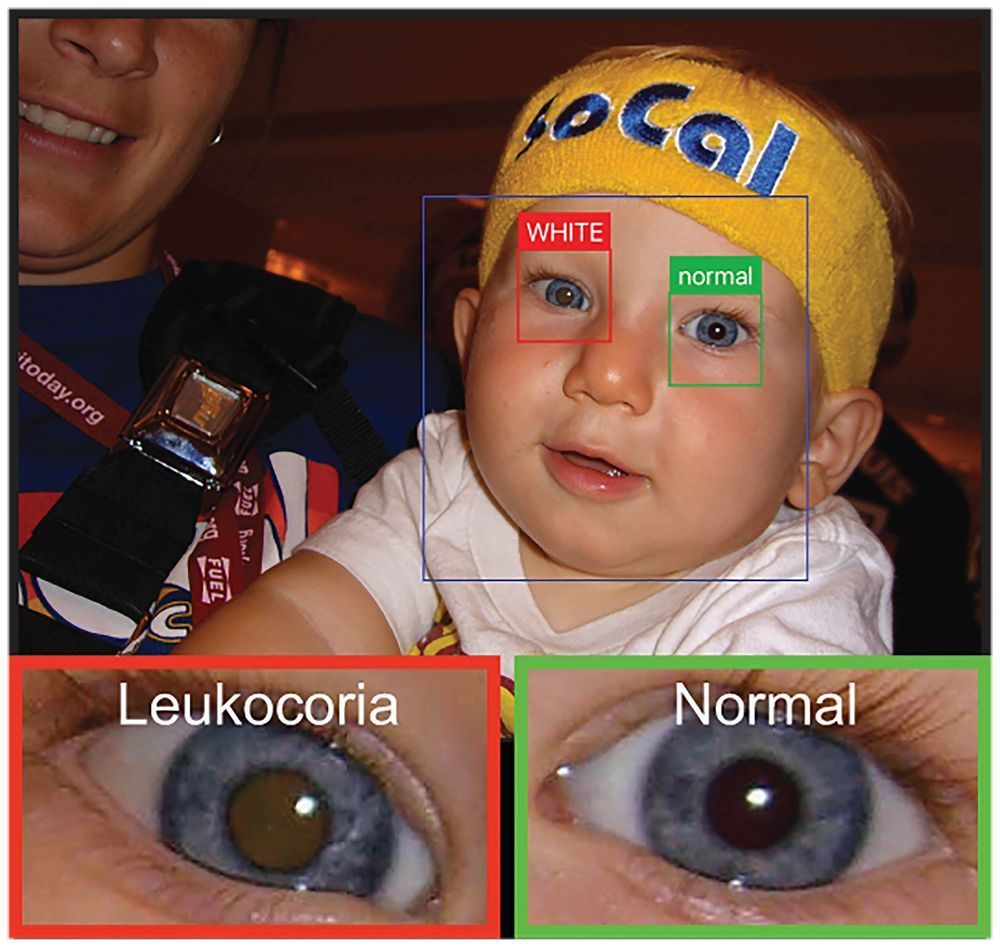
Oct 4, 2019
This quantum physics breakthrough could be the origin story for time travel
Posted by Paul Battista in categories: cosmology, quantum physics, time travel
An international team of researchers recently placed an entire molecule into a state of quantum superposition. This huge breakthrough represents the largest object to ever be observed in such a state – essentially occupying two places at once. And it may just be the eureka moment that defines our species’ far-future technology.
Quantum physics is about as close to a faith-based field of scientific study as there is. It’s not our fault, the universe is infinite and complex and we’ve been here for a relatively short amount of time. It’s excusable that we still don’t understand all the rules and, in lieu of a blueprint, we’re forced to come up with theories to explain the things we don’t know.