Breakthrough modeling technology reveals how cells lose their organization in leading cause of vision loss.


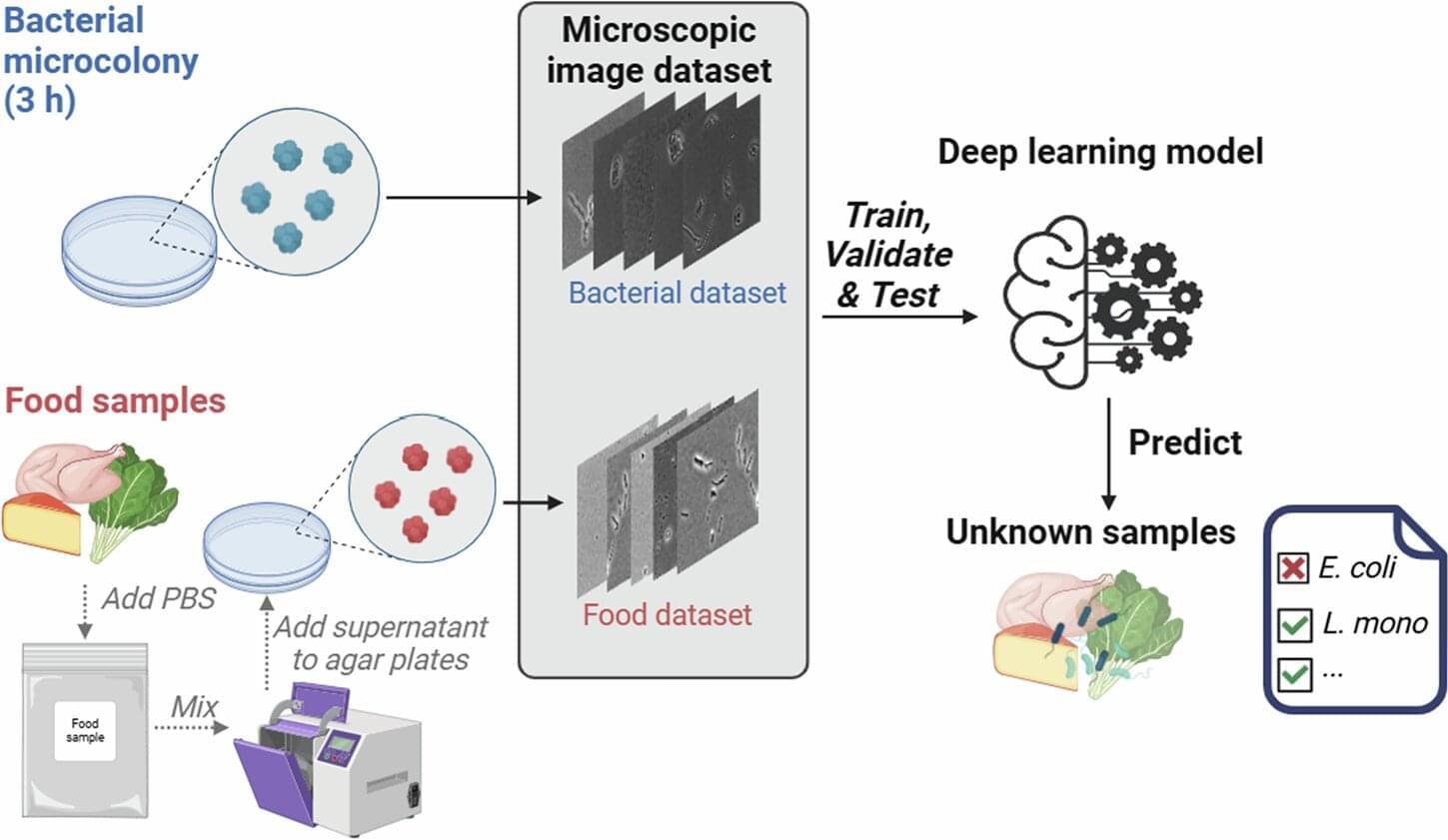
Researchers have significantly enhanced an artificial intelligence tool used to rapidly detect bacterial contamination in food by eliminating misclassifications of food debris that looks like bacteria. Current methods to detect contamination of foods such as leafy greens, meat and cheese, which typically involve cultivating bacteria, often require specialized expertise and are time-consuming—taking several days to a week.
