Apr 23, 2024
The big quantum chill: Scientists modify common lab refrigerator to cool faster with less energy
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: energy, quantum physics
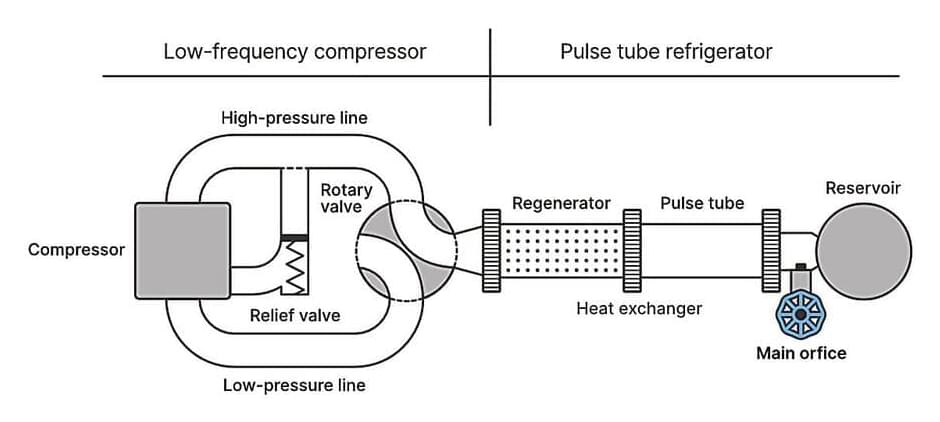
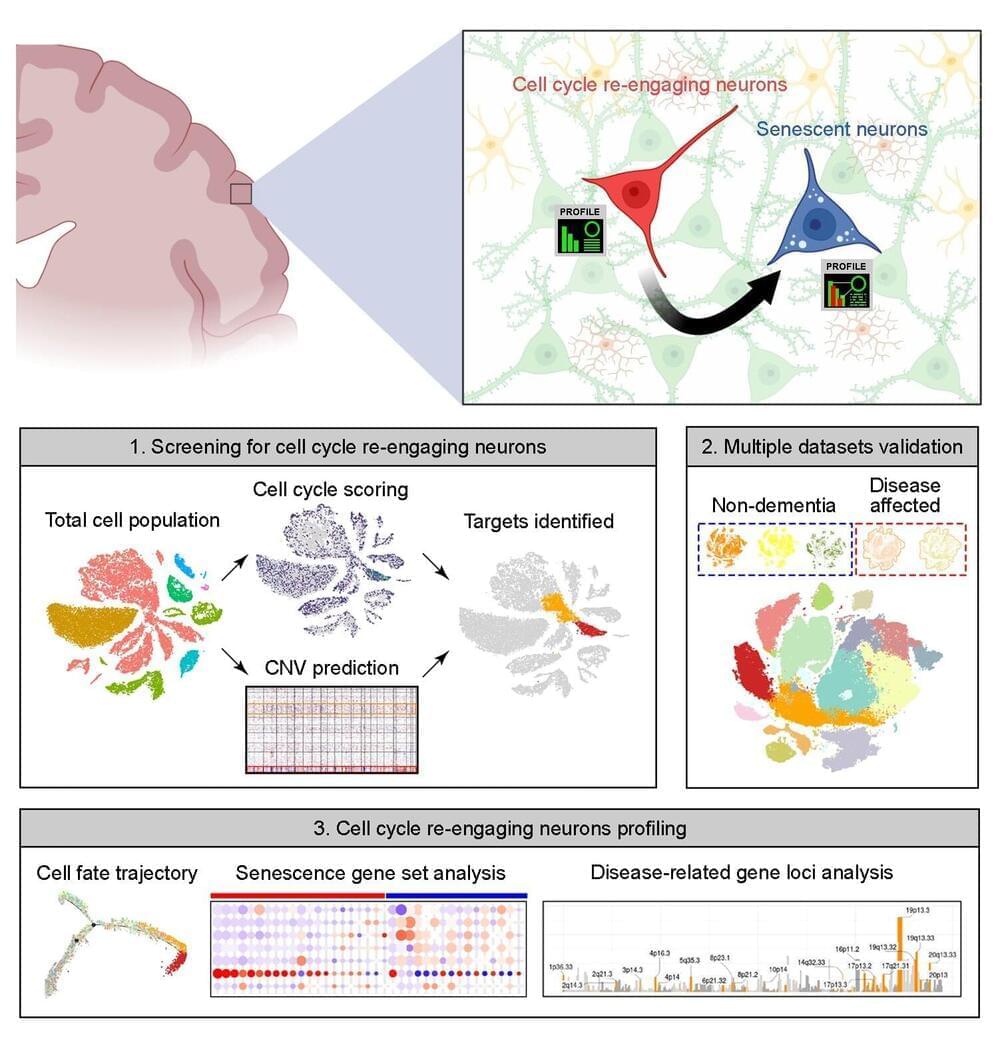
By modifying a refrigerator commonly used in both research and industry, researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have drastically reduced the time and energy required to cool materials to within a few degrees above absolute zero.