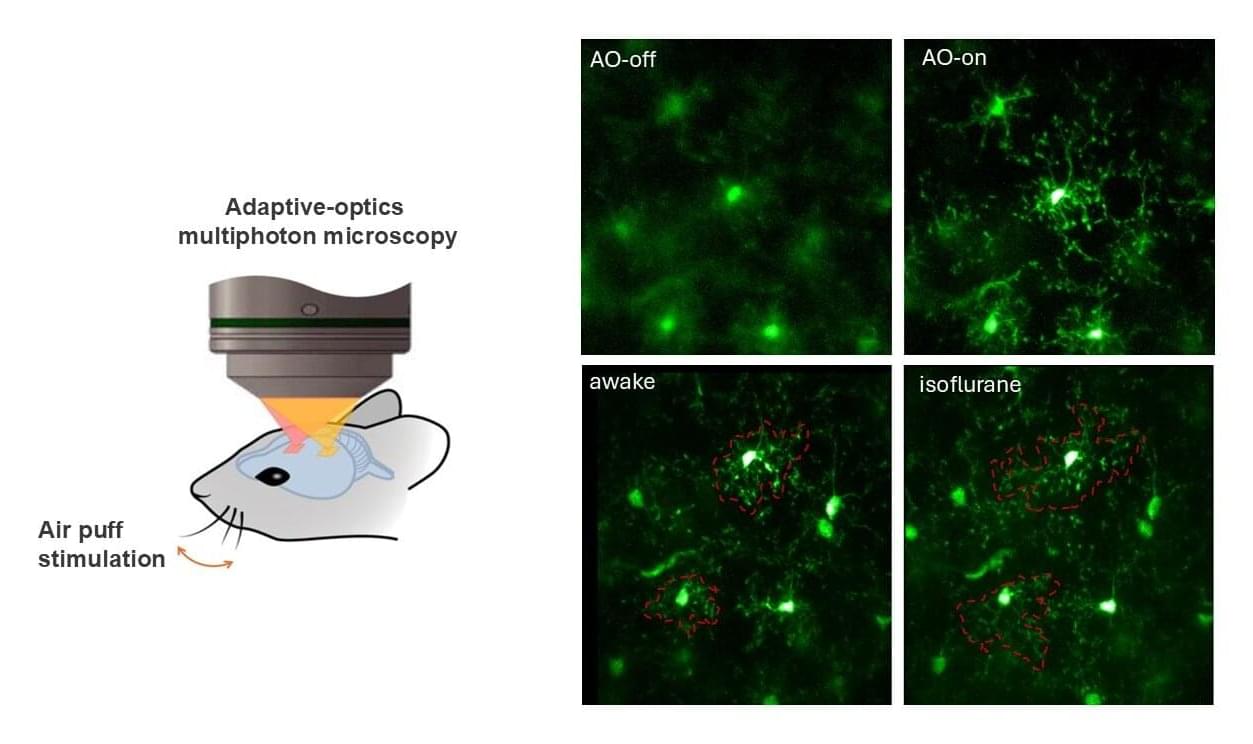
Alzheimer’s disease (AD), the leading cause of dementia, affects nearly 40 million individuals globally, resulting in a gradual loss of memory and independence. Despite extensive research over the past decades, no treatments have been found that can halt or reverse the progression of this devastating disease.
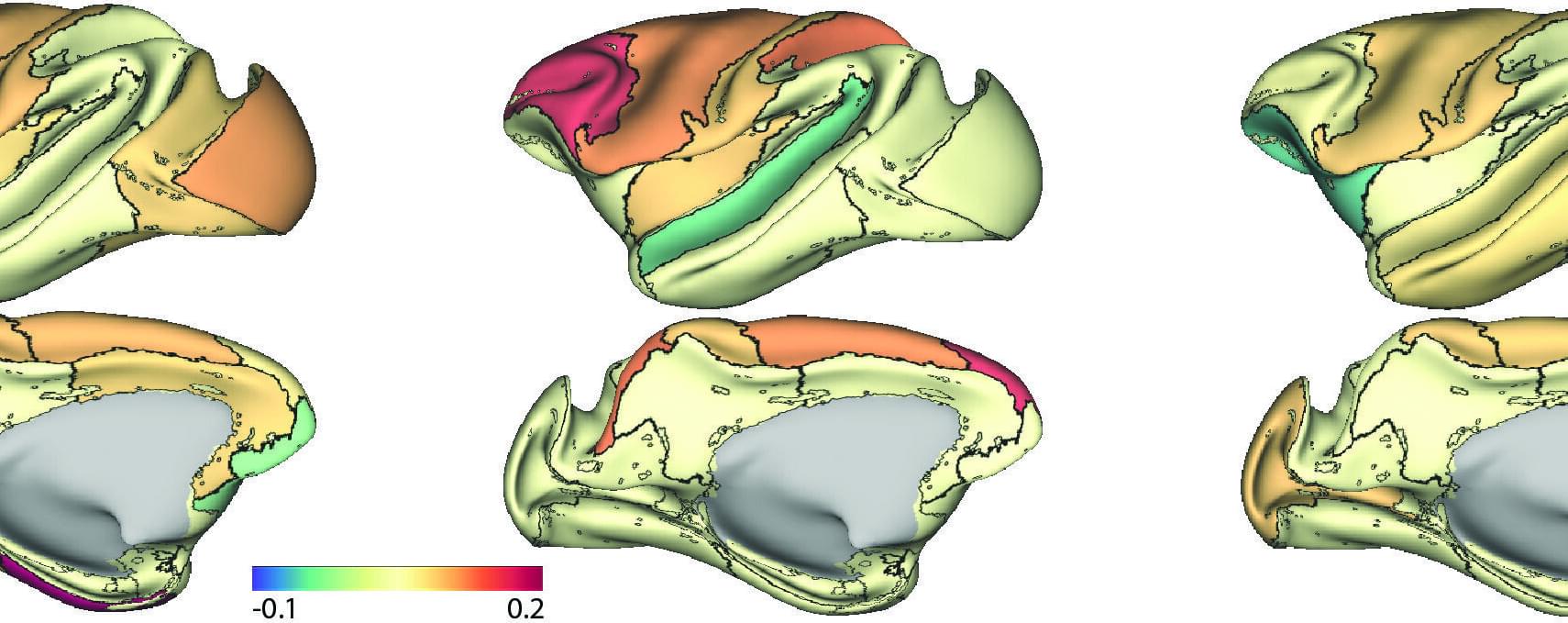
