Betelgeuse’s long-standing mystery has been cracked: a hidden companion star is literally reshaping the giant from the inside out.


Our sun spins on its axis about once every 28 days. Because of that, any active region can be watched from earth for only around two weeks before it turns out of view, then it stays hidden for roughly another two weeks on the far side.
“Fortunately, the Solar Orbiter mission, launched by the European Space Agency (ESA) in 2020, has broadened our perspective,” says Ioannis Kontogiannis, solar physicist at ETH Zurich and the Istituto ricerche solari Aldo e Cele Daccò (IRSOL) in Locarno.
Why 2026 Changes Everything for Tesla, Grok & SpaceX
## Elon Musk’s companies, including Tesla and SpaceX, are expected to experience significant breakthroughs and growth in 2026, driven by advancements in AI, robotics, and space technology.
## Questions to inspire discussion.
Tesla Robotaxi & Cybercab Strategy.
🚖 Q: When will Tesla’s Cybercab production begin and what regulatory hurdle must be cleared first? A: Cybercab production is set to begin on April 1, 2026, but requires federal regulations on autonomous ride-hailing since current rules mandate steering wheels and pedals for non-experimental vehicles.
🚗 Q: How will Tesla’s robotaxis function as an advertising strategy? A: Robotaxis will serve as Tesla’s primary advertising strategy by acting as an Uber-like service that demonstrates the cars’ capabilities and encourages personal ownership, potentially reducing the need for traditional advertising.

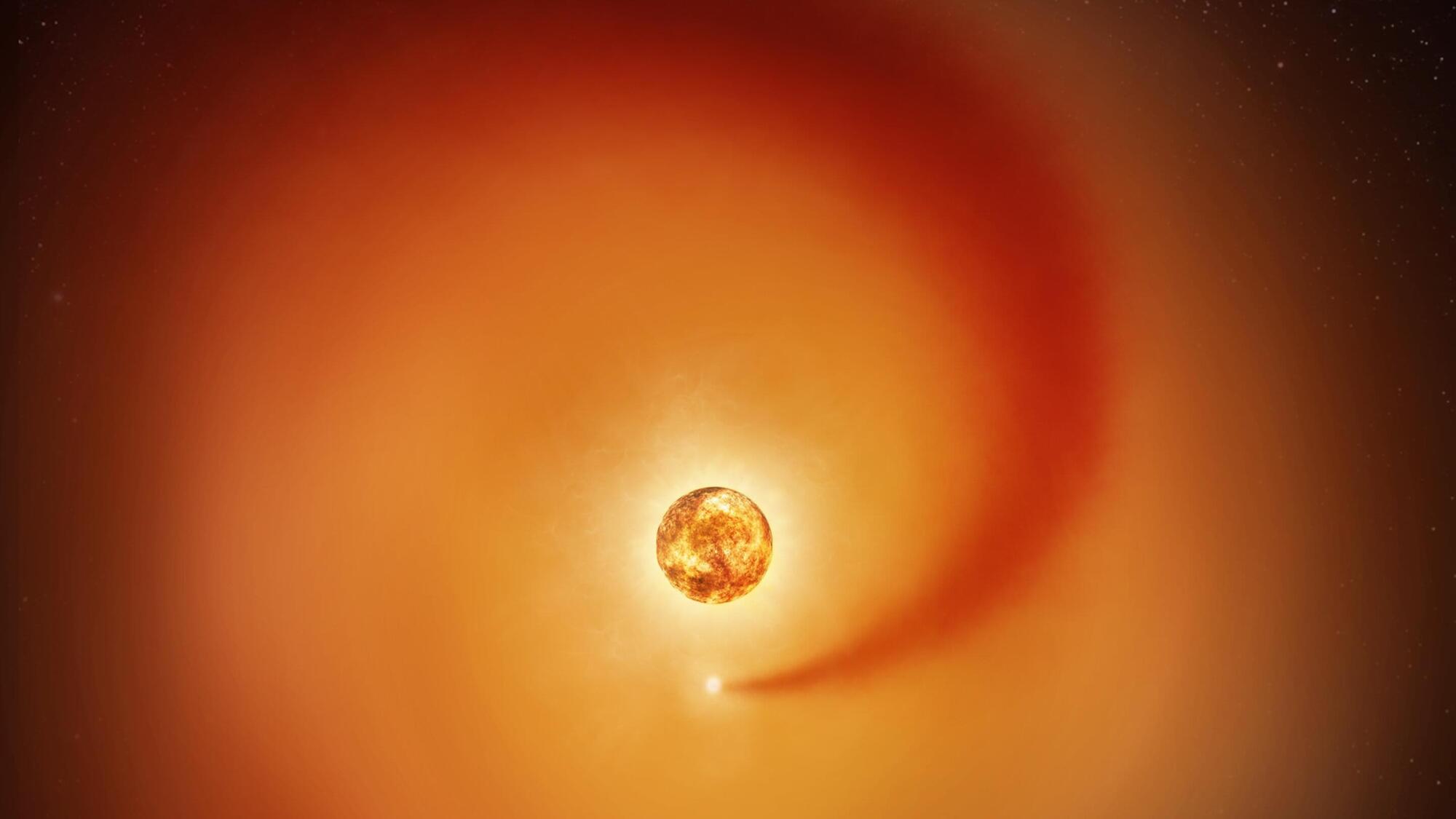
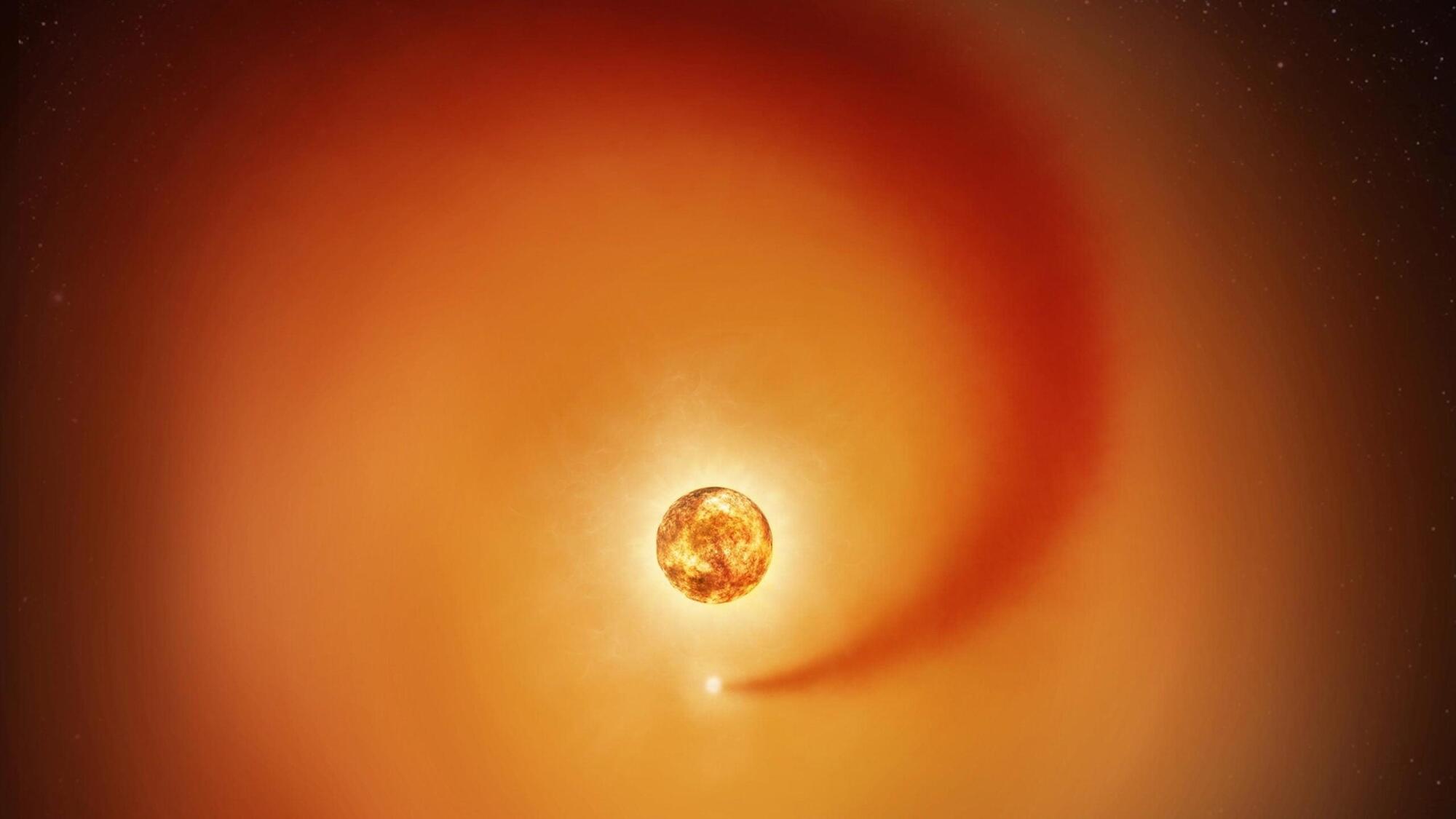
Using new observations from NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope and ground-based observatories, astronomers have tracked the influence of a recently discovered companion star, Siwarha, on the gas around Betelgeuse. The research, by scientists at the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian (CfA), reveals a trail of dense gas swirling through Betelgeuse’s vast, extended atmosphere, shedding light on why the giant star’s brightness and atmosphere have changed in strange and unusual ways.
