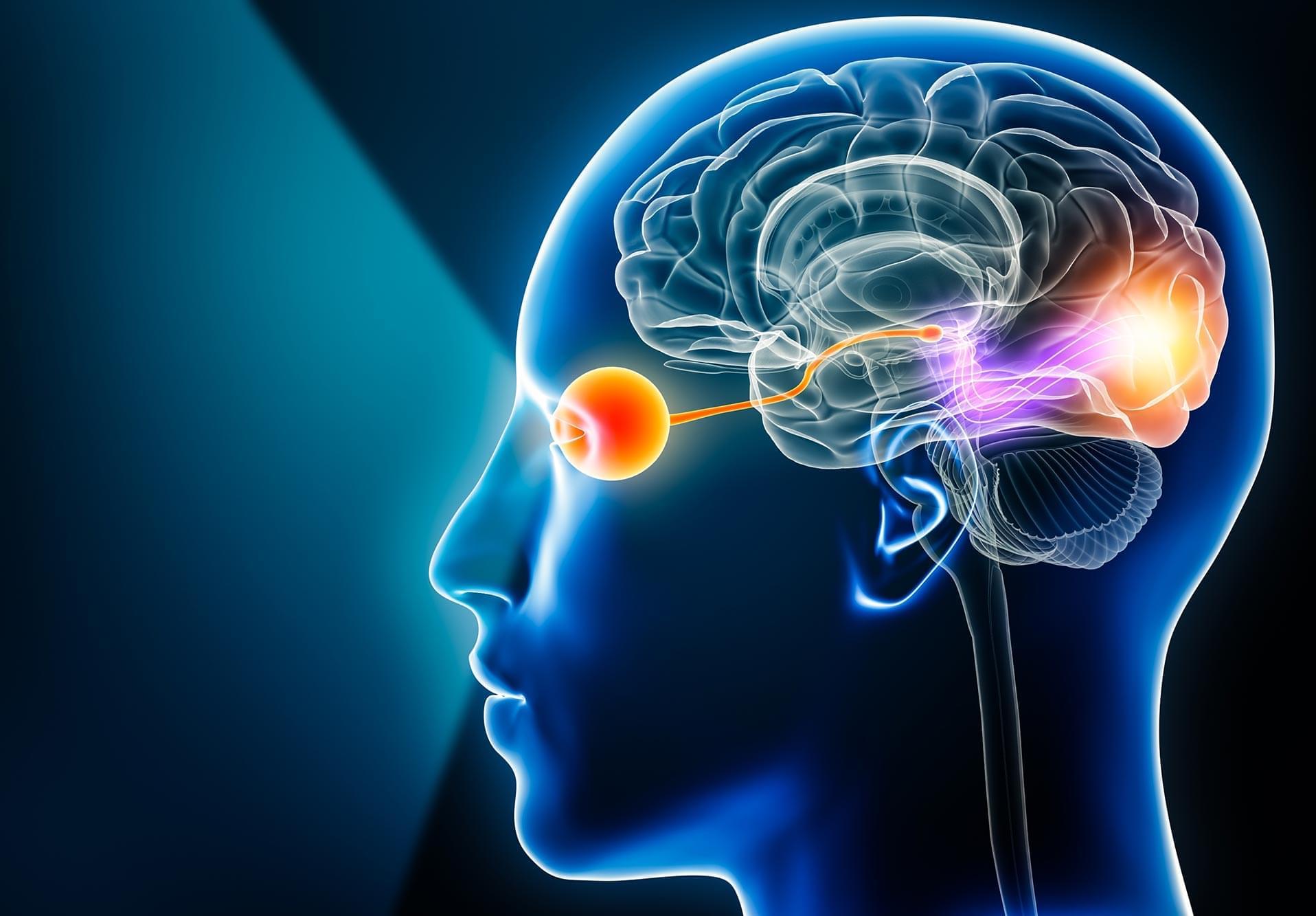
Your ability to notice what matters visually comes from an ancient brain system over 500 million years old.

