Germany’s BSI and BfV warn of state-linked Signal phishing using fake support chats, PIN theft, and device linking to access sensitive accounts.




SmarterTools confirmed last week that the Warlock ransomware gang breached its network after compromising an email system, but it did not impact business applications or account data.
The company’s Chief Commercial Officer, Derek Curtis, says that the intrusion occurred on January 29, via a single SmarterMail virtual machine (VM) set up by an employee.
“Prior to the breach, we had approximately 30 servers/VMs with SmarterMail installed throughout our network,” Curtis explained.

Microsoft is investigating an ongoing Exchange Online issue that mistakenly flags legitimate emails as phishing and quarantines them.
The incident began on February 5 and continues to affect Exchange Online customers, preventing them from sending or receiving emails.
“Some users’ legitimate email messages are being marked as phish and quarantined in Exchange Online,” Microsoft said in a service alert when it acknowledged the bug on Thursday.

For life to develop on a planet, certain chemical elements are needed in sufficient quantities. Phosphorus and nitrogen are essential. Phosphorus is vital for the formation of DNA and RNA, which store and transmit genetic information, and for the energy balance of cells. Nitrogen is an essential component of proteins, which are needed for the formation, structure, and function of cells. Without these two elements, no life can develop out of lifeless matter.
A study led by Craig Walton, postdoc at the Center for Origin and Prevalence of Life at ETH Zurich, and ETH professor Maria Schönbächler has now shown that there must be sufficient phosphorus and nitrogen present when a planet’s core is formed. The study is published in Nature Astronomy.
“During the formation of a planet’s core, there needs to be exactly the right amount of oxygen present so that phosphorus and nitrogen can remain on the surface of the planet,” explains Walton, lead author of the study. This was exactly the case with Earth around 4.6 billion years ago—a stroke of chemical good fortune in the universe. This finding may affect how scientists search for life elsewhere in the universe.

Sodium-ion batteries (NIBs) are gaining traction as a next-generation technology to complement the widely used lithium-ion batteries (LIBs). NIBs offer clear advantages versus LIBs in terms of sustainability and cost, as they rely on sodium—an element that, unlike lithium, is abundant almost everywhere on Earth. However, for NIBs to achieve widespread adoption, they must reach energy densities comparable to LIBs.
State-of-the-art NIB designs use hard carbon (HC), a porous and amorphous type of carbon, as an anode material. Scientists believe that sodium ions aggregate into tiny quasi-metallic clusters within HC nano-pores, and this “pore filling” process remains as the main mechanism contributing to the extended reversible capacity of the HC anode.
Despite some computational studies on this topic, the fundamental processes governing sodium storage and transport in HC remain unclear. Specifically, researchers have struggled to explain how sodium ions can gather to form clusters inside HC pores at operational temperatures, and why the overall movement of sodium ions through the material is sluggish.


Medical artificial intelligence (AI) is often described as a way to make patient care safer by helping clinicians manage information. A new study by the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and collaborators confronts a critical vulnerability: when a medical lie enters the system, can AI pass it on as if it were true?
Analyzing more than a million prompts across nine leading language models, the researchers found that these systems can repeat false medical claims when they appear in realistic hospital notes or social-media health discussions.
The findings, published in The Lancet Digital Health, suggest that current safeguards do not reliably distinguish fact from fabrication once a claim is wrapped in familiar clinical or social-media language. The paper is titled “Mapping LLM Susceptibility to Medical Misinformation Across Clinical Notes and Social Media.”
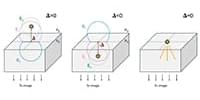
The University of Texas at Arlington researchers resolved a largely unnoticed modeling gap in how researchers interpret the behavior of single molecules at interfaces:
By treating emitters as finite-sized surface currents in contact with both media within finite-element simulations, this study provides the first physically self‑consistent framework for describing dipoles at arbitrary dielectric interfaces.
Spotlight by Matthew D. Lew.
A longstanding but largely unnoticed modeling gap has been skewing how researchers interpret the behavior of single molecules at interfaces—this work finally resolves it. Defocused fluorescence microscopy is widely used to infer molecular orientation, yet conventional models of dipole emission near refractive‑index boundaries diverge from one another depending on which side of the interface the molecule approaches. The result has been hidden, systematic biases in measured orientations. By treating emitters as finite-sized surface currents in contact with both media within finite-element simulations, this study provides the first physically self‑consistent framework for describing dipoles at arbitrary dielectric interfaces.