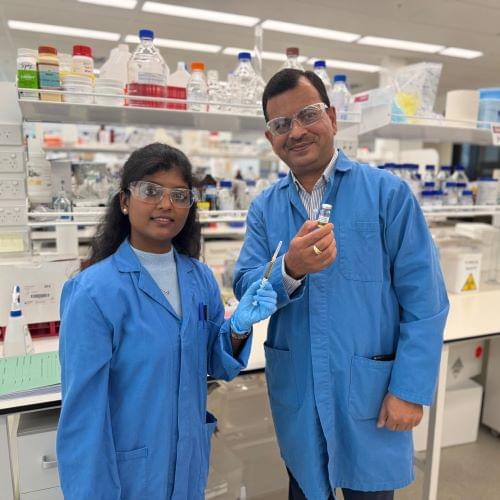
Malicious GitHub repositories used by threat actors to host Amadey payloads and steal data, impacting targeted entities.





Google has filed a lawsuit against the anonymous operators of the Android BadBox 2.0 malware botnet, accusing them of running a global ad fraud scheme against the company’s advertising platforms.
The BadBox 2.0 malware botnet is a cybercrime operation that utilizes infected Android Open Source Project (AOSP) devices, including smart TVs, streaming boxes, and other connected devices that lack security protections, such as Google Play Protect.
These devices become infected either by threat actors purchasing low-cost AOSP devices, modifying the operating system to include the BadBox 2 malware, and then reselling them online, or by tricking users into downloading and installing malicious apps on their devices that contain the malware.

Humanoid robots — long seen as futuristic — are already here, walking, talking, and working among us. Here are 10 advanced examples.

At the forefront of discovery, where cutting-edge scientific questions are tackled, we often don’t have much data. Conversely, successful machine learning (ML) tends to rely on large, high-quality data sets for training. So how can researchers harness AI effectively to support their investigations?
In Physical Review Research, scientists describe an approach for working with ML to tackle complex questions in condensed matter physics. Their method tackles hard problems which were previously unsolvable by physicist simulations or by ML algorithms alone.
The researchers were interested in frustrated magnets— magnetic materials in which competing interactions lead to exotic magnetic properties. Studying these materials has helped to advance our understanding of quantum computing and shed light on quantum gravity. However, frustrated magnets are very difficult to simulate, because of the constraints arising from the way magnetic ions interact.
Most cancer genome studies have focused on mutations in the tumor itself and how such gene variants allow a tumor to grow unchecked. A new study, led by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, takes a deep dive into inherited cancer mutations measured in a healthy blood sample and reports how those mutations might take a toll on the body’s cells starting at birth, perhaps predisposing a person to develop cancers at various stages of life.
The authors analyzed the inherited genomes of more than 1,000 cancer patients and determined how inherited mutations — also known as germline variants — result in malfunctioning proteins, which in turn can impair physiological activities. The findings have implications for determining an individual’s inherited cancer risk and informing potential new strategies for prevention, early detection and treatment.
The study appears April 14 in the journal Cell.
Findings could help predict cancer risk over a person’s lifetime, develop prevention strategies.

