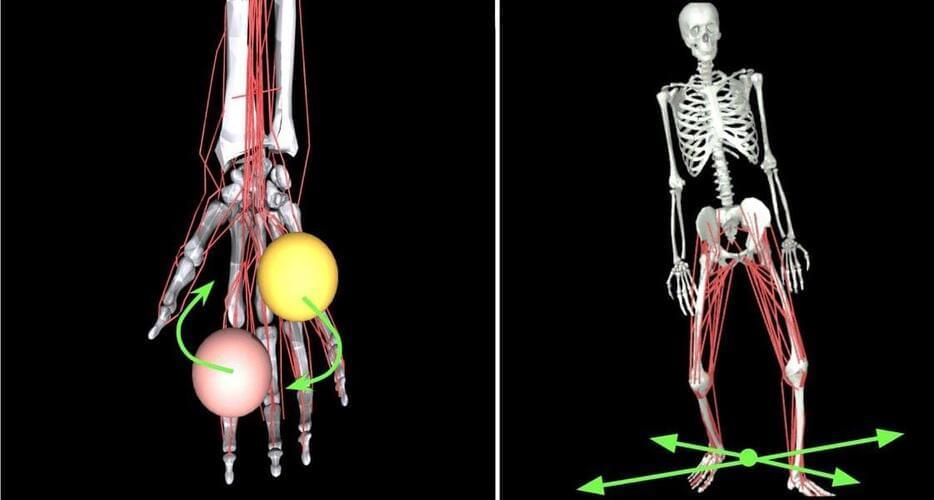
Similarly, allowing the MyoLegs to flail around for a while in a seemingly aimless fashion gave them better performance with locomotion tasks, as the researchers described in another paper presented at the recent Robotics Science and Systems meeting. Vittorio Caggiano, a Meta researcher on the project who has a background in both AI and neuroscience, says that scientists in the fields of neuroscience and biomechanics are learning from the MyoSuite work. “This fundamental knowledge [of how motor control works] is very generalizable to other systems,” he says. “Once they understand the fundamental mechanics, then they can apply those principles to other areas.”
This year, MyoChallenge 2023 (which will also culminate at the NeurIPS meeting in December) requires teams to use the MyoArm to pick up, manipulate, and accurately place common household objects and to use the MyoLegs to either pursue or evade an opponent in a game of tag.
Emo Todorov, an associate professor of computer science and engineering at the University of Washington, has worked on similar biomechanical models as part of the popular Mujoco physics simulator. (Todorov was not involved with the current Meta research but did oversee Kumar’s doctoral work some years back.) He says that MyoSuite’s focus on learning general representations means that control strategies can be useful for “a whole family of tasks.” He notes that their generalized control strategies are analogous to the neuroscience principle of muscle synergies, in which the nervous system activates groups of muscles at once to build up to larger gestures, thus reducing the computational burden of movement. “MyoSuite is able to construct such representations from first principles,” Todorov says.