Apr 8, 2018
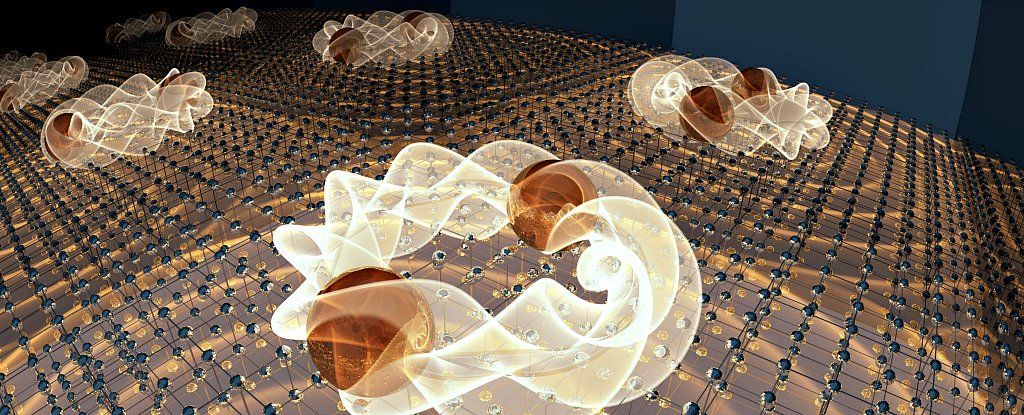
Physicists Just Discovered an Entirely New Type of Superconductivity
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: materials, physics
One of the ultimate goals of modern physics is to unlock the power of superconductivity, where electricity flows with zero resistance at room temperature.
Progress has been slow, but physicists have just made an unexpected breakthrough. They’ve discovered a superconductor that works in a way no one’s ever seen before — and it opens the door to a whole world of possibilities not considered until now.
In other words, they’ve identified a brand new type of superconductivity.
Continue reading “Physicists Just Discovered an Entirely New Type of Superconductivity” »