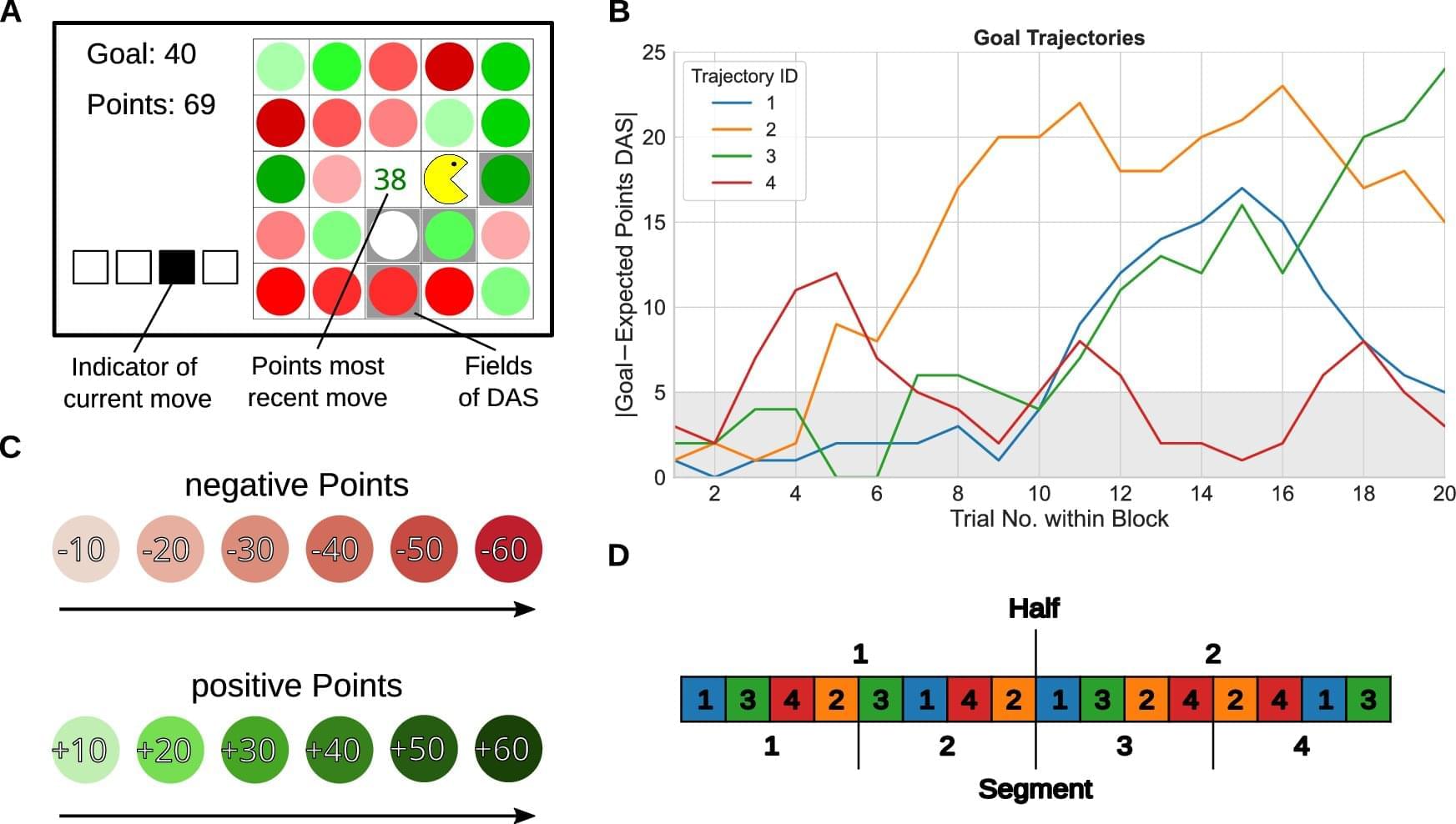
Behavioral scientists have been trying to uncover the patterns that humans follow when making decisions for decades. The insights gathered as part of their studies can help shape public policies and interventions aimed at prompting people to make better decisions, both for society and for their own well-being.
In many cases, humans are known to make decisions that they think will maximize the rewards they receive while minimizing their losses. Sometimes, however, people’s choices are guided by automatic processes that they are unaware of and can be adversely impacted by so-called biases, systematic tendencies to fall into specific patterns of thought or behavior.
Researchers at TUD Dresden University of Technology recently carried out a study exploring the possibility that repeating specific decisions over time could bias decision-making, even in instances in which people’s actions affect the rewards they will receive. Their findings, published in Communications Psychology, suggest that when making sequential decisions (i.e., when asked to make a series of choices back-to-back), humans often tend to repeat familiar actions, even if alternative ones would yield greater rewards.