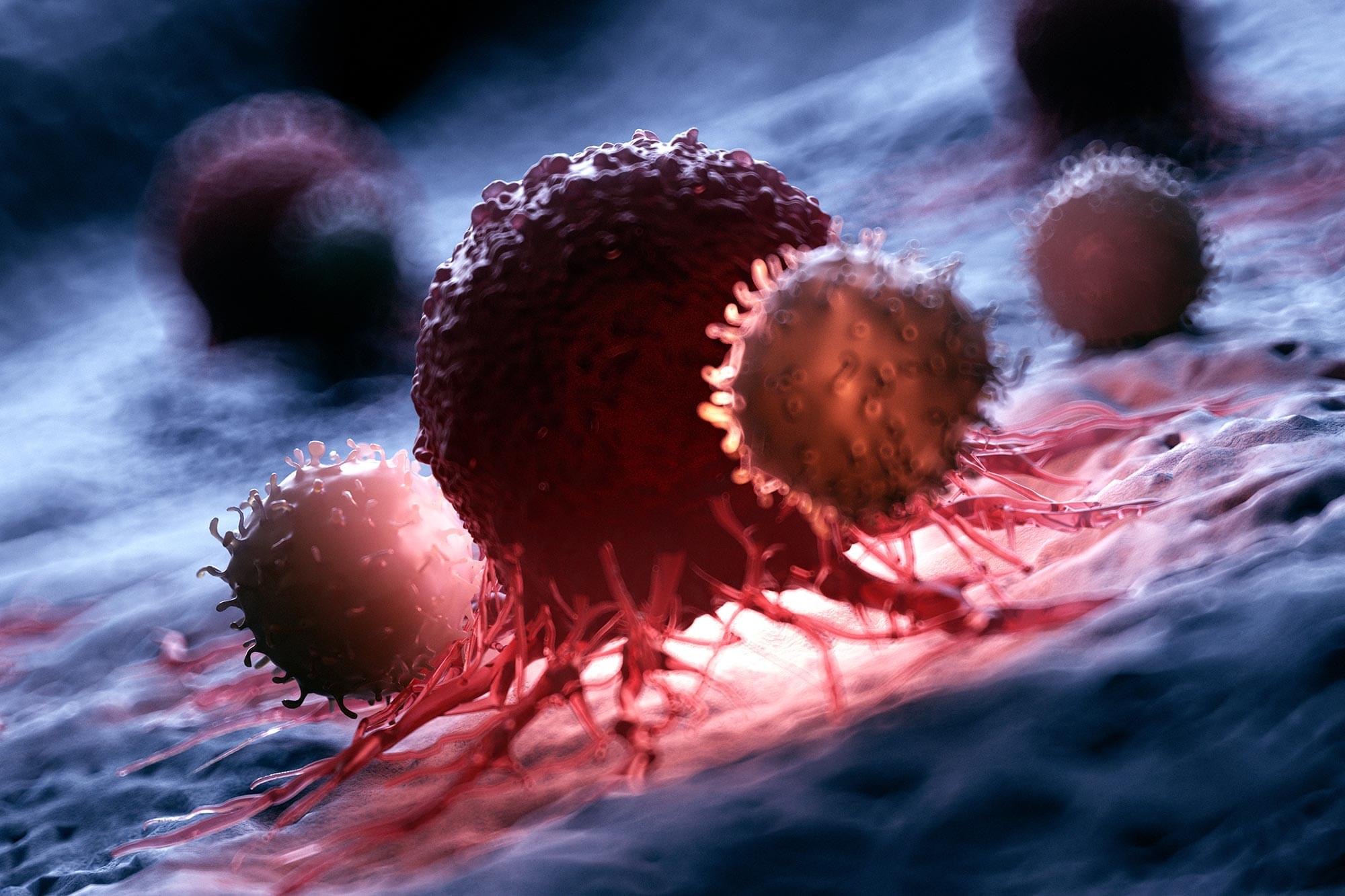
Researchers at the University of Southampton have identified a new strategy that could strengthen how the immune system responds to cancer.
Reporting their findings in Nature Communications, the scientists describe the use of specially engineered antibodies designed to more effectively switch on T cells that are capable of destroying cancer cells.
