Journalism professor Shen Yang plans to detail his creation process so anyone can ‘create good fiction with AI’


Even though the guts of General Relativity are obtusely mathematical, and for decades was relegated to math departments rather than proper physics, you get to experience the technological gift of relativity every time you navigate to your favorite restaurant. GPS, the global positioning system, consists of a network of orbiting satellites constantly beaming out precise timing data. Your phone compares those signals to figure out where you are on the Earth. But there is a difference in spacetime between the surface of the Earth and the orbit of the satellites. Without taking general relativity into account, your navigation would simply be incorrect, and you’d be late for dinner.
As revolutions go, general relativity is a big one. And as unifications go, it’s a warning. To make this union happen Einstein had to radically, permanently alter not just our conceptions of gravity as a force acting through space and time, but our conceptions of space and time itself. It took no less than a complete overhaul of our entire philosophical understanding of the relation between space and time to bridge the gap.
And as Einstein would find in the ensuing decades, all the way to the time of his death, that bringing other forces like electromagnetism into the same unified fold would be all but impossible. Electromagnetism, and the other forces, cannot be conceptualized in the same way. Instead we have to use quantum probabilities to make predictions, and when we apply the same technique to gravity we just get infinities.
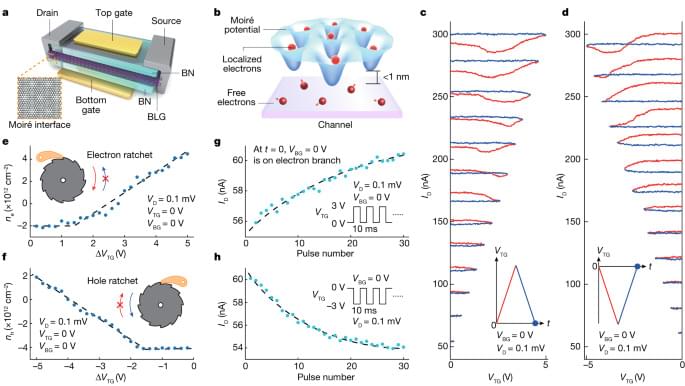

