With a new mathematical model, a team of biophysicists has revealed fresh insights into how biological tissues are shaped by the active motion of structural imperfections known as “topological defects.” Published in Physical Review Letters, the results build on our latest understanding of tissue formation and could even help resolve long-standing experimental mysteries surrounding our own organs.
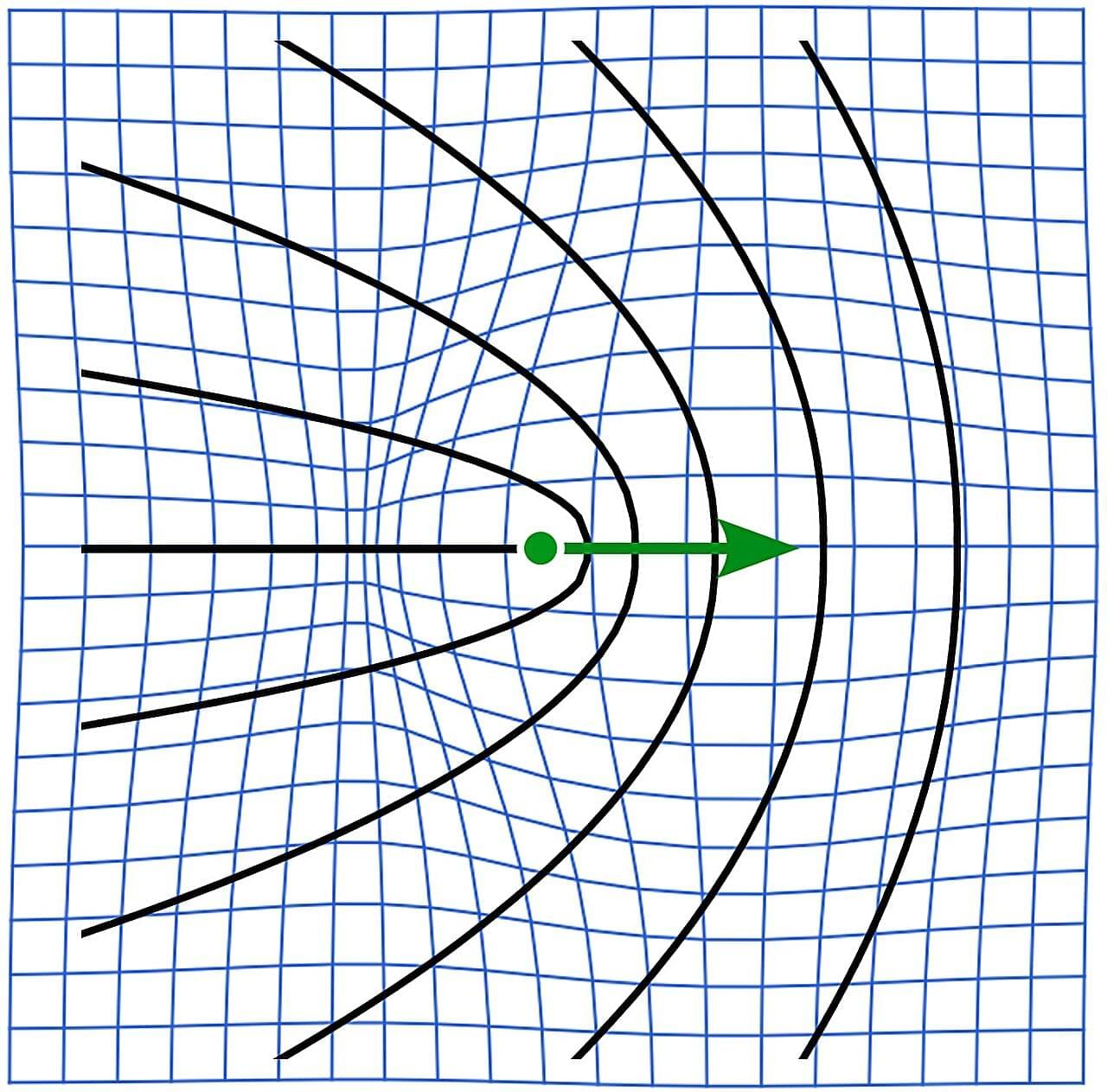
Topological defects are structural imperfections that emerge in systems hosting multiple, incompatible configurations of particles. They can be found in many different kinds of systems—both natural and manmade—but are especially important for describing “active fluids,” which are composed of particles that constantly harvest energy from their surroundings and convert it into motion, generating their own propulsion.
This behavior also underpins the physics of liquid crystal displays, where topological defects emerge in 2D systems of rod-shaped molecules and help determine how light is modulated to produce the images and colors we see every day on our phones, laptops, and TV screens.