The results of the new study were presented Monday at a news conference at the 247th meeting of the American Astronomical Society in Phoenix. The paper has been accepted for publication in The Astrophysical Journal and is available on the arXiv preprint server.
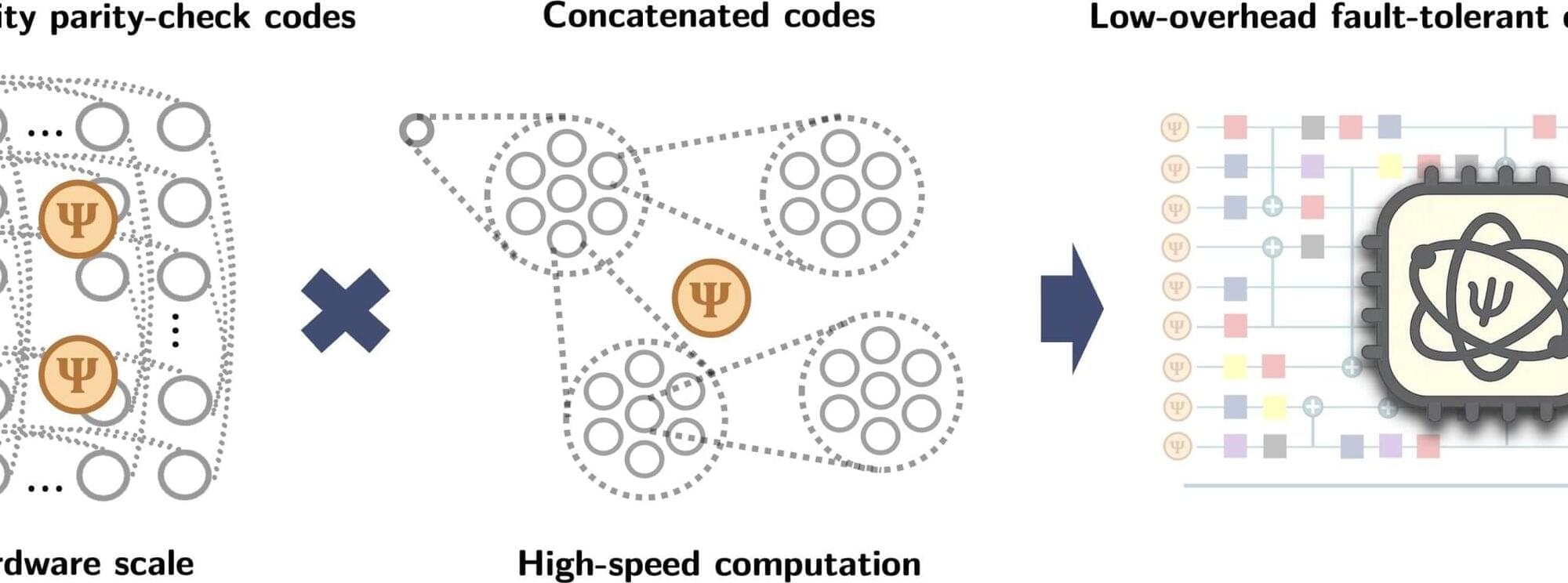
Quantum computers, systems that process information leveraging quantum mechanical effects, could soon outperform classical computers on some complex computational problems. These computers rely on qubits, units of quantum information that share states with each other via a quantum mechanical effect known as entanglement.
Qubits are highly susceptible to noise in their surroundings, which can disrupt their quantum states and lead to computation errors. Quantum engineers have thus been trying to devise effective strategies to achieve fault-tolerant quantum computation, or in other words, to correct errors that arise when quantum computers process information.
Existing approaches work either by reducing the extra number of physical qubits needed per logical qubit (i.e., space overhead) or by reducing the number of physical operations needed to perform a single logical operation (i.e., time overhead). Effectively tackling both these goals together, which would enable more scalable systems and faster computations, has so far proved challenging.