In AD, a major contributor to neuronal dysfunction is the protein tau. Tau typically plays a crucial role in keeping the internal structure of neurons stable, much like train tracks help trains stay on course. However, in some diseases, tau undergoes abnormal modifications and starts to aggregate, disrupting this transport system, thus leading to neuronal damage and subsequent memory loss.
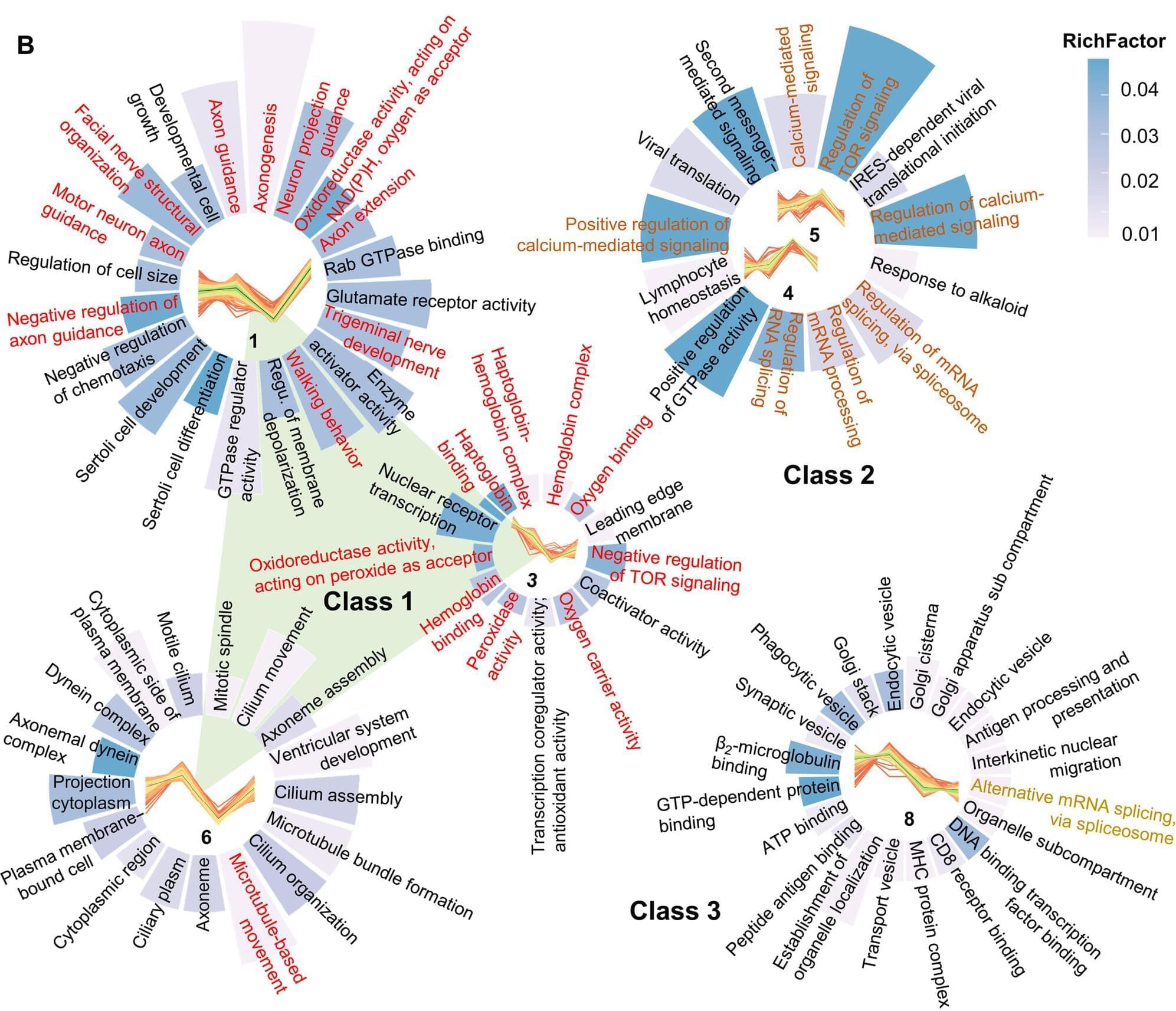