Luyao Ma, an assistant professor at Oregon State University, and her collaborators from the University of California, Davis, Korea University and Florida State University, have developed a deep learning-based model for rapid detection and classification of live bacteria using digital images of bacteria microcolonies. The method enables reliable detection within three hours. The findings are published in the journal npj Science of Food.
Their latest breakthrough involves training the model to distinguish bacteria from microscopic food debris to improve its accuracy. A model trained only on bacteria misclassified debris as bacteria more than 24% of the time. The enhanced model, trained on both bacteria and debris, eliminated misclassifications.

How do you design a living space where there’s no up or down? That’s one of the challenges facing Teague, a Seattle-based design and innovation firm that advises space companies such as Blue Origin, Axiom Space and Voyager Technologies on how to lay out their orbital outposts.
Mike Mahoney, Teague’s senior director of space and defense programs, says the zero-gravity environment is the most interesting element to consider in space station design.
“You can’t put things on surfaces, right? You’re not going to have tables, necessarily, unless you can attach things to them, and they could be on any surface,” he told GeekWire. “So, directionality is a big factor. And knowing that opens up new opportunities. … You could have, let’s say, two scientists working in different orientations in the same area.”

A fundamental desideratum of AI is the ability to model environment dynamics and transitions in response to both their own actions and external control signals. This capability, commonly referred to as world modeling (WM), is essential for prediction, planning, and generalization. Learning world models using deep learning has been an active area of research for nearly a decade. In recent years, the field has witnessed significant breakthroughs driven by advances in deep neural architectures and scalable learning paradigms. Multiple