These antibodies act by ‘grabbing’ and ‘clustering’ several immune cell receptors at once, increasing the strength of the signal that instructs T cells to attack tumors.
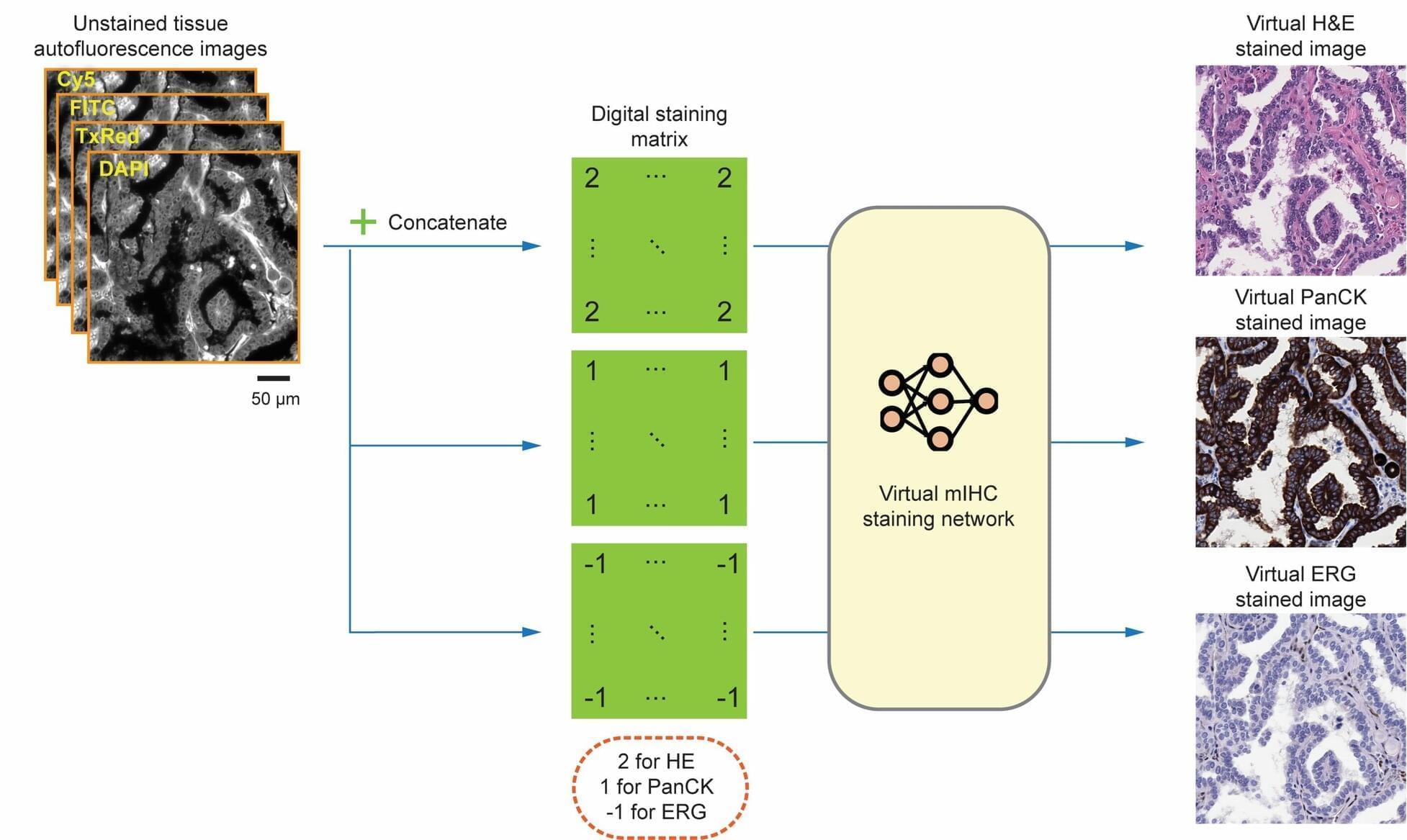
Researchers at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), in collaboration with pathologists from Hadassah Hebrew University Medical Center and the University of Southern California, have developed a deep learning–based method that can digitally generate multiple immunohistochemical stains from a single, unstained tissue section.