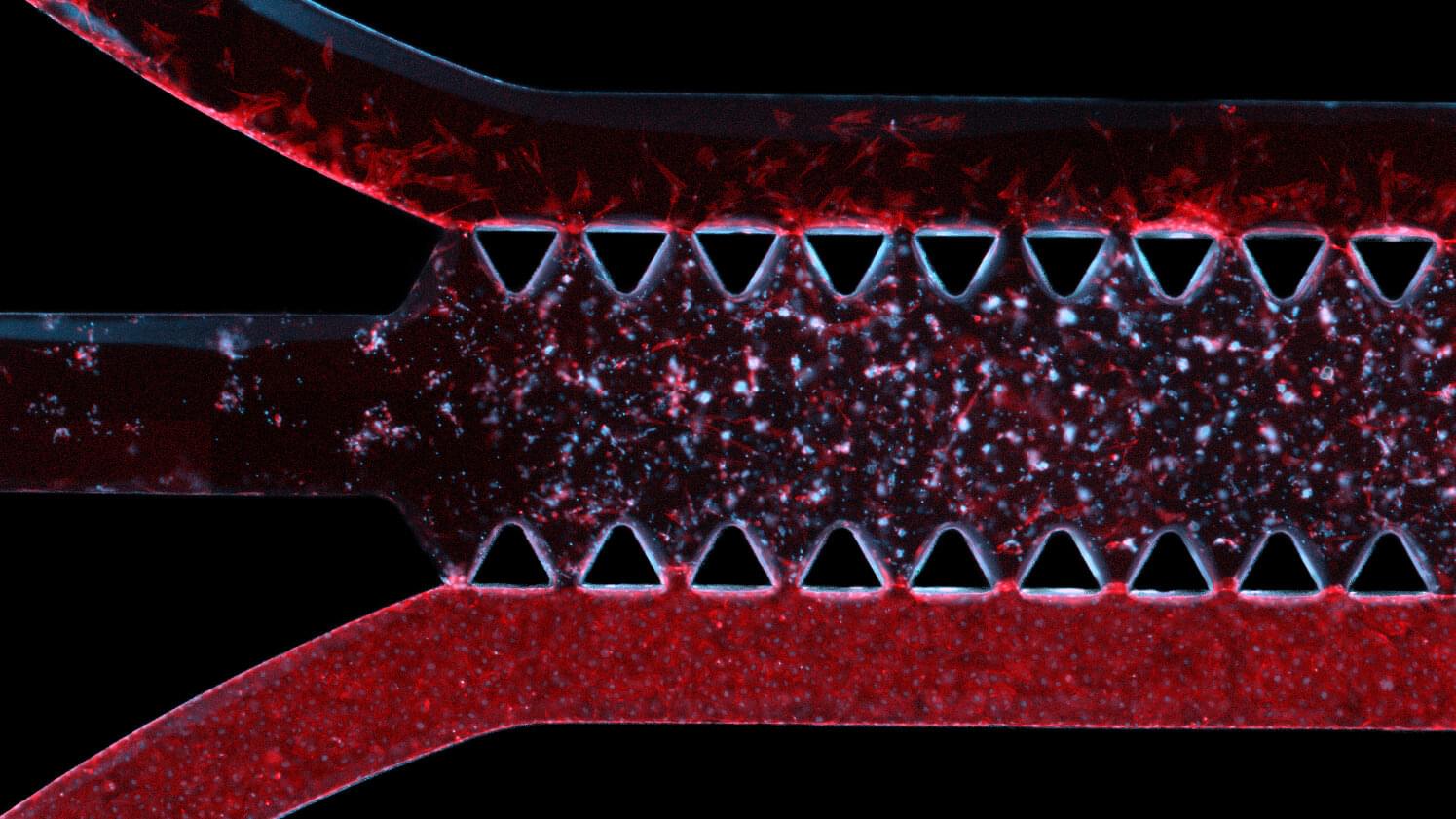
An international team of researchers has reported a new mechanism by which boosting the natural metabolite NAD⁺ can protect the brain from the degeneration associated with AD. Their paper, titled “NAD⁺ reverses Alzheimer’s neurological deficits via regulating differential alternative RNA splicing of EVA1C,” is published in Science Advances.