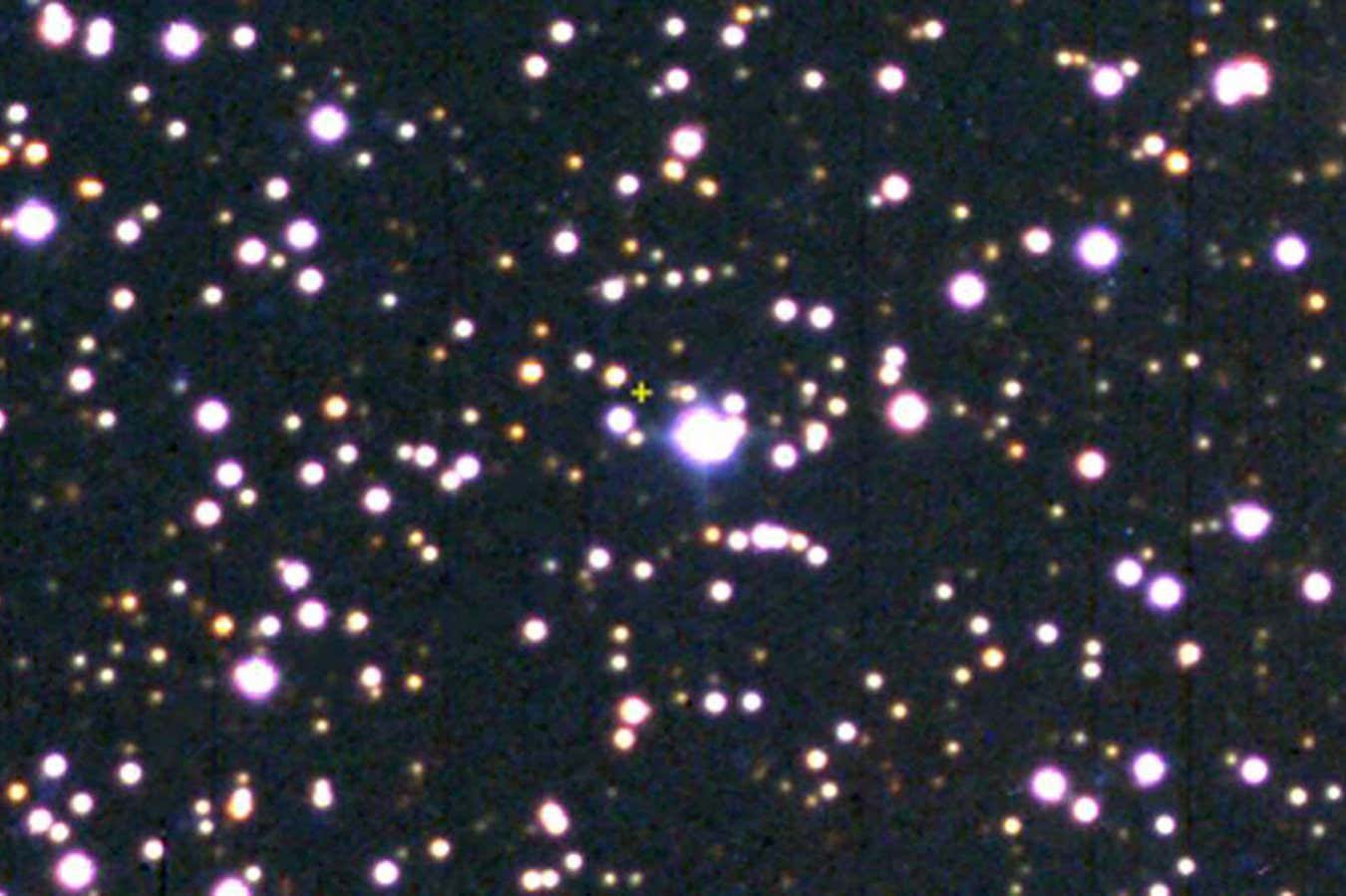




Not all planets are lucky enough to live in a neighborhood like our Solar System – some are doomed to roam the cosmos alone. Astronomers have now, for the first time, measured the mass of, and distance to, one of these lonely worlds.
The planet packs about a fifth of the mass of Jupiter, and is located a little under 10,000 light-years away from Earth, towards the center of our galaxy. That size suggests it most likely formed as part of a planetary system, before being exiled by a game of gravitational billiards.
Related: Record-Smashing Rogue Planet Caught Growing at 6 Billion Tons Per Second.