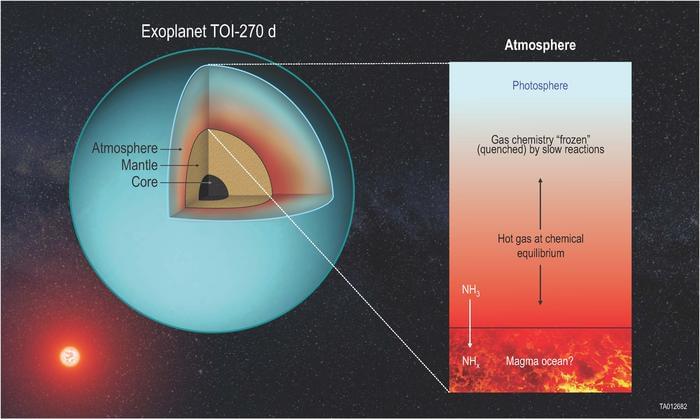
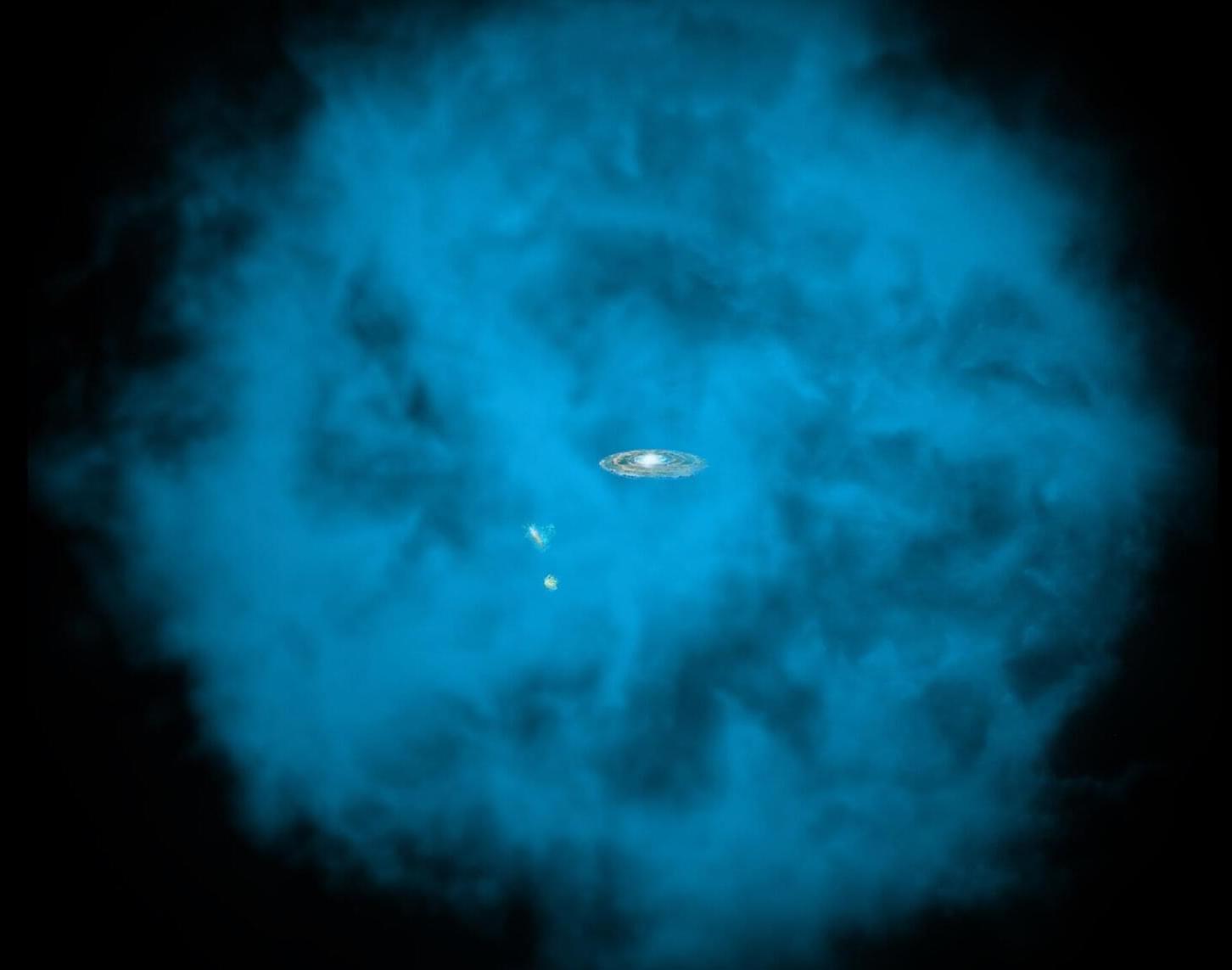
Join to get access to perks:
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCmgh6UWmZuJmHZZIGwISCug/join.
Astronomers analyzing Webb’s data have found that early galaxies seem to favor a particular spin direction—an observation that defies the Cosmological Principle. If confirmed, this could suggest that the universe was born with a fundamental rotation, pointing toward radical theories like black hole cosmology.
But this is just the beginning. The telescope has also spotted galaxies forming far earlier than they should have, some potentially dating back to just 168 million years after the Big Bang. These findings contradict existing models of cosmic evolution, raising the possibility that our understanding of time, expansion, and even reality itself may be flawed.
Adding to the mystery, supermassive black holes have been detected in the early universe, defying expectations of how they should form. Could they be remnants of a previous cosmic cycle? Some researchers are now revisiting the Cyclical Universe Theory, which suggests our universe may be part of an infinite loop of creation and destruction.
With every new revelation, JWST is not just answering questions—it’s creating new ones. Are we on the verge of a fundamental shift in physics, or is there a simpler explanation we have yet to uncover?
The James Webb Space Telescope has uncovered some of the most perplexing discoveries in modern astronomy, challenging everything we thought we knew about the cosmos. From galaxies that appear too massive and too developed for their age to a potential imbalance in galactic rotation, these findings are shaking the foundations of the Big Bang model. Could our universe itself have been born inside a black hole?