The work is published in the journal BME Frontiers.
The approach enables accurate assessment of vascular invasion—a key indicator of cancer aggressiveness—without the need for conventional chemical staining procedures.
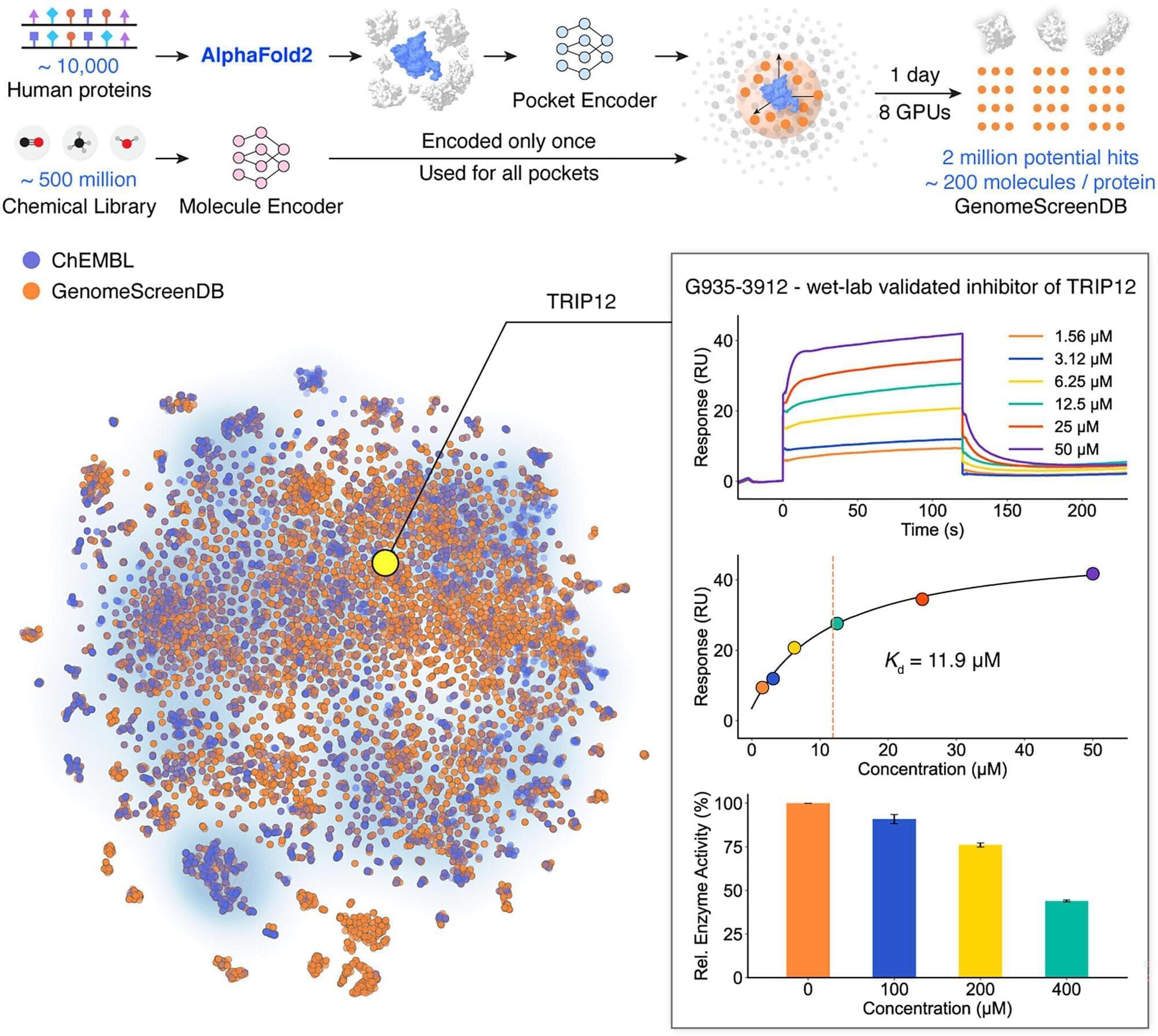
Researchers in China have unveiled a new AI framework that could accelerate the discovery of new medicines. DrugCLIP can scan millions of potential drug compounds against thousands of protein targets in just a few hours—ten million times faster than current virtual screening methods.
