Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science & Technology (DGIST, President Yang Kook) Professor Hongsoo Choi’s team of the Department of Robotics and Mechatronics Engineering collaborated with Professor Sung-Won Kim’s team at Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, Catholic University of Korea, and Professor Bradley J. Nelson’s team at ETH Zurich to develop a technology that produces more than 100 microrobots per minute that can be disintegrated in the body.
Microrobots aiming at minimal invasive targeted precision therapy can be manufactured in various ways. Among them, ultra-fine 3D printing technology called two-photon polymerization method, a method that triggers polymerization by intersecting two lasers in synthetic resin, is the most used. This technology can produce a structure with nanometer-level precision. However, a disadvantage exists in that producing one microrobot is time consuming because voxels, the pixels realized by 3D printing, must be cured successively. In addition, the magnetic nanoparticles contained in the robot can block the light path during the two-photon polymerization process. This process result may not be uniform when using magnetic nanoparticles with high concentration.
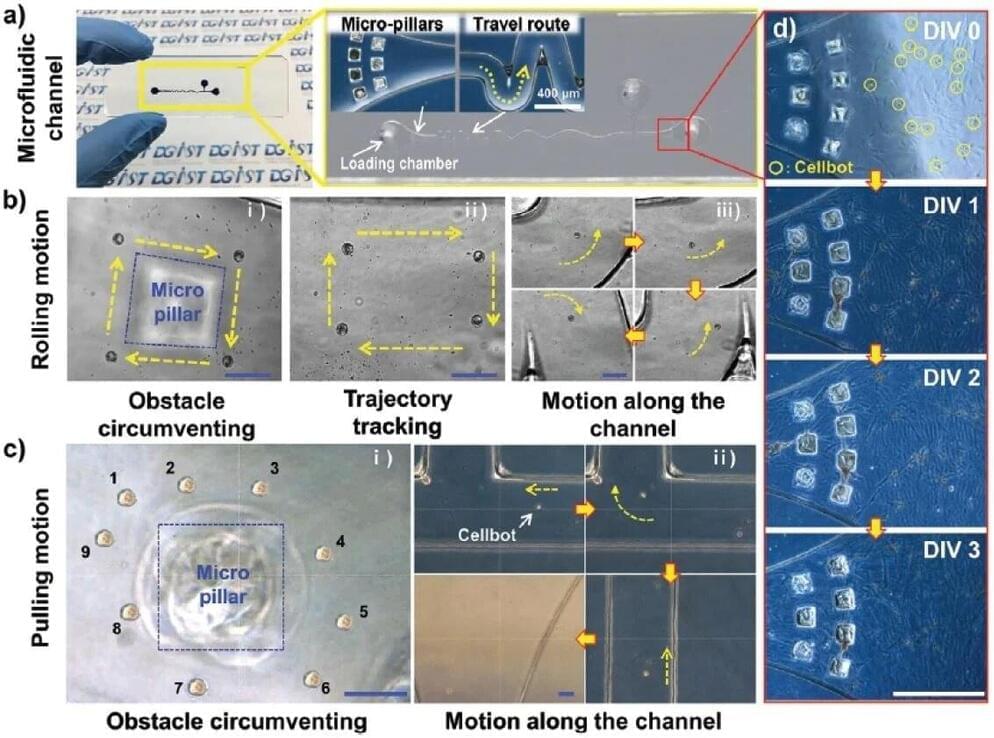
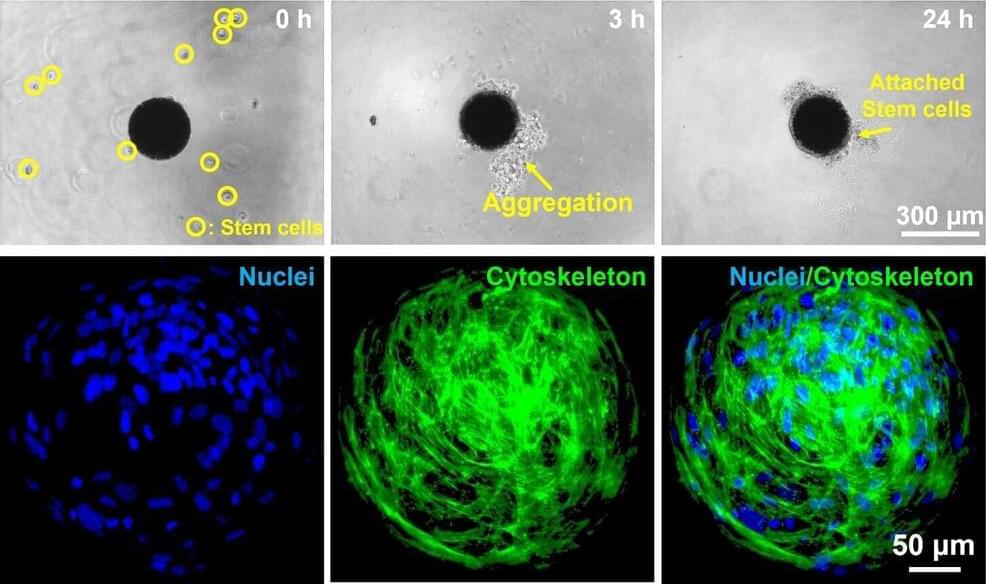
To overcome the limitations of the existing microrobot manufacturing method, DGIST Professor Hongsoo Choi’s research team developed a method to create microrobots at a high speed of 100 per minute by flowing a mixture of magnetic nanoparticles and gelatin methacrylate, which is biodegradable and can be cured by light, into the microfluidic chip. This is more than 10,000 times faster than using the existing two-photon polymerization method to manufacture microrobots.