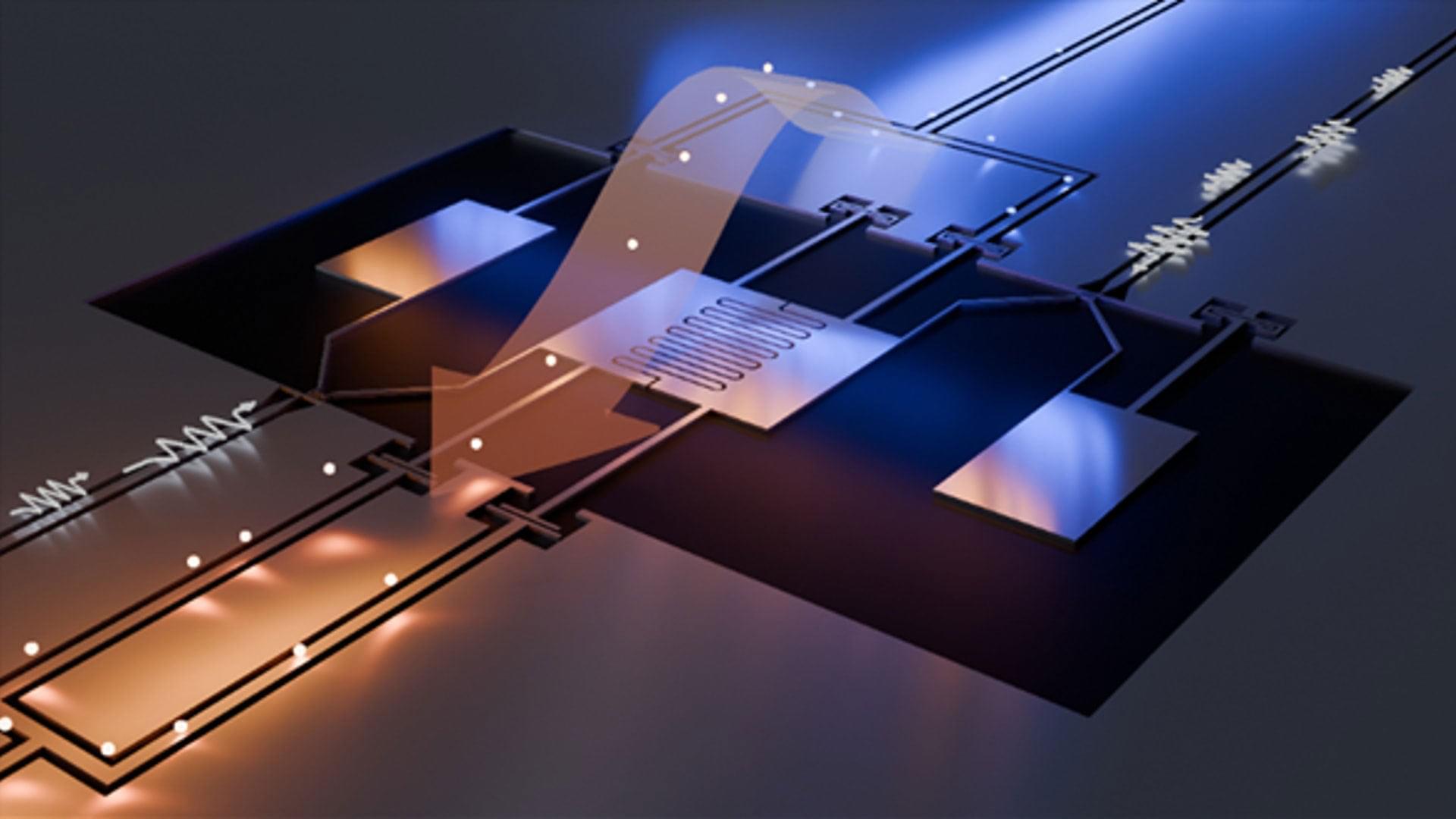
Quantum physics may sound abstract, but Ph.D. candidates Kirsten Kanneworff and David Dechant show that quantum research can also be very concrete. Together, they are investigating how quantum technology can change the world. While Kanneworff worked in the lab to study how quantum optics can be used to prove someone’s location, Dechant focused on quantum computing for dynamic systems, such as the financial world. The two researchers are defending their doctoral theses this week.
