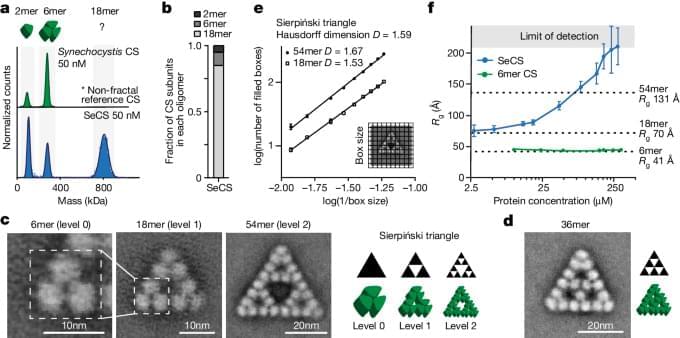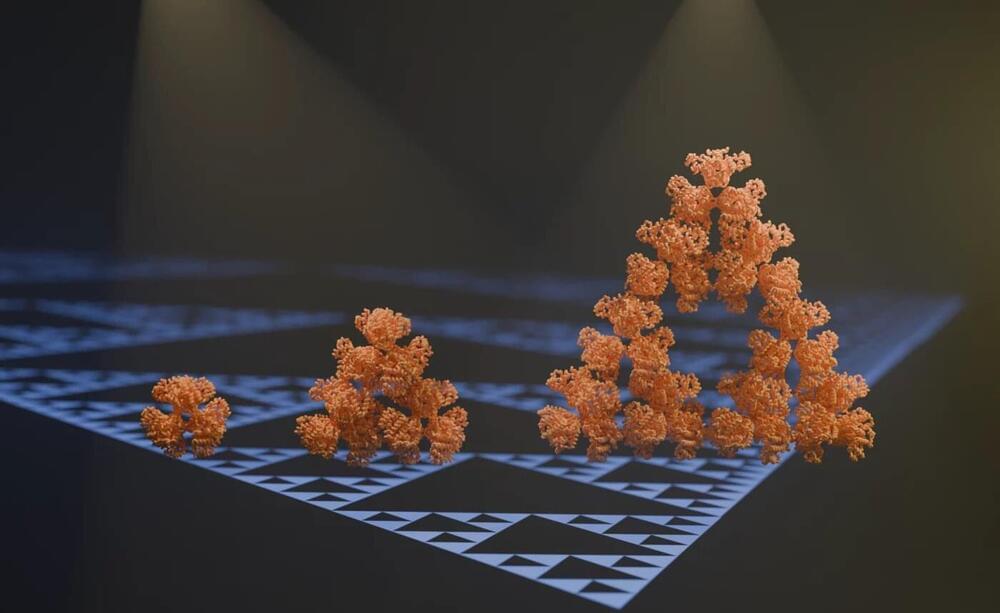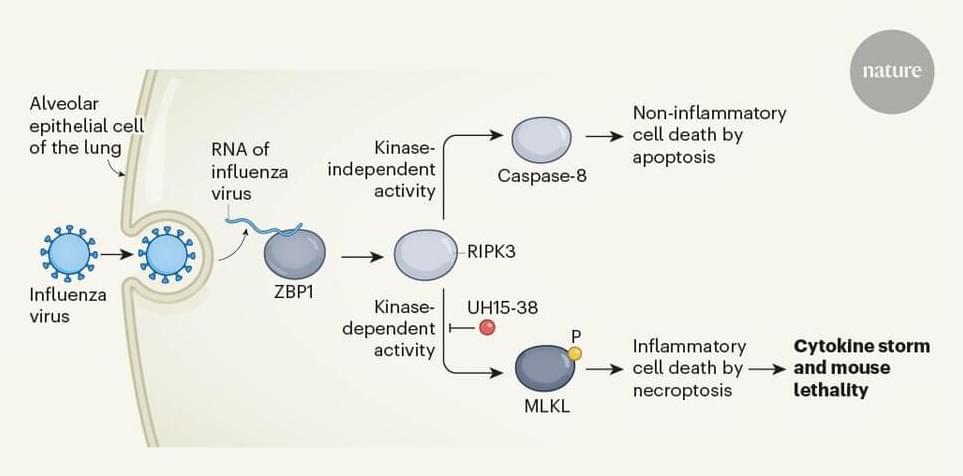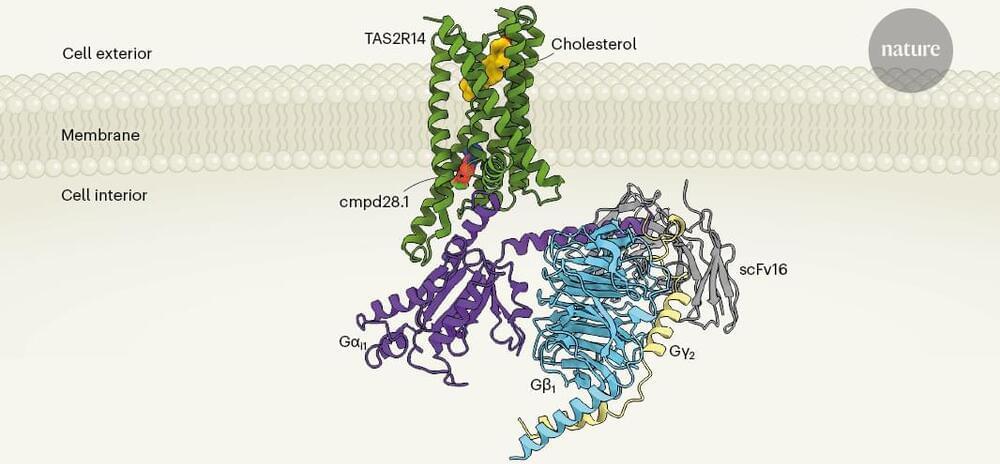
In this weeks continuation article of Dark Energy and what it is, we will be looking at Quintessence: which could be what dark matter is made of.
Quintessence. It is a “time-evolving and spatially dependent form of energy with negative pressure sufficient to drive the accelerating expansion” (Cladwell R.R. and Steinhardt P.J., 2000a, para 41).
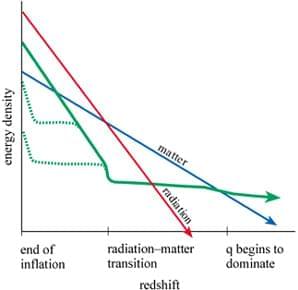
Since it has negative pressure, it also has negative gravity. This negative gravity could explain the expansion of the universe. There are many models to describe quintessence, the simplest being, the fact that quintessence might be a quantum field with very long wavelength stretching across the universe. Negative gravity arises in this field by the negative pressure, and we can calculate the pressure by subtracting the Kinetic and Potential energies of the rate of oscillations in the field strength. This model is also successful, because it explains how the density of Dark Energy, or quintessence, changed over time, and fits in with the idea that dark energy must have been insignificant during the early universe to allow the large scale structures to form.