Super-agers have the memory and focus on people decades younger. A neurologist said he’s on track to be one with a brain-boosting daily routine.


Dr. Cody shows takes a look Graph Theory related to Brain Circuitry and Neurofeedback.
►►►Muse Headband 15% off Discount (applied at checkout): https://choosemuse.com/codyrallmd.
►►►Want to connect with a Myndlift Neurocoach? $60 off with this link: https://signup.myndlift.com/subscription. Enter CODYRALL at checkout.
►►► GET YOUR FREE MEDITATION GUIDE HERE: https://bit.ly/2XIRDNa.
►►► INSTAGRAM (Behind The Scenes with Cody Rall MD): https://www.instagram.com/codyrall_techforpsych/
Cody Rall, M.D., is a United States Navy trained Psychiatrist who specializes in neurotechnology wearables. He is a co-founder of Stanford Brainstorm, the world’s first academic laboratory dedicated to transforming brain health through entrepreneurship.
Dr. Rall also served as a board member of the psychiatry innovation lab, an annual national competition at the American Psychiatric Association that works as an incubator for groups developing technological solutions to problems in mental health care. He is the founder of Techforpsych, a media and relations company that covers advancements in technology related to neuroscience.
To apply for Dr. Cody’s Brain Circuit Training program head to this link: https://www.techforpsych.com/coaching

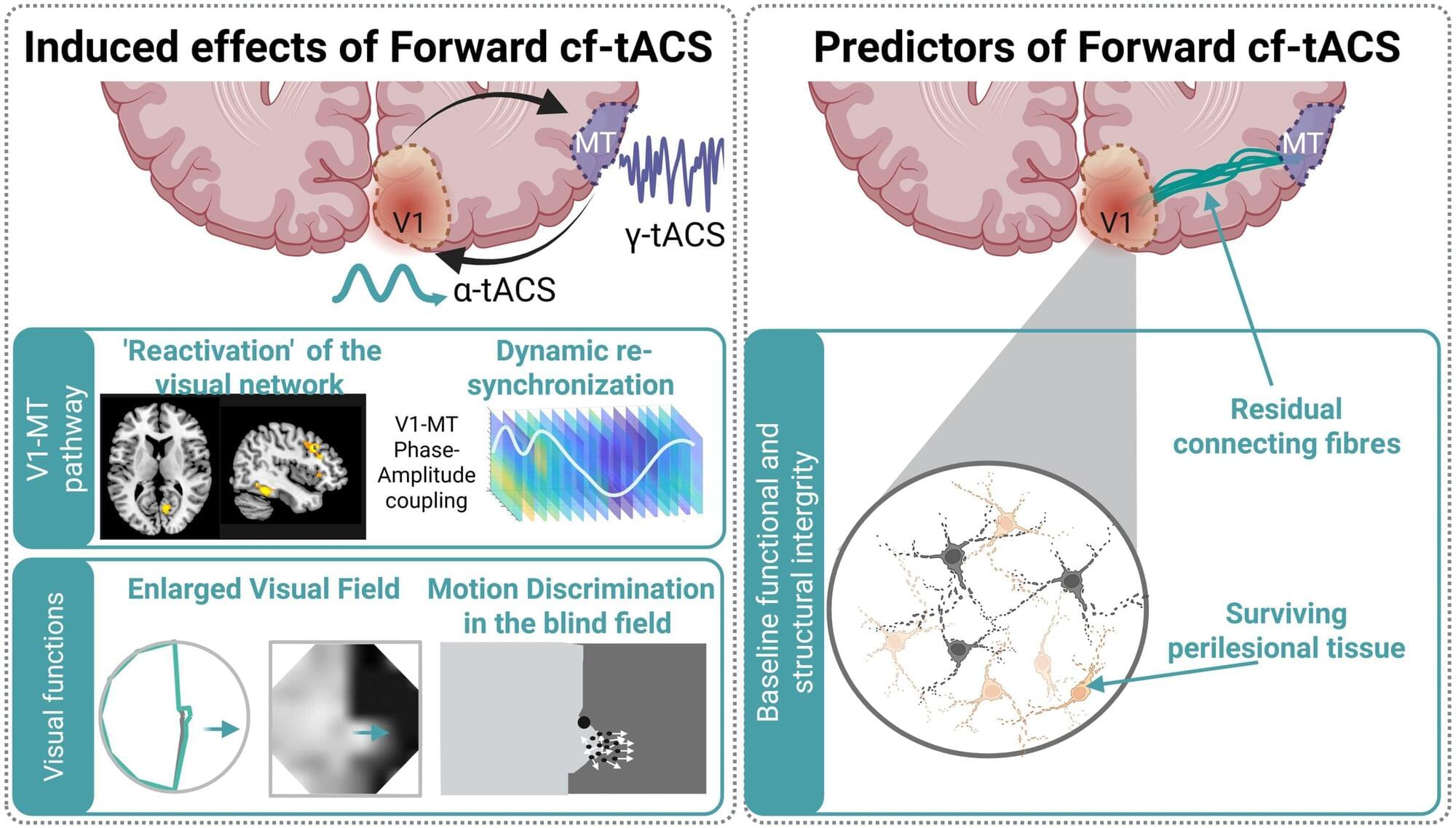
Scientists at EPFL have developed an innovative, non-invasive brain stimulation therapy to significantly improve visual function in stroke patients who have suffered vision loss following a stroke. The approach could offer a more efficient and faster way to regain visual function in such cases.
Each year, thousands of stroke survivors are left with hemianopia, a condition that causes loss of half of their visual field (the “vertical midline”). Hemianopia severely affects daily activities such as reading, driving, or just walking through a crowded space.
There are currently no treatments that can restore lost visual function in hemianopia satisfactorily. Most available options focus on teaching patients how to adapt to loss of vision rather than recovering it. To achieve some degree of recovery, months of intensive neurorehabilitative training are required for only moderate restoration at best.