Typically, when scientists develop new medicines, they use complex computer simulations to fit a 3D drug molecule into a protein pocket. This indicates that it is likely to interact with the protein’s binding site and function. However, the process is incredibly time-consuming and expensive.
Now to see where it goes.

Editorial: Proposals to apply clinician-style licensure to AI tools may allow adaptive oversight as AI models grow more complex. Implementation challenges include defining responsible parties and ensuring adequate regulatory expertise.
In this issue of JAMA Internal Medicine, Bressman et al1 propose a clever thought experiment: what if medical tools incorporating artificial intelligence (AI) were licensed as advanced practitioners, rather than solely regulated by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)? This strategy seeks to provide an alternative or complement to FDA clearance in regulation of medical software incorporating AI. The authors suggest this may allow the necessary flexibility to keep up with the pace of change in AI, the breadth of applications for a given model, and the need to ensure that such tools demonstrate clinical utility.2
Many instances of more specific, single-purpose AI applications can be adequately regulated within existing frameworks. However, generative AI may be deployed in a wide range of contexts, and models may continue to develop over time. Because these models are probabilistic rather than deterministic, they may make errors that are analogous to human errors, for example, mistakes due to inadequate knowledge or lapses in judgment. Bressman et al1 argue that an appropriately flexible framework for certification already exists in the form of licensing oversight of advanced practitioners. With this approach, the extent of supervision depends on the particular activity, with some tasks requiring more oversight than others.