subfields, including self-supervised learning (SSL), generative modeling, reinforcement learning (RL), robotics, and large language models (LLMs), have tackled aspects of world modeling, often with different tools and methodologies. While these communities address overlapping challenges, they frequently operate in isolation. As a result, insights and progress in one area may go unnoticed in another, limiting opportunities for synthesis and collaboration. This workshop aims to bridge this gap between subfields of world modeling by fostering open dialogue, critical discussion, and cross-disciplinary exchange. By bringing together researchers from diverse backgrounds, from early-career researchers to established experts, we hope to establish a shared vocabulary, identify common challenges, and surface synergies that can move the field of world modeling forward.
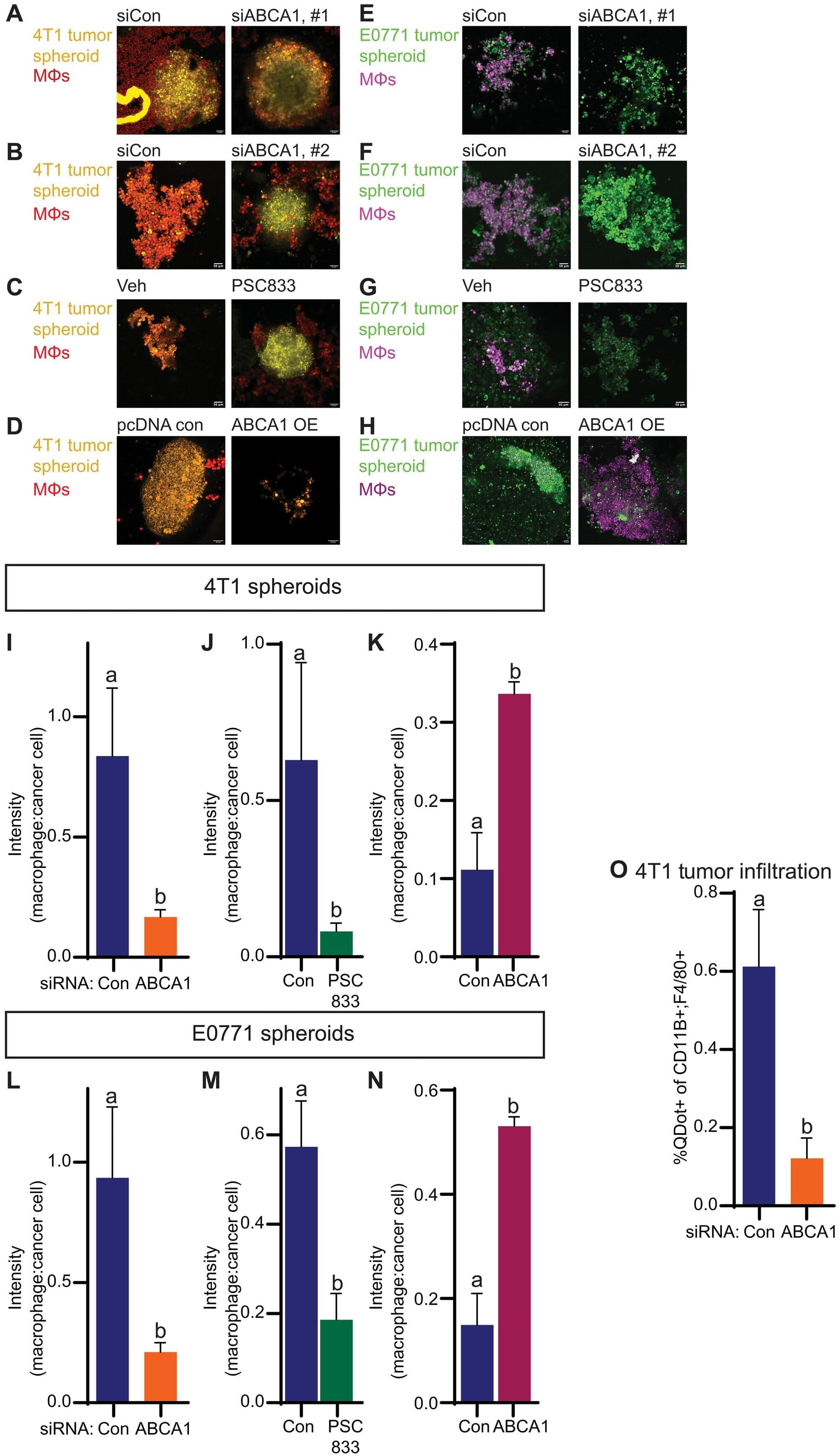
In recent years, cancer researchers have made major breakthroughs by using the body’s immune system to fight cancer. One of the most promising approaches, known as immune checkpoint blockade, works by releasing molecular “brakes” on T cells. This allows them to better recognize and attack cancer cells. While these therapies can be very effective for some patients, many solid tumors, including most forms of breast cancer, remain largely unaffected. Cancer Center at Illinois (CCIL) Program Co-leader Erik Nelson and his research group are working to understand why these treatments fail.
Elevated blood concentrations of cholesterol have long been linked to cancer outcomes. In a new study, they found that a protein called ABCA1 is involved in transporting cholesterol out of a type of immune cell called macrophages, and in so-doing shifts them to an “attack cancer” mode.
“Immune based therapies have revolutionized how we can treat cancer, basically taking the brakes off of a type of immune cell called T cells so they can attack cancer,” Nelson said. “While this approach works well for some patients, many so-called solid tumors fail to respond or develop resistance mechanisms.”
