Mar 18, 2024
Unlocking the Future of Microelectronics With Argonne’s Redox Gating Breakthrough
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: energy, quantum physics
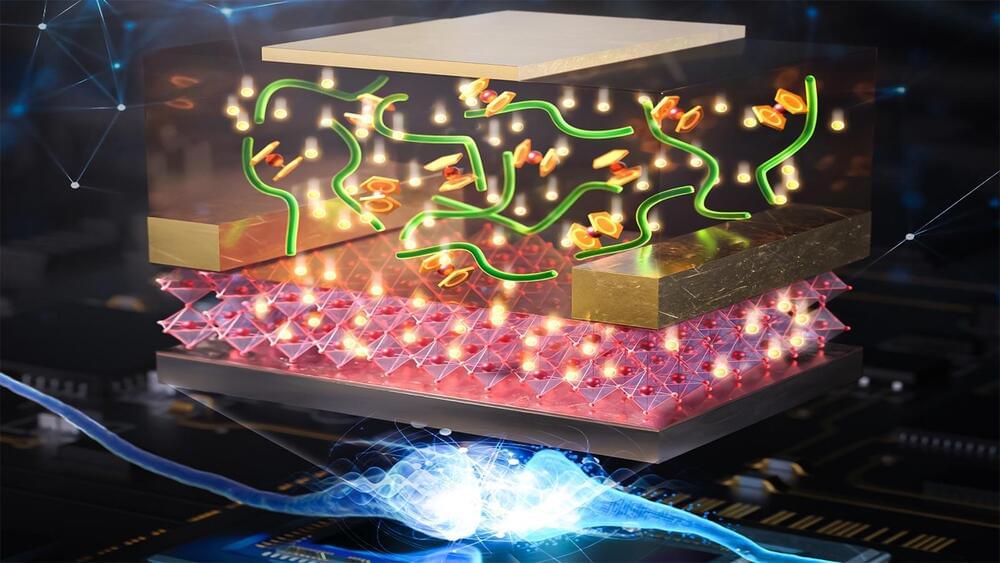
Argonne researchers pioneer “redox gating” — a new way to precisely modulate electron flow.
Breakthrough could help lead to the development of new low-power semiconductors or quantum devices.
As the integrated circuits that power our electronic devices get more powerful, they are also getting smaller. This trend of microelectronics has only accelerated in recent years as scientists try to fit increasingly more semiconducting components on a chip.