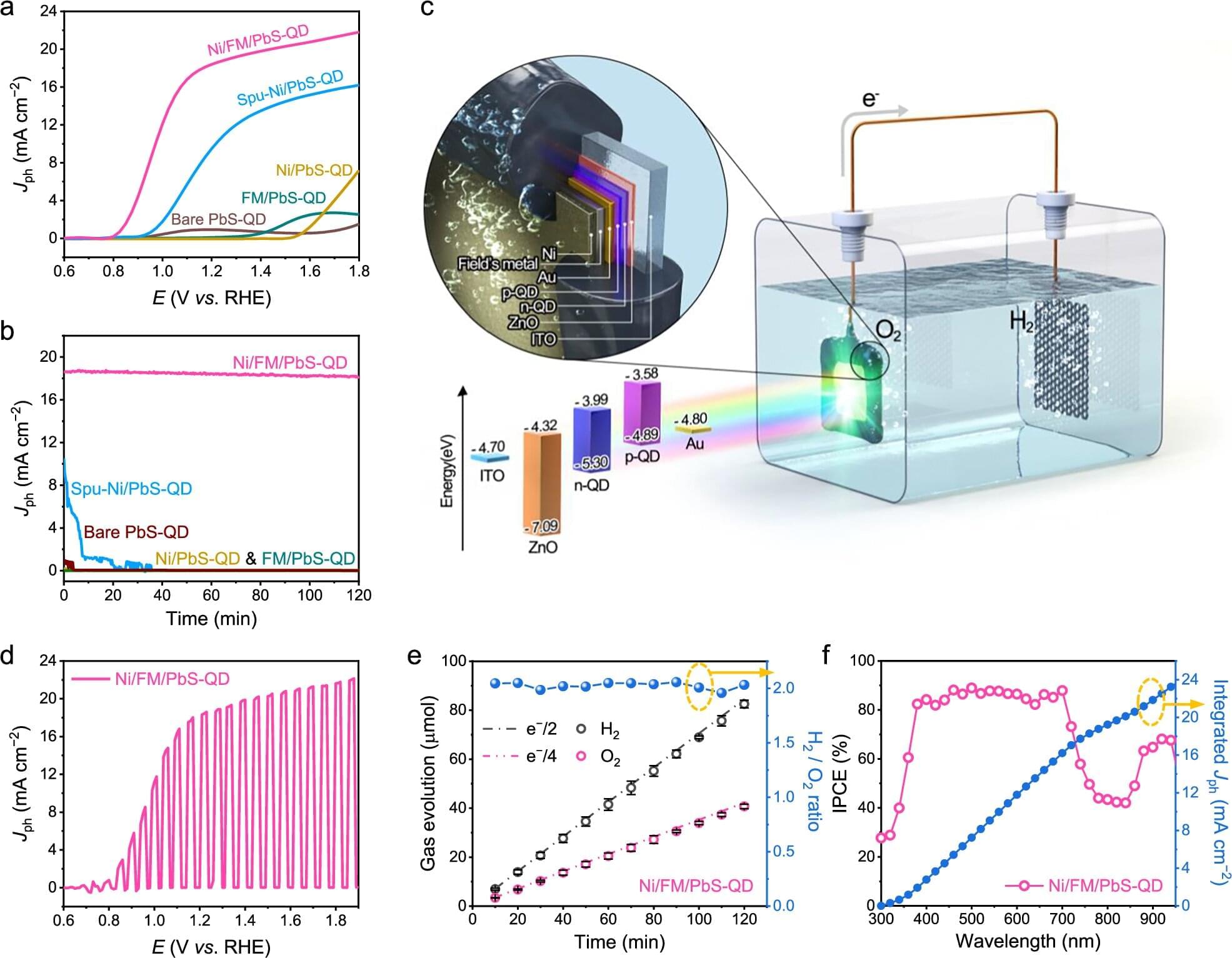
Even supercomputers can stall out on problems where nature refuses to play by everyday rules. Predicting how complex molecules behave or testing the strength of modern encryption can demand calculations that grow too quickly for classical hardware to keep up. Quantum computers are designed to tackle that kind of complexity, but only if engineers can build systems that run with extremely low error rates.
One of the most promising routes to that reliability involves a rare class of materials called topological superconductors. In plain terms, these are superconductors that also have built-in “protected” quantum behavior, which researchers hope could help shield delicate quantum information from noise. The catch is that making materials with these properties is famously difficult.