High-frequency terahertz waves have great potential for a number of applications including next-generation medical imaging and communication. Researchers at Linköping University, Sweden, have shown, in a study published in the journal Advanced Science, that the transmission of terahertz light through an aerogel made of cellulose and a conducting polymer can be tuned. This is an important step to unlock more applications for terahertz waves.
The terahertz range covers wavelengths that lie between microwaves and infrared light on the electromagnetic spectrum. It has a very high frequency. Thanks to this, many researchers believe that the terahertz range has great potential for use in space exploration, security technology and communication systems, among other things.
In medical imaging, it can also be an interesting substitute for X-ray examinations as the waves can pass through most non-conductive materials without damaging any tissue.
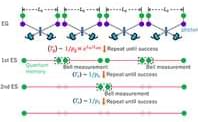
Quantum technology is now at a point where practical work can begin on creating the quantum internet. However, numerous challenges must be overcome before this vision becomes a reality. A global-scale quantum internet requires the development of the quantum repeater, a device that stores and manipulates qubits while interacting with or emitting entangled photons. This review examines different approaches to quantum repeaters and networks, covering their conceptual frameworks, architectures, and current progress in experimental implementation.
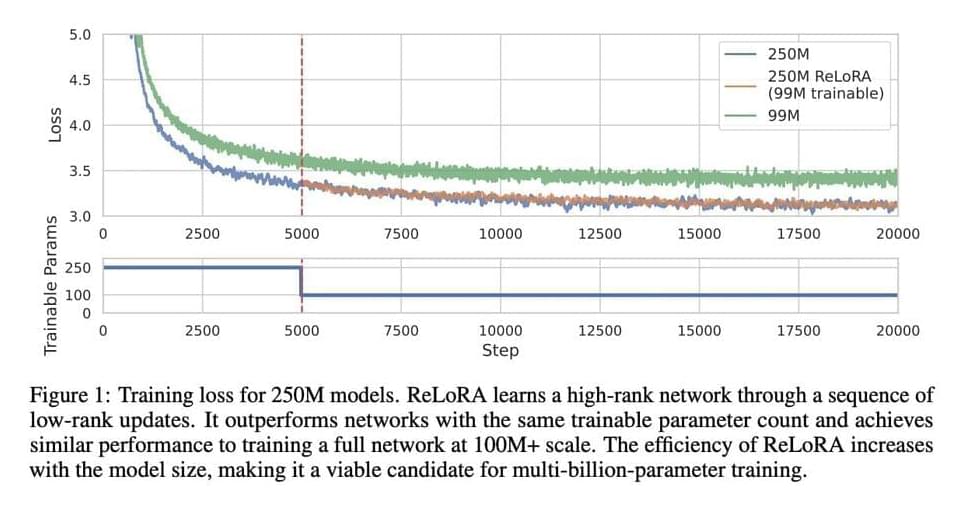
In machine learning, larger networks with increasing parameters are being trained. However, training such networks has become prohibitively expensive. Despite the success of this approach, there needs to be a greater understanding of why overparameterized models are necessary. The costs associated with training these models continue to rise exponentially.
A team of researchers from the University of Massachusetts Lowell, Eleuther AI, and Amazon developed a method known as ReLoRA, which uses low-rank updates to train high-rank networks. ReLoRA accomplishes a high-rank update, delivering a performance akin to conventional neural network training.
Scaling laws have been identified, demonstrating a strong power-law dependence between network size and performance across different modalities, supporting overparameterization and resource-intensive neural networks. The Lottery Ticket Hypothesis suggests that overparameterization can be minimized, providing an alternative perspective. Low-rank fine-tuning methods, such as LoRA and Compacter, have been developed to address the limitations of low-rank matrix factorization approaches.
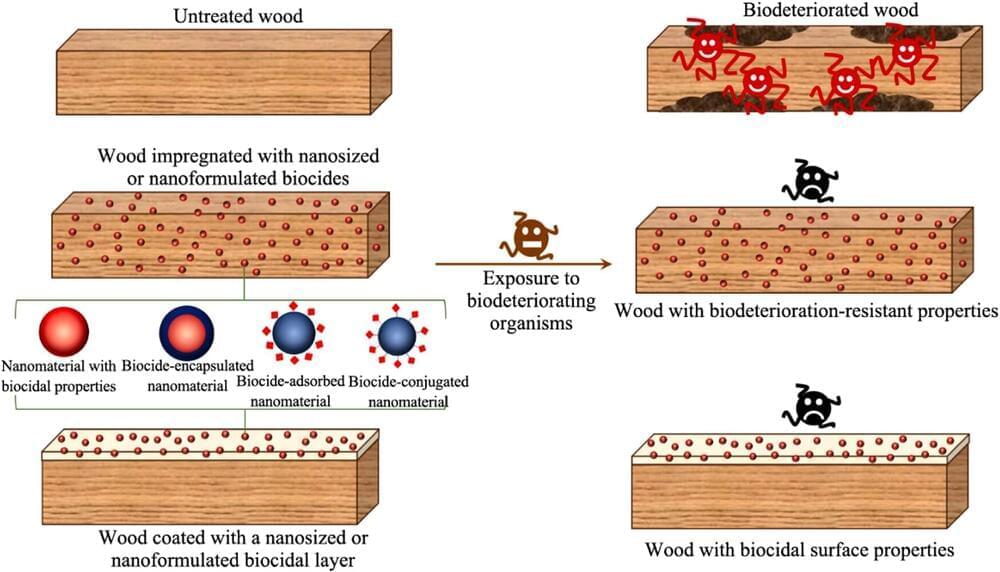
Emerging technologies such as nanotechnology can provide efficient approaches by which new materials with broad functions, such as durable and fire-retardant properties, can be developed and subsequently used for the treatment of wood materials.
In a study published in the Journal of Bioresources and Bioproducts, an international team from New Zealand (Scion) and China (Northeast Forestry University) report a review that nanotechnology-based methods can be employed to mitigate these weaknesses and create durable, sustainable wood materials.
These wood nanotechnologies also can be employed to develop wood products with antimicrobial surfaces for various applications. Furthermore, analytical tools used in nanoscience and nanotechnology enable the precise study of wood structure and its components on a nanometer scale, particularly those aspects that can affect wood products’ biodeterioration resistance properties.
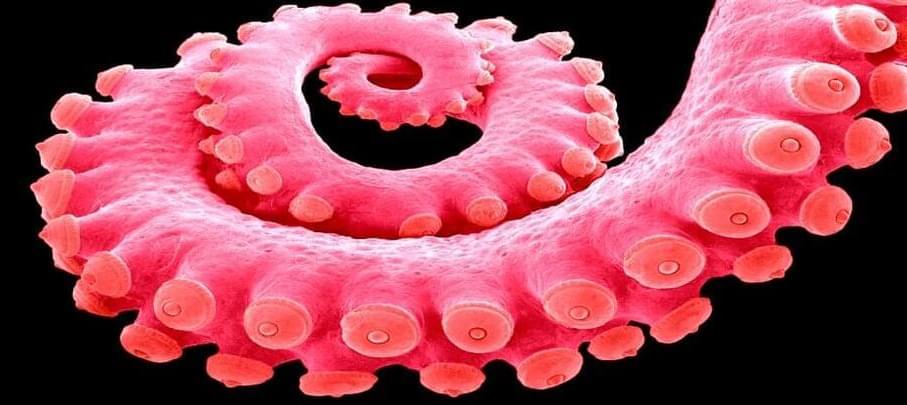
Ocean bays that pinch West Antarctica are home to two distinct populations of Turquet’s octopus (Pareledone turqueti). The shared secrets of their ancestors do not bode well for the future health of our planet.
A new DNA analysis of the two geographically separated octopus populations indicates they were once part of one big family.
This direct historical connection suggests that around 125,000 years ago, the massive 2.2 million cubic kilometer (530,000 cubic mile) West Antarctic Ice Sheet (WAIS) that separates the two bays had fully collapsed into the sea.

Scientists have developed a new material from a mineral abundant on Mars that they claim could open the door to sustainable habitation on the red planet.
Researchers assessed the potential of a type of nanomaterials – ultrasmall components thousands of times smaller than a human hair – for clean energy production and building materials on Mars.
The study, published in the journal Advanced Functional Materials, found that a material typically considered a waste product by NASA can be altered to provide clean energy and sustainable electronics.
Researchers have had an unprecedented and exceptional encounter with a humpback whale, allowing them to learn more about humpback whale communication systems. The encounter happened earlier this year when a group of researchers known as Whale-SETI held a 20-minute “conversation” with a humpback named Twain.
The conversation is heavily detailed in a paper published in the journal Peer J and it showcases the first conversation between humans and humpback whales using “humpback language.” To pull off such a wonderful breakthrough, researchers used a recorded humpback contact call to get Twain’s attention. From there, the whale responded with a greeting signal and began to circle their boat.
Lead author Dr. Brenda McCowan from U.C. Davis says that the conversation goes a long way to emphasizing the intelligence of these creatures, and highlights how complex humpback communication systems are. The fact that they can create nets made of bubbles to catch fish, and even communicate extensively through their songs and calls is mind-boggling.