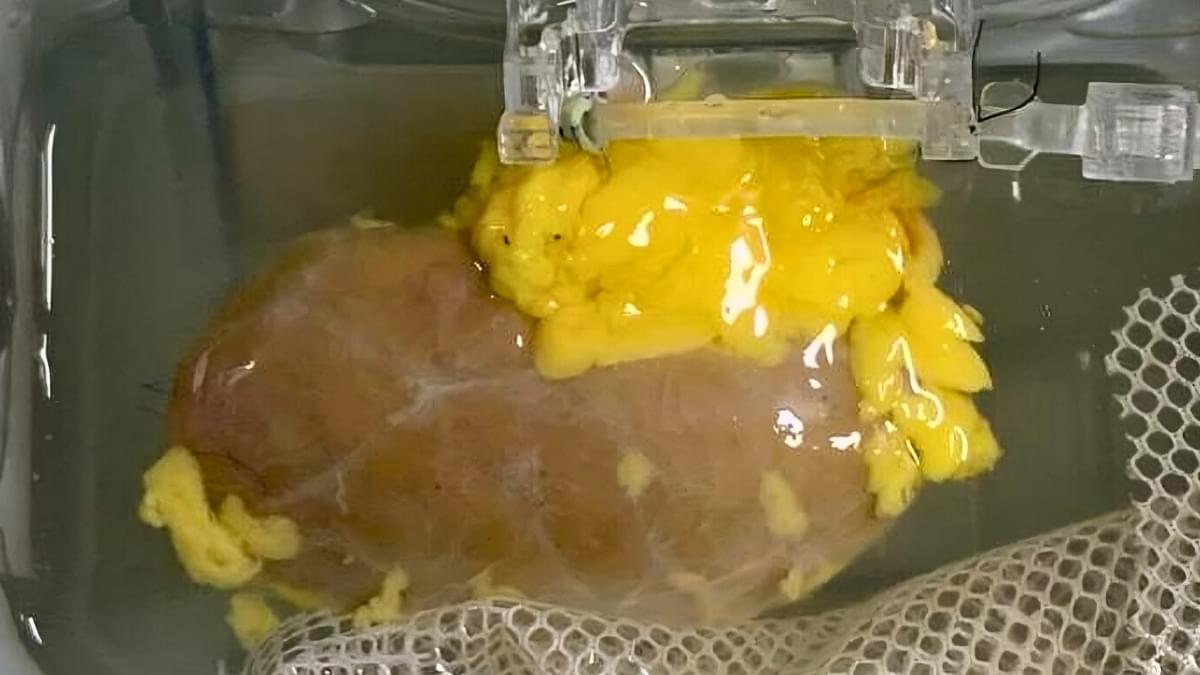
After a decade of work, researchers are closer than ever to a key breakthrough in kidney transplants: being able to transfer kidneys from donors with different blood types than the recipients, which could significantly speed up waiting times and save lives.
In research published last year, a team from institutions across Canada and China reported creating a ‘universal’ kidney that, in theory, can be accepted by any patient.
Their test organ survived and functioned for several days in the body of a brain-dead recipient, whose family consented to the research.
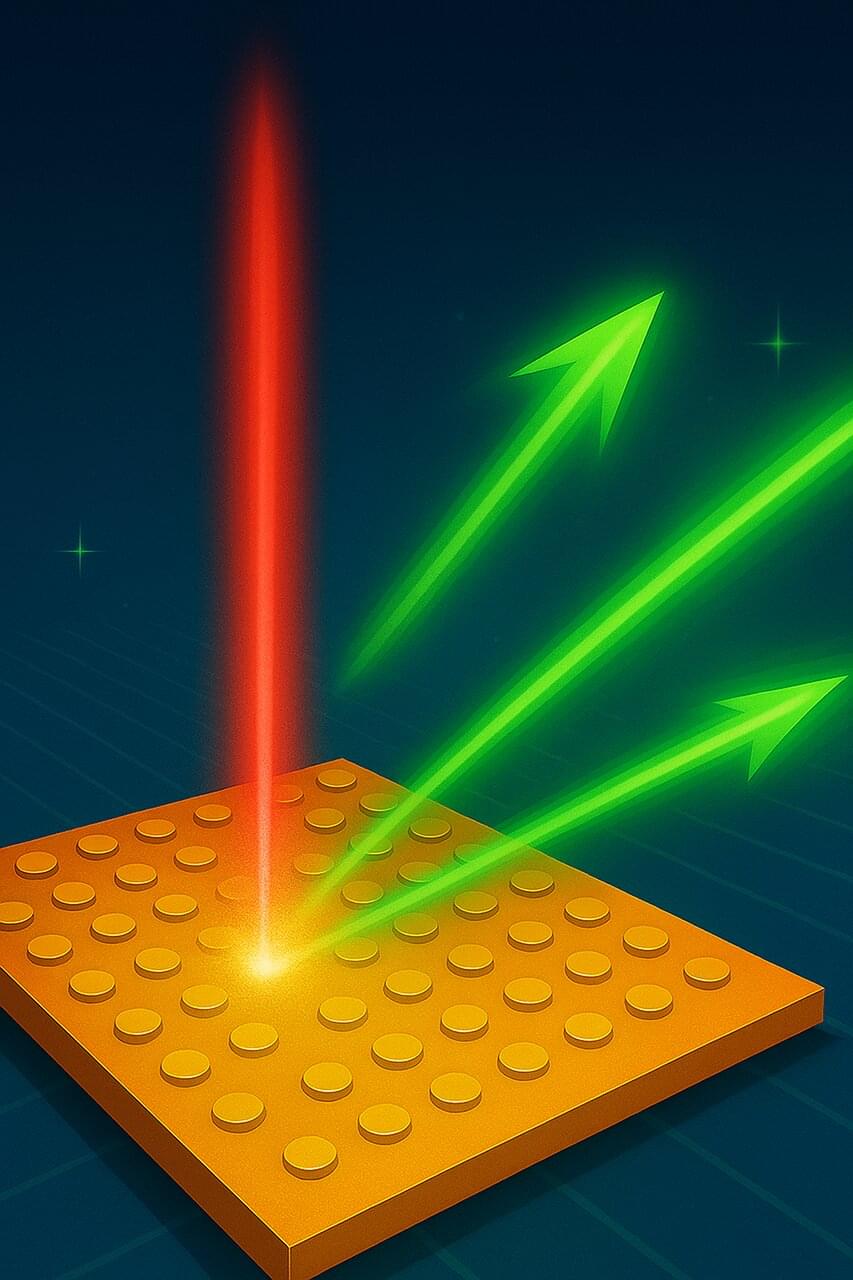
The invention of tiny devices capable of precisely controlling the direction and behavior of light is essential to the development of advanced technologies. Researchers at the Advanced Science Research Center at the CUNY Graduate Center (CUNY ASRC) have taken a significant step forward with the development of a metasurface that can turn invisible infrared light into visible light and aim it in different directions—without any moving parts. The details of their work are explained in a paper published in the journal eLight.
The novel metasurface is constructed of an ultra-thin chip patterned with tiny structures smaller than the wavelength of light. When hit with an infrared laser, the chip converts the incoming light to a higher color (or frequency) and sends the new light out as a narrow beam that can be steered simply by changing how the incoming light is polarized.
In their experiments, the team converted infrared light around 1,530 nanometers—similar to the light used in fiber-optic communications—into visible green light near 510 nanometers and steered it to chosen angles.
New preprint reports 17-month lifespan extension in mice with some living nearly 5 years. The intervention targets immune aging through CD4+ T cells and is expected to enter human trials in 2026.
Some links are affiliate links so we will earn a commission when they are used to purchase products.
If you would like to support our channel please consider joining our patreon / modernhealthspan.
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Renue By Science (10% off: MHS) https://tinyurl.com/bdew4bfs NMN Powder • Lipo NR
BiOptimizers (15% off: MHBIO) https://bit.ly/47VAa8f — Magnesium Breakthrough.
Seeking Health (10% off: Richard10) https://crrnt.app/SEEK/-dm0MyrQ, Histamine Nutrients https://crrnt.app/SEEK/EpM7paAO
Stemregen (15% off: MODERN) US only https://tinyurl.com/45z968yr.
Wellness Extract (10% off: MODERNWE) http://wellnessextract.com/RICHARDWE Geranylgeraniol • Vit E
AX3 Life (20% off: MODERN20) https://tinyurl.com/2t3w26nw — Astaxanthin.
