Apr 22, 2024
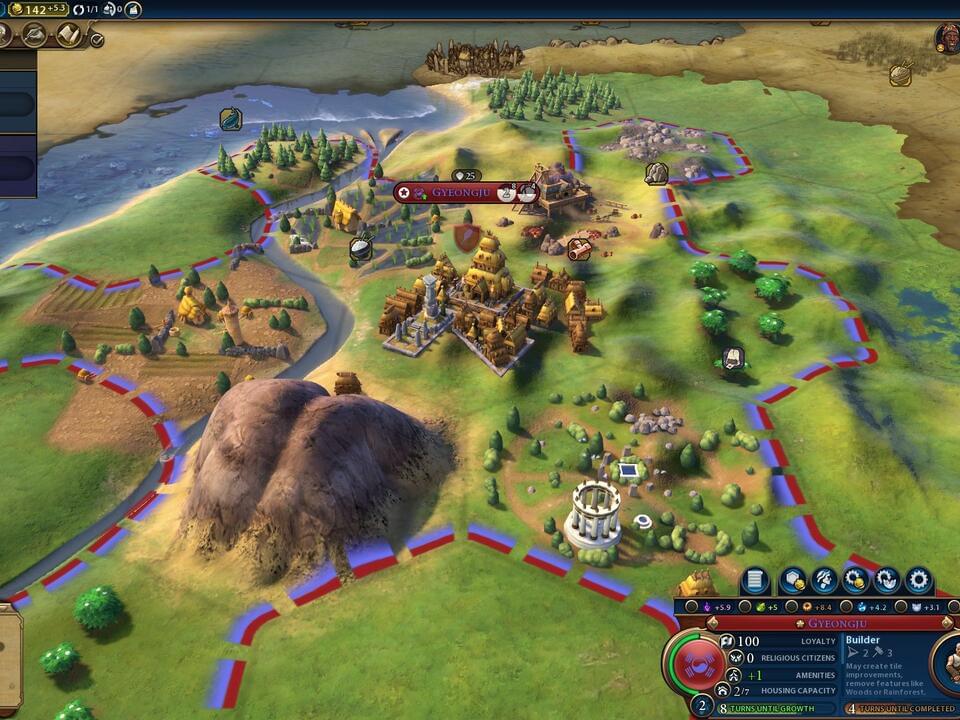
A new physics paper suggests that we may all be living in the ultimate 4X strategy game after all
Posted by Dan Breeden in categories: entertainment, physics, robotics/AI
I found this on NewsBreak: A new physics paper suggests that we may all be living in the ultimate 4X strategy game after all.
My money’s on the universe being like Civ 6, with its borked-n-bonkers AI.