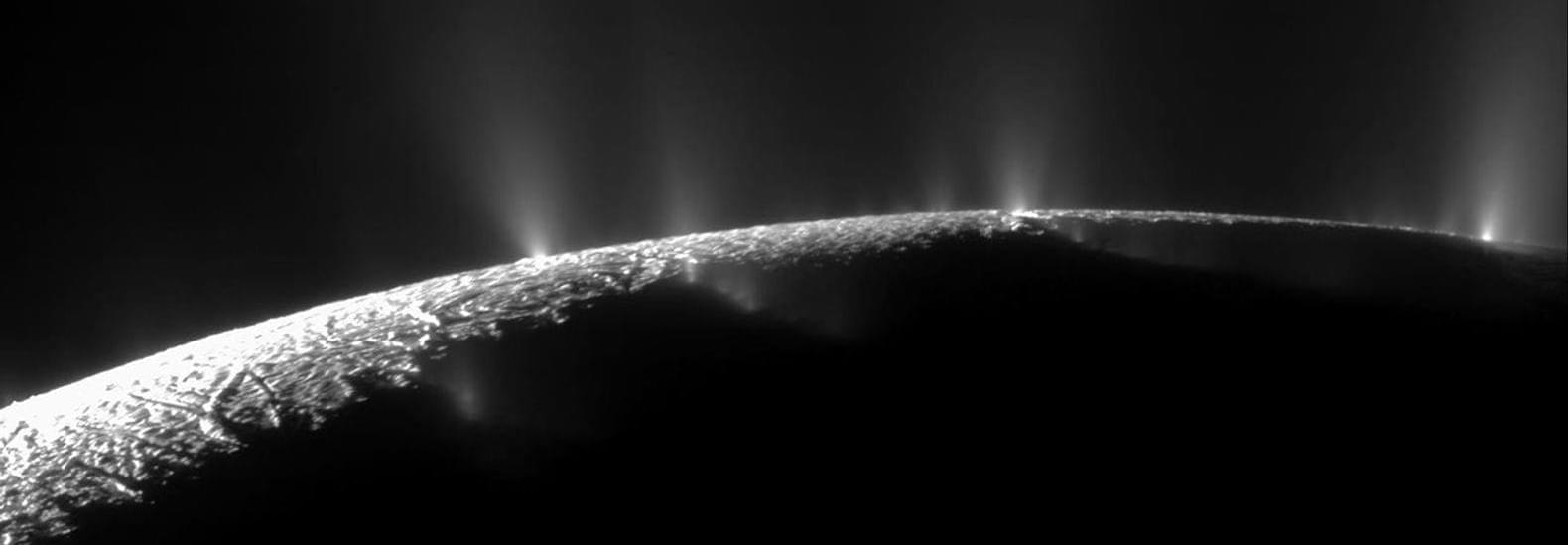
“The mass flow rates from Enceladus are between 20 to 40 percent lower than what you find in the scientific literature,” said Dr. Arnaud Mahieux.
How much ice is Saturn’s moon, Enceladus, losing to space when it discharges its interior ocean? This is what a recent study published in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets hopes to address as a team of scientists investigated whether Enceladus’ plume environments, including discharge rates, temperatures, and ice particle sizes could be determined strictly from observational data. This study has the potential to help scientists develop new methods for exploring icy bodies, especially those like Enceladus that could harbor life within its liquid water ocean.
For the study, the researchers used a series of computer models to analyze data obtained from NASA’s now-retired Cassini spacecraft, which intentionally burned up in Saturn’s atmosphere in 2017 after running low on fuel. This was done to avoid potentially contaminating moons like Enceladus with microbes from Earth and interfere with potential life there. During its journey at Saturn and its many moons, Cassino both discovered and flew through the plumes of Enceladus, which are at the moon’s south pole and emit large quantities of water ice and other substances into space from its subsurface liquid water ocean. It’s the amount of water and ice these plumes discharge that have intrigued scientists, and the results were surprising.