Imagine that you receive an email from someone posing as your bank, asking you to enter your personal details on a website. How can you verify the sender’s identity?
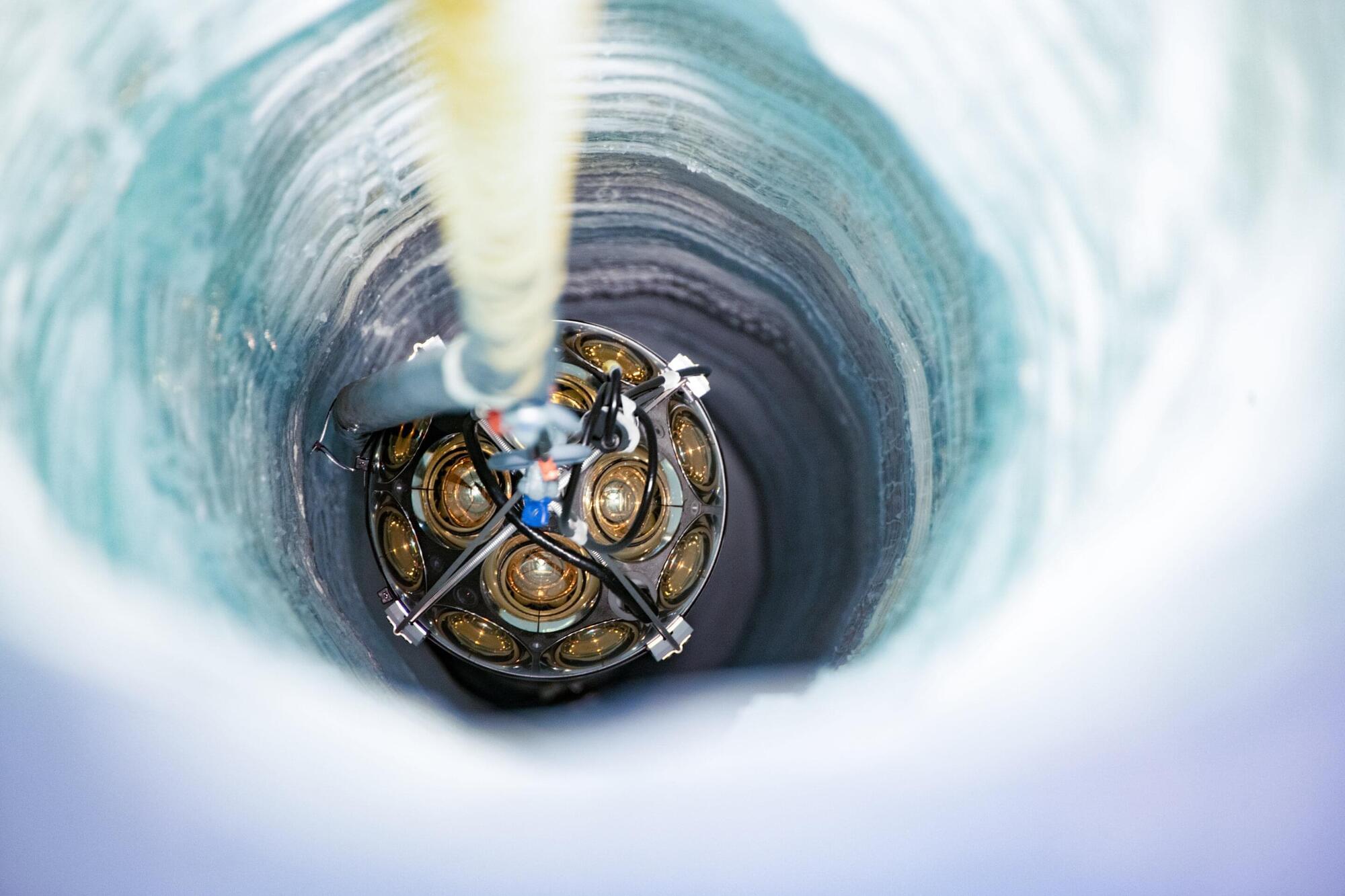
Kanneworff investigated a smart way to check whether someone is really in a certain place: quantum position verification. “The idea for this project came about during my master’s degree,” she says. “I found it an interesting subject. The combination of optics and quantum communication really appealed to me, especially since it has a clear application.”