When it comes to understanding the mystery of human consciousness, scientists have long sought the hidden mechanism that transforms mere neural firing into the rich experience of thought.
Now, a leading MIT neuroscientist believes he’s found a clue that suggests the brain’s electrical waves don’t just reflect our thoughts, but actually create them.
At the Society for Neuroscience’s annual meeting on November 15, Dr. Earl K. Miller, a professor at MIT’s Picower Institute for Learning and Memory, will unveil a provocative proposal: that cognition and consciousness emerge from the fast, flexible organization of the brain’s cortex—powered by analog computations performed by traveling brain waves.
In other words, the rhythm of the brain may be more than background noise—it may be the very pulse of thought itself.
“The brain uses these oscillatory waves to organize itself,” Dr. Miller said in a press statement. “Cognition is large-scale neural self-organization. The brain has got to organize itself to perform complex behaviors. Brain waves are the patterns of excitation and inhibition that organize the brain, and this leads to consciousness because consciousness is this organized knitting together of the cortex.”
Dr. Miller’s theory revives the concept of analog computation. Unlike digital computers, which rely on discrete binary bits, analog systems process continuous information—waves interacting to produce a vast range of possible values.
Dr. Miller argues that the brain’s natural oscillations—electrical waves generated by millions of neurons—function as analog computers, sculpting information in a fast, flexible, and energy-efficient way.
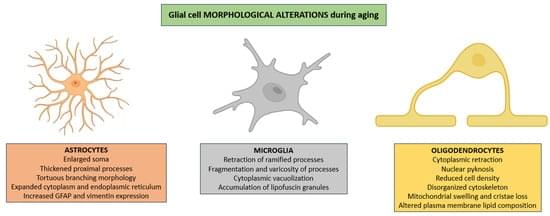
Aging is accompanied by complex cellular and molecular changes that compromise CNS function. Among these, glial cells (astrocytes, microglia, and oligodendrocytes) play a central role in maintaining neural homeostasis, modulating synaptic activity, and supporting metabolic demands. Emerging evidence indicates that aging disrupts glial cell physiology through processes including mitochondrial dysfunction, impaired proteostasis, chronic low-grade inflammation, and altered intercellular signaling. These alterations contribute to synaptic decline, myelin degeneration, and persistent, low-grade inflammation of the CNS. This review synthesizes current knowledge on the bidirectional relationship between aging and glial cell dysfunction, highlighting how age-related systemic and CNS-specific factors exacerbate glial impairments and, in turn, accelerate neural deterioration.

You know that feeling when a song from your teenage years comes on, and suddenly you’re right back in your old bedroom, feeling everything as vividly as you did decades ago? Scientists call this the “reminiscence bump”—our strange tendency to form the most powerful, lasting emotional bonds with music we hear between ages 15 and 25. But until now, no one knew if this was just a Western phenomenon or if it looked the same for everyone, everywhere.
The study also revealed we’re not limited to just one “memory bump.” Three distinct patterns emerge: we connect with music our parents loved (cross-generational), music from our own coming-of-age years (the classic reminiscence bump), and music from recent years (the recency effect). Age and gender act like equalizers, turning up some bumps while fading others.
From the “reminiscence bump” to cross-generational musical connections, we’ll unpack the psychology and neuroscience behind your most meaningful playlists.
Some songs stay with us for a lifetime. Even decades later, a few familiar notes can unlock vivid memories. Yet the life periods from which these songs originate and their prominence across age and gender remain underexplored. This study examines lifespan patterns in music-related memory, focusing on age trends, gender differences, and the global presence of the “reminiscence bump”, a peak in emotional connection to music from adolescence and early adulthood. While this phenomenon is well-documented in Western samples, its global manifestation, gendered dimensions and variation across life stages remains unexplored. Using responses collected from 1891 participants across diverse geographical backgrounds, we analysed the release years of personally meaningful songs.

Soft drink consumption is linked to an increased risk of major depressive disorder and greater depressive symptom severity, mediated by changes in gut microbiota, particularly Eggerthella abundance.
Question Is soft drink consumption related to depression diagnosis and severity, and is this association mediated by gut microbiome alteration?
Findings In this cohort study, soft drink consumption was significantly associated with diagnosis of major depressive disorder, as well as depression severity, across a single-study cohort of 932 clinically diagnosed patients and healthy controls. This association was significantly mediated by Eggerthela abundance in female patients and controls.
Meaning Education, prevention strategies, and policies aiming to reduce soft drink consumption are urgently required to mitigate depressive symptoms; in addition, interventions for depression targeting the microbiome composition appear promising.
