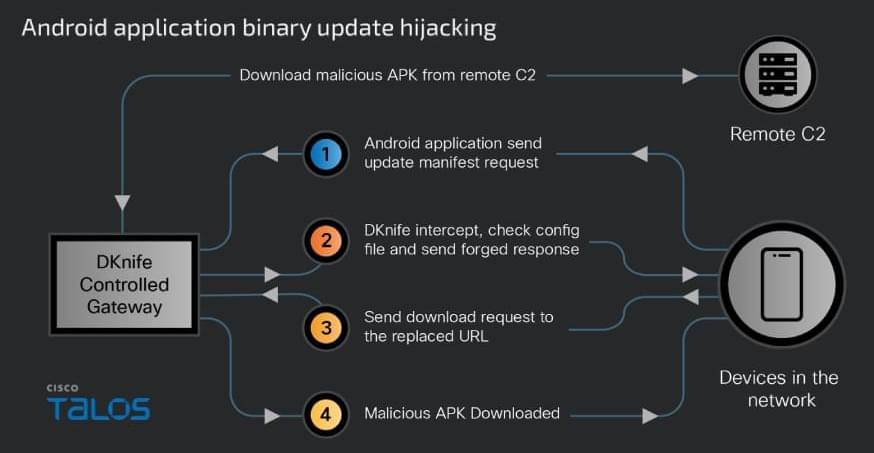
China-linked DKnife framework uses router-level AitM implants for traffic hijacking, credential theft, and malware delivery targeting edge devices.



Germany’s domestic intelligence agency is warning of suspected state-sponsored threat actors targeting high-ranking individuals in phishing attacks via messaging apps like Signal.
The attacks combine social engineering with legitimate features to steal data from politicians, military officers, diplomats, and investigative journalists in Germany and across Europe.
The security advisory is based on intelligence collected by the Federal Office for the Protection of the Constitution (BfV) and the Federal Office for Information Security (BSI).
A newly discovered toolkit called DKnife has been used since 2019 to hijack traffic at the edge-device level and deliver malware in espionage campaigns.
The framework serves as a post-compromise framework for traffic monitoring and adversary-in-the-middle (AitM) activities. It is designed to intercept and manipulate traffic destined for endpoints (computers, mobile devices, IoTs) on the network.
Researchers at Cisco Talos say that DKnife is an ELF framework with seven Linux-based components designed for deep packet inspection (DPI), traffic manipulation, credential harvesting, and malware delivery.


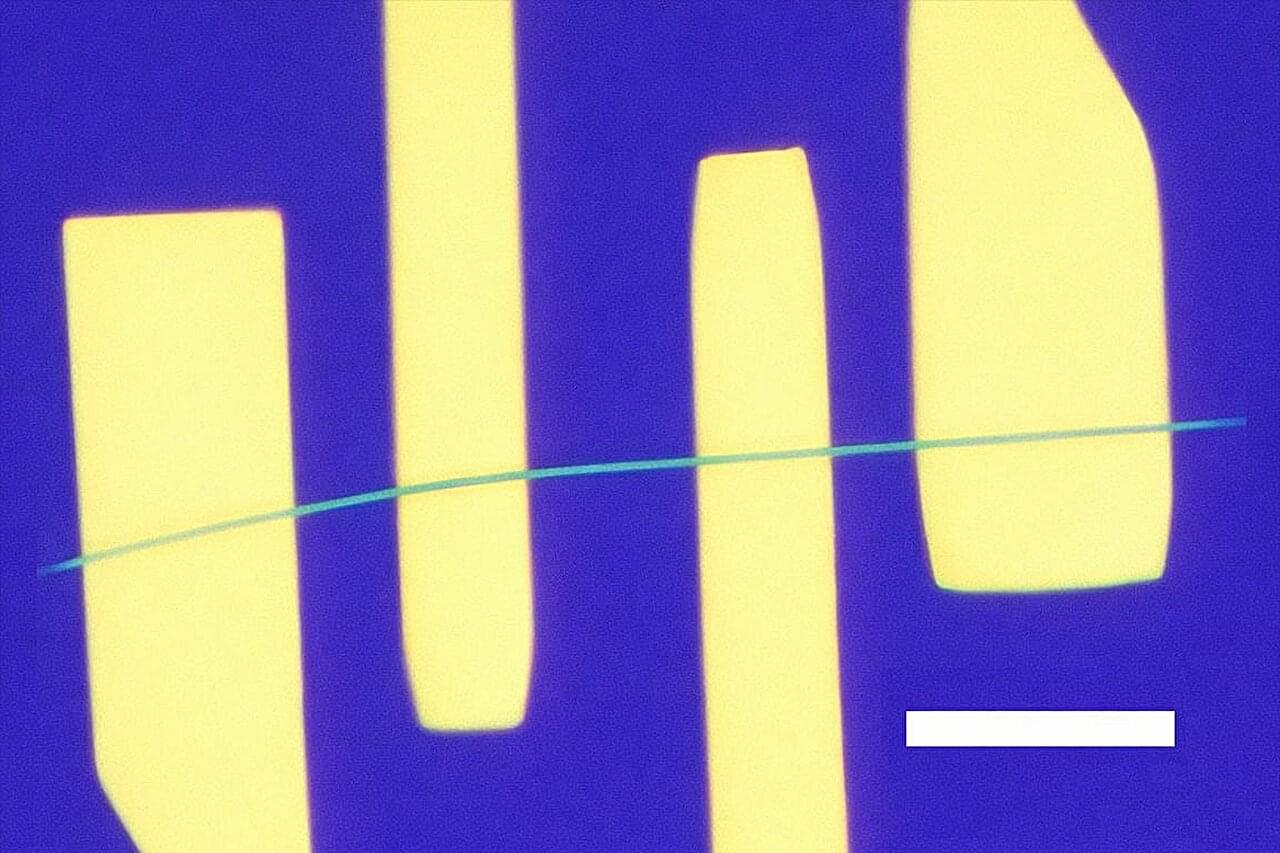
That low-frequency fuzz that can bedevil cellphone calls has to do with how electrons move through and interact in materials at the smallest scale. The electronic flicker noise is often caused by interruptions in the flow of electrons by various scattering processes in the metals that conduct them.
The same sort of noise hampers the detecting powers of advanced sensors. It also creates hurdles for the development of quantum computers—devices expected to yield unbreakable cybersecurity, process large-scale calculations and simulate nature in ways that are currently impossible.
A much quieter, brighter future may be on the way for these technologies, thanks to a new study led by UCLA. The research team demonstrated prototype devices that, above a certain voltage, conducted electricity with lower noise than the normal flow of electrons.

Multiple critical vulnerabilities in the popular n8n open-source workflow automation platform allow escaping the confines of the environment and taking complete control of the host server.
Collectively tracked as CVE-2026–25049, the issues can be exploited by any authenticated user who can create or edit workflows on the platform to perform unrestricted remote code execution on the n8n server.
Researchers at several cybersecurity companies reported the problems, which stem from n8n’s sanitization mechanism and bypass the patch for CVE-2025–68613, another critical flaw addressed on December 20.