The proposal leaves a number of critical details to be resolved. Any AI licensing system will need to be able to evaluate and address a model’s specific potentials for harm before deployment; thus, some central regulation likely will continue to be required. In addition, determining who will take on the responsibility and oversight for decisions and treatment pathways generated by AI, as well as assume the liability for errors or adverse events, remains a thorny question. These considerations are again analogous to those of clinician licensing, but although medical boards are well positioned for licensing, the extent to which a similar approach could be developed with the necessary expertise for AI in medicine remains to be seen.
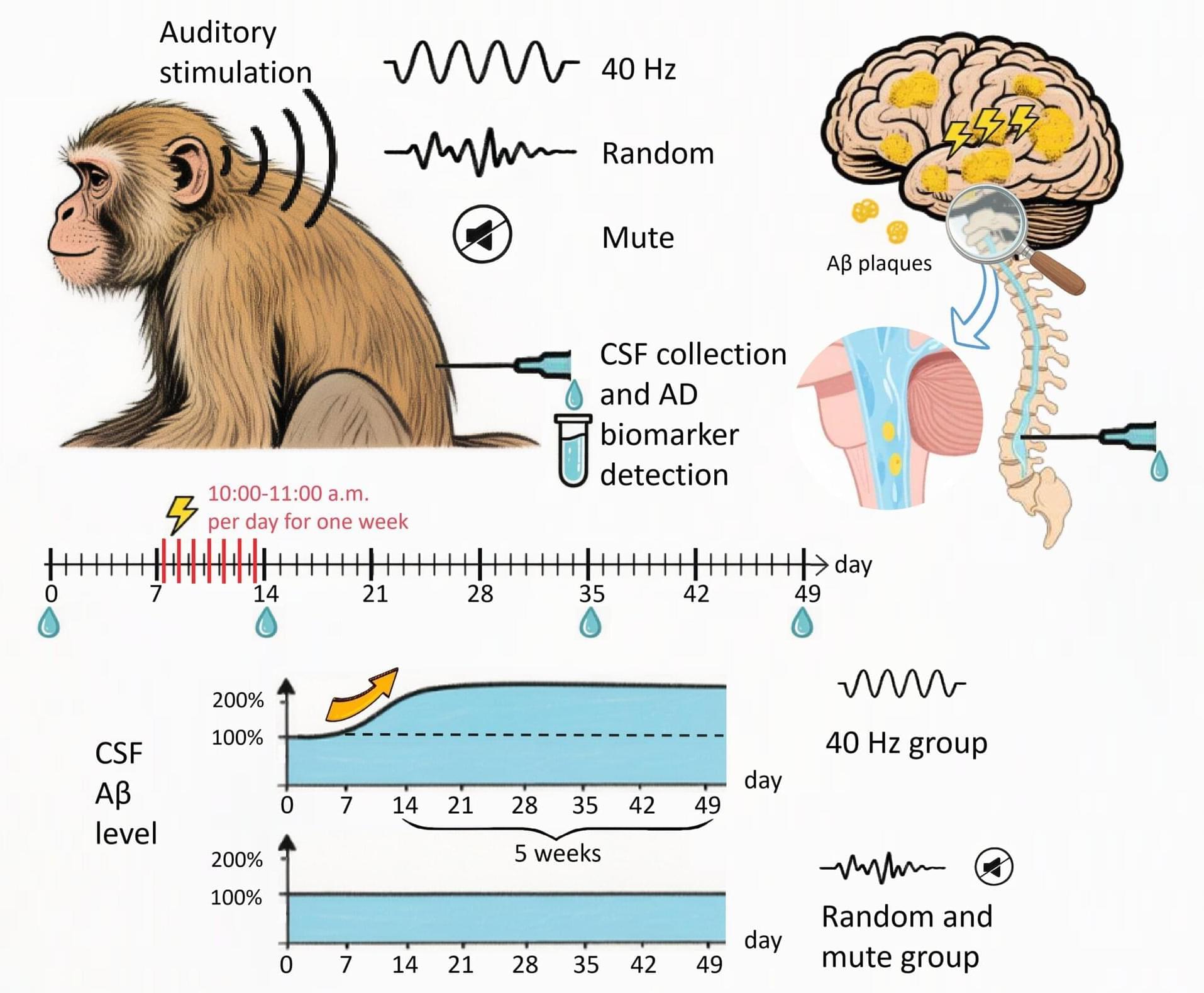
A research team from the Kunming Institute of Zoology (KIZ) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has demonstrated for the first time in non-human primates that auditory stimulation at 40 Hz significantly elevates β-amyloid levels in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of aged rhesus monkeys, with this effect persisting for over five weeks.
The study, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences on January 5, provides the first non-human primate experimental evidence supporting the use of 40-Hz stimulation as a noninvasive physical therapy for Alzheimer’s disease (AD), revealing significant differences between primate and rodent models.
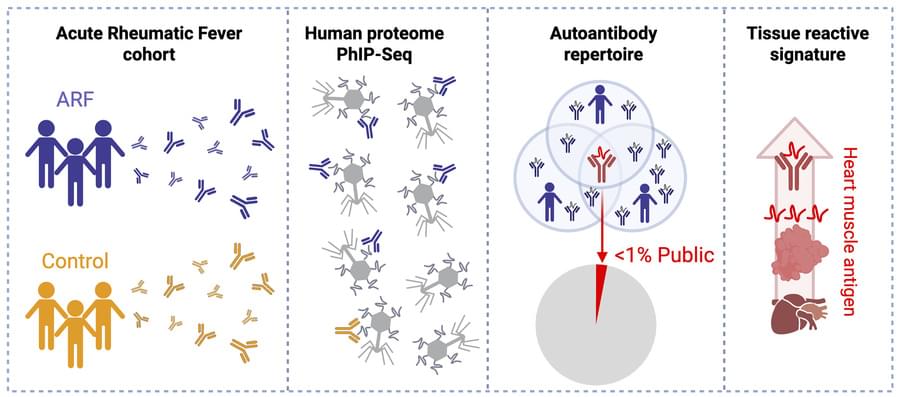
Here, Nicole J. Moreland & team report widespread antibody heterogeneity between cases, yet identify a protein expressed in cardiac muscle as an immunodominant autoantigen with potential as a diagnostic biomarker.
1Department of Molecular Medicine, and.
2Maurice Wilkins Centre for Biodiscovery, The University of Auckland, Auckland, New Zealand.
3Department of Genetics and Genomic Sciences, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, New York, USA.