Oxford Healthspan (15% off: MHS) https://tinyurl.com/hrxfnzpn — Spermidine.
Qitone (10% off: HEALTH10) https://tidd.ly/4jGklry Qitone Esters Powder.
ProHealth (15% off: MODERN) https://prohealth.pxf.io/aObQRR NMNH 500mg.
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
A new preprint by Lanna et al. reports one of the largest lifespan extensions ever seen in mice; approximately 17 months, with some mice living close to 5 years. The study focuses on metabolically reprogramming CD4+ T cells from aged mice using a peptide called DOS, which enables these cells to produce \.
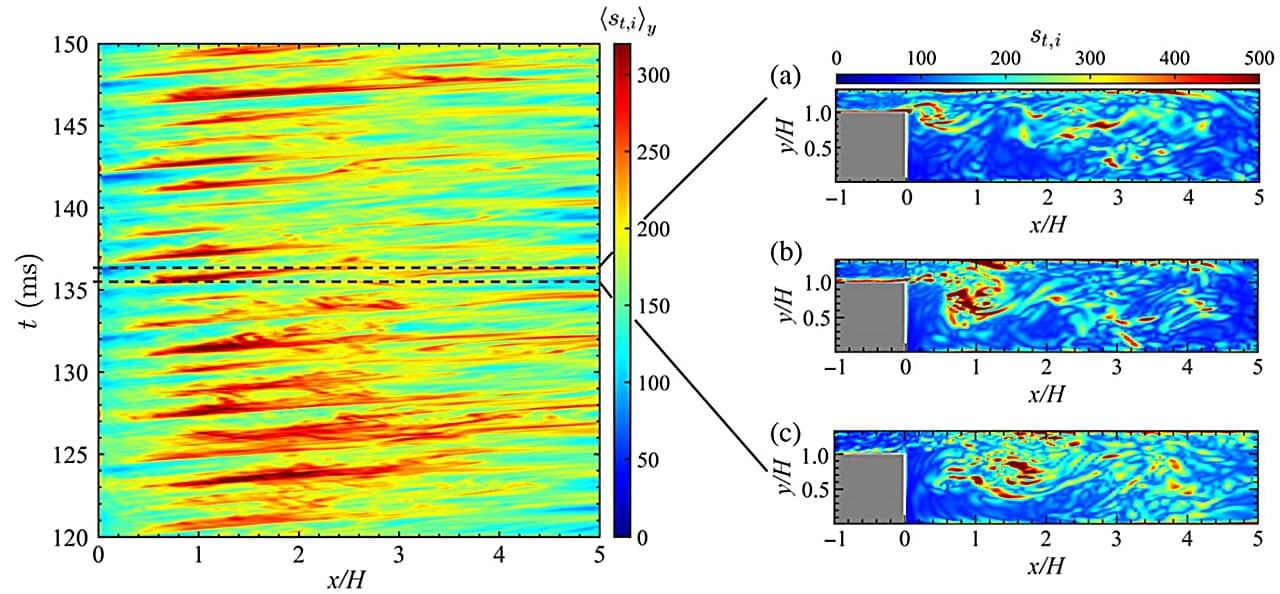
Engineers have long battled a problem that can cause loud, damaging oscillations inside gas turbines and aircraft engines: combustion instability. These unwanted pressure fluctuations create vibrations so intense that they can cause fatal structural damage to combustor walls, posing a serious threat in many applications. Combustion instability occurs when acoustic waves, heat release, and flow patterns interact in a strong feedback loop, amplifying each other until the entire system becomes unstable.
The complex interaction has made it difficult to predict when and where dangerous oscillations will emerge. This challenge has motivated researchers to seek new analytical frameworks that can capture the key driving regions of combustion instability.
Now, a research team led by Professors Hiroshi Gotoda from Tokyo University of Science and Ryoichi Kurose from Kyoto University, Japan, has developed an innovative approach using network science to understand and suppress combustion instability. Their paper, published in the journal Physical Review Applied on July 1, 2025, applies complex network analysis to spray combustion instability in a backward-facing step combustor.